Subtractive color model, or "subtractive color mixing", helps to understand what will be the color of light bounced off paper covered with some layers of inks or dyes.
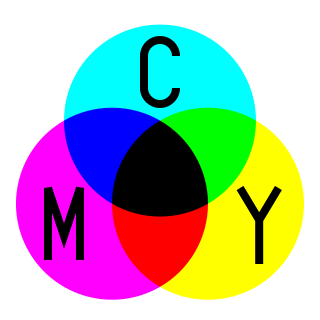
This model is the principle of how dyes and inks are used in color printing and photography printing. When the perceived color is obtained after white light passes through microscopic layers of ink or dye allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye, but not others.
In color printing, the usual primary colors are cyan, magenta and yellow (CMY).
Cyan is the complement of red. So, the cyan is a filter that does not allow red color through. The amount of cyan ink put on a white sheet of paper controls how much of the red (in white light) will be reflected back from the paper. Magenta is the complement of green (does not pass it), and yellow the complement of blue (does not pass it). Combinations of different amounts of the three hues can produce a wide range of colors.
In inkjet color printing and typical mass production printing processes, a black ink called K (Key) component is also used, resulting in the CMYK color model.

RYB (red, yellow, blue) is an older standard set of subtractive primary colors used for mixing pigments. It is used in art, particularly in painting.
Red, yellow, and blue are the primary colors of the RYB color "wheel". Their secondary colors are violet (or purple), orange, and green (VOG).
- Berns, Roy S. (2000). Billmeyer and Saltzman's Principles of Color Technology, 3rd edition. Wiley, New York. ISBN 0-471-19459-X.
- Stroebel, Leslie, John Compton, Ira Current, and Richard Zakia (2000). Basic Photographic Materials and Processes, 2nd edition. Focal Press, Boston. ISBN 0-240-80405-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wyszecki, Günther & W. S. Stiles (1982). Colour Science: Concept and Methods, Quantitative Data and Formulae. Wiley, New York. ISBN 0-471-02106-7.
- Stanford University CS 178 interactive Flash demo comparing additive and subtractive color mixing.
Italic text
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.