North Germanic language spoken in Norway From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Norwegian language is the official language of Norway. It is spoken by over four and a half million people, and it belongs to the group of North Germanic languages which are spoken in Scandinavia. These include Swedish, Danish, Icelandic and Faeroese.
| Norwegian | |
|---|---|
| norsk | |
| Pronunciation | [nɔʂk] (East and North) [nɔʁsk] (West) |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Norwegians |
Native speakers | 4.3 million (2012)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | Old Norse
|
Standard forms | written Bokmål (official)
written Nynorsk (official)
• written Høgnorsk (unofficial)
|
| Latin (Norwegian alphabet) Norwegian Braille | |
| Norwegian Sign Language | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Language Council of Norway (Bokmål and Nynorsk) Norwegian Academy (Riksmål) Ivar Aasen-sambandet (Høgnorsk) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | |
| ISO 639-2 | nor – inclusive codeIndividual codes: nno – Nynorsk |
| ISO 639-3 | nor – inclusive codeIndividual codes: nob – Bokmålnno – Nynorsk |
| Glottolog | norw1258 |
| Linguasphere | 52-AAA-ba to -be;52-AAA-cf to -cg |
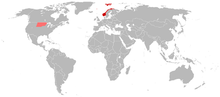 Areas where Norwegian is spoken, including North Dakota (where 0.4% of the population speaks Norwegian) and Minnesota (0.1% of the population) (Data: U.S. Census 2000). | |
Two forms of the language exist: bokmål (which means "book language") and nynorsk (which means "new Norwegian").
Old Norse is the language that was spoken hundreds of years ago in Scandinavia at the time of the Vikings. It is very similar to today’s Icelandic language. This is because many Vikings sailed from Norway to Iceland in order to escape from the rule of the Norwegian kings who were making people pay lots of tax.
During the 13th century the Black Death killed two thirds of the population of Norway. The Danish kings and queens noticed that Norway was weak and defenceless, so they annexed Norway (made it part of Denmark). For hundreds of years Norway was ruled by the Danes. All the rulers, priests, estate owners and noblemen were Danish. Many of them settled in Norway. This is why today’s standard Norwegian (Bokmål) is similar to Danish. Norwegians were not allowed to print books in Norwegian. Anyone wanting to study had to go to Denmark or Germany.
In 1814 Denmark lost a war and had to give Norway to Sweden. Then the Norwegians were allowed to have their own university. Gradually the Danish language was mixed up with the Norwegian dialects and became today’s Norwegian language. Norwegian and Danish look very similar when they are written, but when they are spoken they sound different. In Danish a lot of the sounds are swallowed.
During the 19th century a slightly different form of Norwegian was made up by several people. This eventually became known as “Nynorsk.” It was based on old forms of Norwegian and dialects. During the 20th century some attempts were made to join Bokmål and Nynorsk into one language, but they did not succeed. Today about one person in nine or ten in Norway writes Nynorsk. Children in school have to learn both forms.
The Norwegian alphabet has 29 letters. These are the same letters as the English alphabet plus three extra vowels: æ ø å
The letters c, q, w, x and z are only used for words that have been borrowed from other languages. However, c and w are more common that q, x, and z, even more common than the letter æ which is used even in original Norwegian words.[2]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.