Caffeine
chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. It is found in parts of plants, for example tea leaves and coffee beans. Its artificial form is also used in some soft drinks and energy drinks. It is the world's most popular psychoactive drug, and is legal in all of the world.[11]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /kæˈfiːn, ˈkæfiːn/ |
| Synonyms | Guaranine Methyltheobromine 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine 7-methyltheophylline[1] Theine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability | Physical: low–moderate[2][3][4][5] Psychological: low[6] |
| Addiction liability | Low[5] / none[2][3][4] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, insufflation, enema, rectal, intravenous |
| Drug class | Stimulant |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 99%[7] |
| Protein binding | 25–36%[8] |
| Metabolism | Primary: CYP1A2[8] Minor: CYP2E1,[8] CYP3A4,[8] CYP2C8,[8] CYP2C9[8] |
| Metabolites | Paraxanthine (84%) Theobromine (12%) Theophylline (4%) |
| Onset of action | ~1 hour[7] |
| Elimination half-life | Adults: 3–7 hours[8] Infants (full term): 8 hours[8] Infants (premature): 100 hours[8] |
| Duration of action | 3–4 hours[7] |
| Excretion | Urine (100%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.329 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
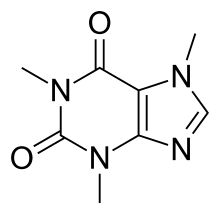
| Formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.19 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 235 to 238 °C (455 to 460 °F) (anhydrous)[9][10] |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |

Sources
Caffeine is naturally found in the fruits, leaves and beans of coffee, cacao, guarana and tea plants.
The plants use caffeine as a pesticide. This is a chemical that kills insects if they eat the plant. It is the way the plant protects itself.
Caffeine was first extracted from cocoa beans into its purest form which is a white powder and the word originated from the German word “Kaffee” and the French word “café” which both mean caffeine.[12]
When it comes from the guarana plant it is called guaranine, when it comes from a tea plant, it is called theine, and in the mate drink it is called mateine (this drink is an infusion made with Yerba mate).
What caffeine is

Caffeine is a stimulant drug. A stimulant is a drug that increases body actions like heart rate, blood pressure, and metabolism. It makes a person more awake and alert.
Caffeine also is a diuretic. This means it makes a person make more urine (the waste liquid a person makes).
The caffeine chemical is called a xanthine alkaloid. This is a group of chemicals that are stimulants. Some xanthine alkaloids (like theophylline) are used to help asthma.
What caffeine is used for
The biggest use of caffeine is as a stimulant. People drink coffee and other drinks with caffeine to stay awake.
In the beginning caffeine was found to relieve hunger, so it was used for weight loss. That did not last because people were using too much. Caffeine can be dangerous when not used in the right way.
Doctors sometimes use caffeine as a medicine.[13] It is added to analgesics (drugs used for pain).[13] This can improve their effect on headaches and other pain.[13] It is sometimes used to help premature babies (babies born very early) to breathe.[14] The short-term risk of this treatment seems to be that the babies treated gain less weight than usual.[15] Caffeine is sometimes given to people after a lumbar puncture.[16] This is when a needle is pushed between the bones of the lower back, normally to check for illnesses[16] like meningitis.[17]
Problems with caffeine

The largest problem with caffeine is addiction. This is when people get bad symptoms when they do not have the drug. When people have withdrawal (feel bad because they do not have the drug) they drink more. This makes them feel better. But if they cannot get more, they are likely to feel some of the symptoms listed below:
- Headaches
- Being tired or need to sleep
- Caffeine can prevent sleep and in the long-term alters brain functions
- Sleep deprivation leads to a weakened connectivity between the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex which regulate mood and emotion.
- This causes the consumer to feel irritable, tired, restlessness, and anxious.
- Sleep deprivation leads to a weakened connectivity between the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex which regulate mood and emotion.
- Nausea (feeling like vomiting)
Caffeine can also hurt people if they drink a lot at once. If a person consumed 10-13 grams of caffeine quickly, between 80 and 100 cups of coffee, they would overdose and may even die.[18] Caffeine overdose is a medical diagnosis. It is called: Caffeine-Induced Organic Mental Disorder or Caffeine Intoxication. People with this can have these symptoms:
Caffeine helps for
Caffeine also has some strong advantages:[19]
- Lower risk of coronary disease
- Cut stroke risk
- Speed up metabolism
- Increases memory
- Helps ward off Alzheimer’s
- Reduces kidney stone risk
How much caffeine is safe
250–300 mg of caffeine a day is a moderate amount. That is as much caffeine that is in three cups of coffee (8oz each cup). More than 750–1000 mg a day is a significant amount, but is very unlikely to kill someone. The Lethal Dose 50 of caffeine is 192 mg per kilogram, in rats. In humans, it is between 150 and 200 mg per kilogram (70-90 per pound.)
Caffeine is in many drinks and foods. This is approximate amounts of caffeine in some food and drink:
- Brewed coffee – 40 to 220 mg in a cup
- Instant coffee – 30 to 120 mg in a cup
- Decaffeinated coffee (with most caffeine taken out) – 3 to 5 mg in a cup
- Tea – 20 to 110 mg in a cup
- Soda drinks with caffeine – 36 to 90 mg in 12 ounces. Some people think that soft drinks which are light in color do not contain caffeine. This is not always true.
- Milk chocolate – 3 to 6 mg in an ounce
- Bittersweet chocolate – 25 mg in an ounce
One ounce – abbreviated oz – is 30 ml.
A 'cup' is 8 oz (240 ml.)
Different ways to get 200mg of caffeine
| Caffeine equivalents[20][21] |
|---|
In general, each of the following contains approximately 200 milligrams[broken anchor] of caffeine:
Notes: A fluid ounce is between 28 and 30 millilitres. a. There may also be large amounts of other chemicals, similar to caffeine in chocolate and other products of cacao. There is theobromine in cacao, for example. These substances can have effects similar to those of caffeine. b. Most tea drunk in North America is not very strong. The figures are for this kind of tea. The tea drunk in most other places of the world is stronger; for these kinds of tea, the figures are probably too small. |
References
Other websites
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

