RAR-srodni orfan receptor alfa
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
RAR-srodni orfan receptor alfa (ROR-alfa), ili NR1F1 (nuklearni receptor potfamilije 1, grupe F, član 1) je nuklearni receptor kodiran genom RORA.
| edit |
| RAR-vezani orfan receptor A | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
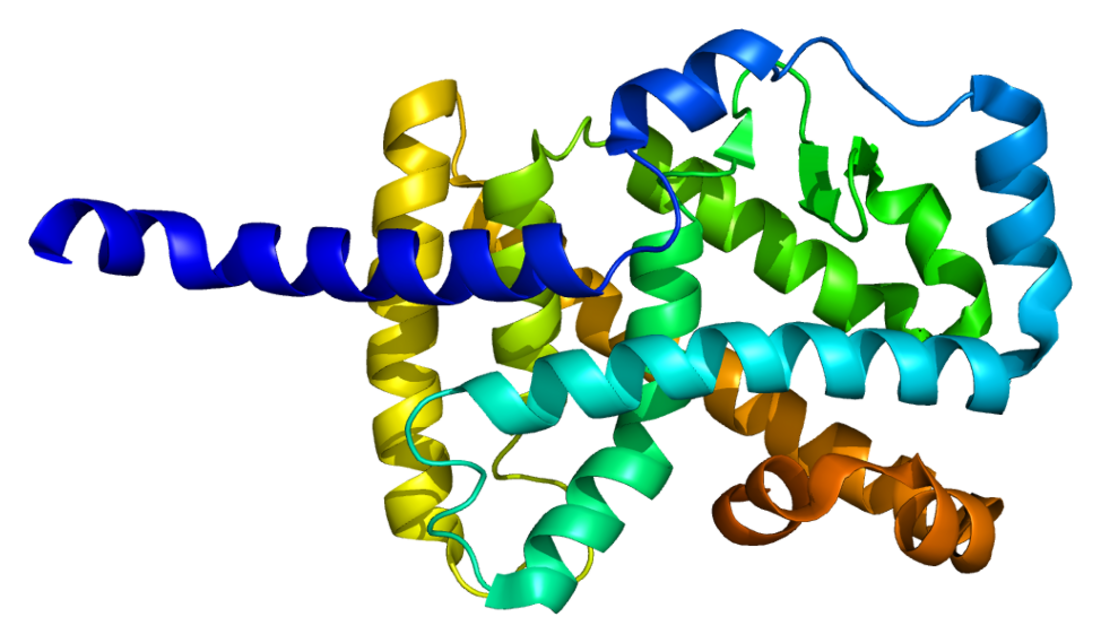
 PDB slika bazirana na 1n83.. | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 1n83, 1s0x | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | RORA; ROR1; ROR2; MGC119326; MGC119329; NR1F1; ROR3; RZRA | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 600825 MGI: 104661 HomoloGene: 56594 GeneCards: RORA Gene | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 6095 | 19883 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000069667 | ENSMUSG00000032238 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P35398 | Q3U1P4 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_002943 | XM_903197 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_002934 | XP_908290 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) | Chr 15: 58.58 - 59.31 Mb | Chr 9: 68.45 - 69.18 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | |||||||||||
Protein kodiran ovim genom je član NR1 potfamilije nuklearnih hormonskih receptora. On može biti vezan kao monomer ili homodimer za elemente hormonskog odgovora uzvodno od nekoliko gena da bi pojačao ekspresiju tih gena. Specifične funkcije ovog proteina su nepoznate, ali je bilo pokazano da ima interakciju sa NM23-2, nukleozid difosfat kinazom koja učestvuje u organogenezi i diferencijaciji, kao i sa NM23-1, produktom tumor metastaznog supresor kandidatnog gena. Četiri transkriptne varijante koje kodiraju različite izoforme su bile opisane za ovaj gen.[1]
Interakcije
Za RAR-srodni orfan receptor alfa je pokazano da uspostavlja interakciju sa EP300[2] i NME1.[3]
Reference
Literatura
Povezano
Vanjske veze
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.