Scots inventions an diskiveries
Wikimedia leet airticle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Remove ads
Scottish inventions an diskiveries are objects, processes or techniques aither pairtly or halely inventit, innovatit, or diskivert bi a body born in or descendit frae Scotland. In some cases, an invention's Scots natur is pitten bi the fact that it pit intae existence in Scotland (e.g., animal cloning), bi fowk no frae Scotland wirkin in the kintra. Aften, things that are diskivert for the first time are cried "inventions" an aw an in mony cases thare isnae a clear line atweesh the twa.
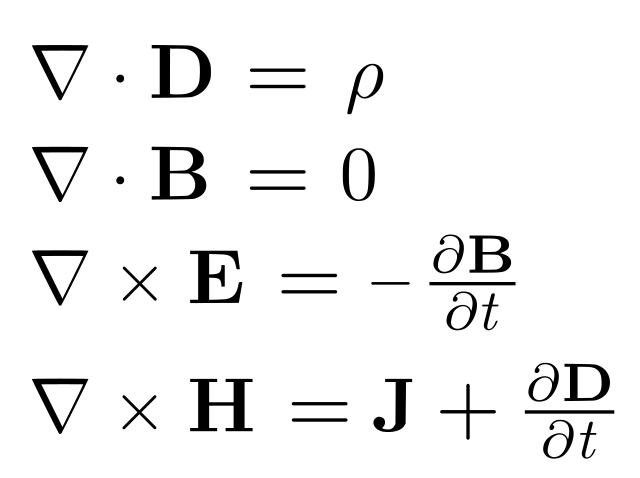
"the maist significant event of the 19t yearhunner will be judged as Maxwell's diskivery o the laws o electrodynamics"
The Scots hae massive pride in the history o Scots inventions an diskiveries. Thare are a lot o beuks scrieved juist on the subject, as weel as a hale wheen o websites pittin doun inventions an diskiveries frae Scotland wi some degree o science.
E'en afore the Industrial Revolution, Scots hae been at the forebreest o innovation an diskivery throu a nummer o depairtments. Some of the maist relevant products o Scots ingenuity include James Watt's steam ingine, impruivin on Thomas Newcomen's,[2] the bicycle,[3] macadamisation (no tae be conflummixit wi tarmac o tarmacadam[4]), Alexander Graham Bell's invention o the first practical telephone,[5] John Logie Baird's invention o the telly,[6] Alexander Fleming's diskivery o penicillin[7] an insulin.[8]
The follaein is a list o inventions, innovations, or diskiveries that are kent as bein frae Scotland.
Remove ads
Road transport innovations
- Macadamised roads (the basis for, but no speceefically, tarmac): John Loudon McAdam (1756–1836)[4]
- The pedal bicycle: Pitten tae baith Kirkpatrick Macmillan (1813–1878)[3] an Thomas McCall (1834–1904)
- The pneumatic tyre: Robert William Thomson an John Boyd Dunlop (1822–1873)[9]
- The overhead valve ingine: David Dunbar Buick (1854–1929)[10]
Civil engineering innovations
- Tubular steel: Sir William Fairbairn (1789–1874)[11]
- The Fawkirk wheel: Stairtin designs bi Nicoll Russell Studios, Architects, RMJM an ingineers Binnie, Black, an Veatch (Appent 2002)[12][13]
- The pautent slip for dockin veshels: Thomas Morton (1781–1832)[14]
- The Drummond Light: Thomas Drummond (1797–1840)[15]
- Canal design: Thomas Telford (1757–1834)
- Dock design impruivements: John Rennie (1761–1821)
- Crane design impruivements: James Bremner (1784–1856)
- "Trac Rail Transposer", a machine tae pit doun rail track pautentit in 2005, uised by Network Rail in the Unitit Kinrick an the New York Toun Subway in the Unitit States.[16][17][18]
Remove ads
Aviation innovations
- Aircraft design: Frank Barnwell (1910) Estaiblishin the core aspects o aircraft design at the Varsity o Glesga.[19]
Pouer innovations
- Condensin steam engine impruivements: James Watt (1736–1819)[2]
- Thermodynamic cycle: William John Macquorn Rankine (1820–1872)[20]
- Coal-gas lichtin: William Murdoch (1754–1839)[21]
- The Stirling heat ingine: Rev. Robert Stirling (1790–1878)[22]
- Carbon brushes for dynamos: George Forbes (1849–1936)[23]
- The Clerk cycle gas ingine: Sir Dugald Clerk (1854–1932)[24]
- The wave-pou0ered electric generator: bi South African Engineer Stephen Salter in 1977[25]
- The Pelamis Wave Energy Converter ("red sea snake" wave energy device): Richard Yemm, 1998[26]
Remove ads
Shipbuilding innovations
- Europe's first passenger steamboat: Henry Bell (1767–1830)[27]
- The first iron–hulled steamship: Sir William Fairbairn (1789–1874)[28]
- The first practical screw propeller: Robert Wilson (1803–1882)
- Marine ingine innovations: James Howden (1832–1913)
- John Elder an Charles Randolph (Marine Compound expansion ingine)
Militar innovations
- Lieutenant-General Sir David Henderson twa area:
- Field intelligence. Argied for the estaiblishin Intelligence Corps. Scrieved Field Intelligence: Its Principles and Practice (1904) and The Art of Reconnaissance (1907) on the tactical intelligence o modren warfare.[29]
- Intelligence: Allan Pinkerton developit the still relevant intelligence techniques of "shadowin" (surveillance) an "pittin yersel in a role" (unnerkiver wirk) in his time as heid o the Union Intelligence Service.
Remove ads
Weichtie industry innovations
- Coal minin extractin in the sea on an artificial island bi Sir George Bruce of Carnock (1575). Kent as ane o the industrial wunners o the late medieval period.
- Makin cast steel frae wrought iron: David Mushet (1772–1847)[30]
- Wrought iron sash bars for gless hooses: John C. Loudon (1783–1865)
- The hot blast uin: James Beaumont Neilson (1792–1865)
- The steam haimer: James Nasmyth (1808–1890)
- Wire raip: Robert Stirling Newall (1812–1889)
- Steam ingine impruivements: William Mcnaught (1831–1881)
- The Fairlie, a narrow gauge, dooble-bogie railway ingine: Robert Francis Fairlie (1831–1885)
- Cordite - Sir James Dewar, Sir Frederick Abel (1889)
Remove ads
Agricultural innovations
- Threshing machine impruivements: James Meikle (c.1690-c.1780) & Andrew Meikle (1719–1811)
- Hollow pipe drainage: Sir Hew Dalrymple, Lord Drummore (1700–1753)
- The Scotch plough: James Anderson o Hermiston (1739–1808)
- Deanstonisation soil-drainage seestem: James Smith (1789–1850)
- The mechanical reapin machine: Rev. Patrick Bell (1799–1869)
- The Fresno scraper: James Porteous (1848–1922)[31]
- The Tuley tree shelter: Graham Tuley in 1979
Remove ads
Communication innovations
- Telephone: Alexander Graham Bell (1847-1922)
- Print stereoteepin: William Ged (1690–1749)[32]
- Roller prentin: Thomas Bell (patented 1783)[33]
- The adhesive postage stamp an the postmerk: claimed bi James Chalmers (1782–1853)[34]
- The Waverley pen nib innovations: Duncan Cameron (1825–1901) The weel kent "Waverley" was sindry in design wi a narrow waist an an upturnt tip designed tae mak the ink flow mair smuith on the paper.[35]
- Universal Standard Time: Sir Sandford Fleming (1827–1915)
- Light signalling between ships: Admiral Philip H. Colomb (1831–1899)
- The underlying principles o radio: James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- The Kinetoscope, a motion picture camera: devised in 1889 by William Kennedy Dickson (1860-1935)
- The teleprinter: Frederick G. Creed (1871–1957)
- The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC): John Reith, 1st Baron Reith (1922) its founder, first general manager and director-general of the British Broadcasting Corporation[36]
- RADAR: A significant contribution made by Robert Watson-Watt (1892–1973) alongside Englishman Henry Tizard (1885-1959) and others[37]
- The automated teller machine and Personal Identification Number system: James Goodfellow (born 1937)[38]
Publishin firsts
- The first edeetion o the Encyclopedia Britannica (1768–81)
- The first textbook on surgery in Inglis (1597)
- The first modren pharmacopaedia, William Cullen (1776). The book endit up bein 'Europe's principal text on the classifeein an treatment o disease'. His ideaes keep gaun wi the terms nervous energy an neuroses (a word that Cullen coined).
- The first postcairds an pictur postcairds in the UK
- The eddicational foondin o Ophthalmology: Stewart Duke-Elder in his first o it's kind wark includin ‘Textbook of Ophthalmology and fifteen volumes of System of Ophthalmology' (Scots: Textbook o Ophthalmology an fifteen vollum o Seestem o Ophthalmology)[39]
Remove ads
Cultur an the airts
- Scottish National Portrait Gallery, designed bi Sir Robert Rowand Anderson (1889): the warld's first purpose-biggit portrait gallery.[40]
Scientific innovations
- Logarithms: John Napier (1550–1617)
- Modren Economics foondit bi Adam Smith (1776) 'The faither of Modren Economics'[41] with the publication of The Wealth of Nations. (Scots: The Walth o nations)[42]
- Modren Sociology: Adam Ferguson (1767) ‘The Faither o Modren Sociology’ wi his wark An Essay on the History of Civil Society (Scots: An Essay on the History o Civil Societie)[43]
- Hypnotism: James Braid (1795–1860) the Faither o Hypnotherapy
- Tropical medicine: Sir Patrick Manson kent as the faither o Tropical Medicine
- Modren Geology: James Hutton ‘The Foonder o Modren Geology’[44][45]
- The theory of Uniformitarianism: James Hutton (1788): an important principle o Geology the features o the geologic time taks millions o years.
- The theory o electromagnetism: James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- The diskivery o the Componin o Saturn's Rings James Clerk Maxwell (1859): pit doun thit the rings o Saturn war componed wi sindry wee pairticles, aw gaun aroond the planet on thair ain. At the time it wis thoucht thit the rings war solid. The Maxwell Ringlet an Maxwell Gap war named in his honor.[46]
- The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution bi James Clerk Maxwell (1860): the basis o the kinetic theory o gases, thit speeds o molecules in a gas will chynge at different temperaturs. The oreeginal theory first pit forrit bi Maxwell an confirmt later on in conjunction wi Ludwig Boltzmann.
- Popularisin the decimal point: John Napier (1550–1617)
- The first theory o the Higgs boson bi Inglis born [47] Peter Higgs particle-physics theorist at the Varsity o Embro (1964)[48]
- The Gregorian telescope: James Gregory (1638–1675)
- The diskivery o Proxima Centauri, the closest kent star tae the Sun, bi Robert Innes (1861–1933)[49]
- One of the earliest measurements o distance tae the Alpha Centauri star seestem, the closest sic seestem ootside the Solar Seestem, bi Thomas Henderson (1798–1844)
- The discovery of Centaurus A, a well-known starburst galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus, by James Dunlop (1793–1848)[50]
- The diskivery o the Horsehead Nebula in the constellation o Orion, bi Williamina Fleming (1857–1911)[51]
- The world's first oil refinery an a process for extractin paraffin frae coal pittin doun the foondations for the modren oil industry: James Young (1811–1883)[52]
- Identifyin the minerals yttrialite, thorogummite, aguilarite and nivenite: bi William Niven (1889)[53]
- The concept o latent heat bi French-born Joseph Black (1728–1799)
- Diskiverin the properties o Carbon dioxide bi French-born Joseph Black (1728–1799)
- The concept o Heat capacity bi French-born Joseph Black (1728–1799)
- The pyroscope, atmometer an aethrioscope scientific instruments: Sir John Leslie (1766–1832)
- Identifyin the nucleus in leevin cells: Robert Brown (1773–1858)
- An early version o the Incandescent light bulb: James Bowman Lindsay (1799-1862)
- Colloid chemistry: Thomas Graham (1805–1869)
- The kelvin SI unit o temperature bi Irishman William Thomson, Lord Kelvin (1824–1907)
- Pittin thegither the diagramatic seestem for representin chemical bonds: Alexander Crum Brown (1838–1922)
- Creeminal fingerprinting: Henry Faulds (1843–1930)
- The noble gases: Sir William Ramsay (1852–1916)
- The clood chamber recordin o atoms: Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959)[54]
- The diskivery o the Wave o Translation, leadin tae the modren general theory o solitons bi John Scott Russell (1808-1882)[55]
- Statistical graphics: William Playfair foonder o the first statistical line chairts, bar chairts, an pie charts in (1786) an (1801) kent as a scientific ‘milestone’ in statistical graphs an data visualin[56]
- The Arithmetic mean density o the Earth: Nevil Maskelyne conductit the Schiehallion experiment conductit at the Scots ben o Schiehallion, Perthshire 1774[57]
- The first isolation o methylated sugars, trimethyl an tetramethyl glucose: James Irvine[58][59]
- Diskivery o the Japp–Klingemann reaction: tae synthesize hydrazones frae β-keto-acids (or β-keto-esters) an aryl diazonium salts 1887[60]
- Pioneerin wark on nutrition an poverty: John Boyd Orr (1880–1971)[61]
- Ferrocene synthetic substances: Peter Ludwig Pauson in 1955
- The first cloned mammal (Dolly the Sheep): Was conductit in The Roslin Institute resairch centre in 1996 bi English scientists Ian Wilmut (born 1944) an Keith Campbell (1954–2012).
- The seismometer innovations thereof: James David Forbes
- Metaflex fabric innovations thereof: University of St. Andrews (2010) appleein the first manufacturin fabrics thit chynge licht bi bendin it aroond a subject. Afore this, sic licht chynge atoms aboot war sortit on flat haurd surfaces. The team at St Andrews are the first tae come up wi the concept tae fabric.[62]
- Tractor beam innovations thereof: St. Andrews University (2013) the warld's first tae succeed in pittin thegither a wirkin Tractor beam thit pulls objects on a microscopic level[63][64]
- Macaulayite: Dr. Jeff Wilson o the Macaulay Institute, Aberdeen.
- Diskivery o Catacol whitebeam bi Scottish Natural Heritage an the Ryal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (1990s): a rare tree endemic an unique tae the Isle o Arran in the sooth wast o Scotland. The trees war confirmt tae be a distinct species bi DNA testin.[65]
- The first positive displacement liquid flowmeter, the reciprocatin piston meter bi Thomas Kennedy Snr.[66]
Sports innovations
Scots hae taen a muckle pairt in the invention an early development o twa-three sports:
- Australian rules fitba Scots were at the forefront wi mony innovations in the early version o the gemme, includin the foondin o the Essendon Football Club byithe McCracken familie frae Ayrshire[67][68][69]
- Twa-three modren athletics events, i.e. shot put an the hammer thraw, come frae Hieland Gemmes an Scotland frae the early 12t yearhunner.
- Curlin
- Gaelic haundba The modren gemme o handball wis first recordit in Scotland in 1427, whan King James I, an ardent haundba player, haed his men block up a cellar windae in his palace courtyard thit was gittin in the wey o his gemme.
- Cycling, invention o the pedal-cycle
- Gowf (see Gowf in Scotland)
- 1848: Association fitba's Glesgae rules (lairgely the sport's rules as we ken thaim the day) estaiblishit at Glesga Vaersity.
- Ice Hockey, inventit bi the Scots regiments in Atlantic Canada bi playin Shinty on frozent lochs.
- Shinty The history o Shinty as a non-staundardtised sport come frae before Scotland as a Nation. The rules war staindardised in the 19t yearhunner bi Archibald Chisholm
- Rugby seivens: Ned Haig an David Sanderson (1883)[70]
- The Dugout was inventit bi Aberdeen FC Coach Donald Colman in the 1920s
- The warld's first Robot Olympics thit teuk place in Glesga in 1990.
Medical innovations
- Stairtin the uise o surgical anaesthesia wi Chloroform: First in 1842 bi Robert Mortimer Glover than pit tae uise on humans bi Sir James Young Simpson (1811–1870) First use o chloroform in dentistry bi Francis Brodie Imlach
- The Saline drip bi Dr Thomas Latta o Leith in 1831/32
- The hypodermic syringe: Alexander Wood (1817–1884)
- First diagnostic uise o an ultrasound scanner: Ian Donald (1910–1987)
- Independent diskivery o inoculation for smallpox: Johnnie Notions (c. 1730 – c. 1803)[71]
- Diskivery o hypnotism (November 1841): James Braid (1795–1860)[72]
- General anaesthetic: Pioneered bi Scotsman James Young Simpson an Inglisman John Snow[73]
- Identifeein the mosquito as the carrier for malaria: Sir Ronald Ross (1857–1932)
- Funnin the cause for brucellosis: Sir David Bruce (1855–1931)
- Diskiverin the vaccine for typhoid fever: Sir William B. Leishman (1865–1926)
- Electrocardiography: Alexander Muirhead (1869)[74]
- Diskivery o Staphylococcus: Sir Alexander Ogston (1880)[75]
- Diskiverin insulin: John J R Macleod (1876–1935) wi ithers[76] The diskivery led him tae be gien the awaird for Nobel prize in Medicine in 1923.[77]
- Penicillin: Sir Alexander Fleming (1881–1955)[78]
- First uise o X-ray cinematography: John Macintyre (1896); the first muivin real time X-ray eemage an the first KUB X-ray diagnostic eemage o a kidney stane in situ[79]
- Estaiblishment o staundardised Ophthalmology: Sir Stewart Duke-Elder, a pioneerin Ophthalmologist in the 1930-50s[39]
- The first hospital Radiation therapy uinit: John Macintyre (1902); tae gie a haun wi the diagnosis an treatment for injuries an illness at Glesga Ryal Infirmary[79]
- The Haldane effect, a property o hemoglobin: Descrived first bi John Scott Haldane (1907)[80]
- The first Decompression tables: John Scott Haldane (1908); tae calculate the safe retour o deep-sea divers tae surface atmospheric pressur[81]
- Oxygen therapy: John Scott Haldane (1922), wi the publishin o ‘The Therapeutic Administration of Oxygen Therapy’, stairtin the modren era o Oxygen therapy[82]
- Transplant rejection: Professor Thomas Gibson (1940s) the first medical doctor tae unnerstaun the relationship atweesh donor graft tissue an host tissue rejection an tissue transplantation bi his work on aviation burns victims durin World War II[83]
- Diskiverin an effective tuberculosis treatment: Sir John Crofton in the 1950s
- Developin the first beta-blocker drugs: Sir James W. Black in 1964; revolutionised the medical management for angina[84] an is seen as ae o the maist important contreebutions tae clinical medicine an pharmacology o the 20t yearhunner.[85] In 1988 Black wis gien the awaird for the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
- Developin modren asthma therapy based on baith bronchodilation (salbutamol) an anti-inflammatory steroids (beclomethasone dipropionate): Sir David Jack (1972)
- Chainsaw inventit bi surgeons John Aitken an James Jeffray for widenin the birth canal during difficult childbirth[86]
- Glasgow coma scale: Graham Teasdale an Bryan J. Jennett (1974)[87]
- Glasgow Outcome Scale: Bryan J. Jennett & Sir Michael Bond (1975): diagnostic tuil for patients wi brain injuries, sic as cerebral traumas[88]
- Diskiverin an developin the anesthetic drug Propofol: Dr. John B. Glen (1977); a surgical anesthetic uised aw aboot the warld, common in general surgery cases. In 2018 Dr. Glen wis gien a Lasker Award.[89]
- Glasgow Anxiety Scale: J.Mindham an C.A Espie (2003)[90]
- Glasgow Depression Scale: Fiona Cuthill (2003); the first accurate self-report scale tae measure the levels o depression in fowk wi lairnin disabilities[91]
- Diskiverin the Human papillomavirus vaccine: Ian Frazer (2006); the seicont cancer forfendin vaccine, an the warld's first vaccine made tae forfend a cancer[92]
- Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS): Strathclyde Varsity (2014); a laser an nanoparticle test tae airt oot Meningitis or multiple pathogenic agents at the same time.[93]
Household innovations
- The telly: John Logie Baird (1923)
- The refrigerator: William Cullen (1748)[94]
- The first electric bread toaster: Alan MacMasters (1893)
- The flush toilet: Alexander Cumming (1775)
- The vacuum flask: Sir James Dewar (1847–1932)
- The first distiller tae triple distill Irish whiskey:[95]John Jameson (Whisky distiller)
- The piano fitpedal: John Broadwood (1732–1812)
- The first automatit can-fillin machine John West (1809–1888)[96]
- The waterpruif macintosh: Charles Macintosh (1766–1843)
- The kaleidoscope: Sir David Brewster (1781–1868)
- Keiller's marmalade Janet Keiller (1797) - The first recipe o rind suspendit marmalade or Dundee marmalade producit in Dundee.
- The modren lawnmower: Alexander Shanks (1801–1845)
- The Lucifer friction match: Sir Isaac Holden (1807–1897)
- The self filling pen: Robert Thomson (1822–1873)
- Cotton-reel thread: J & J Clark of Paisley
- Lime cordial: Lauchlan Rose in 1867
- Bovril beef howkin: John Lawson Johnston in 1874
- The electric clock: Alexander Bain (1840)
- Chemical Telegraph (Automatic Telegraphy) Alexander Bain (1846) In Ingland Bain's telegraph wis uised on the wires o the Electric Telegraph Company tae a limitit stent, an in 1850 it wis uised in America.
Wapens innovations
- The carronade cannon: Robert Melville (1723–1809)[97]
- The Ferguson rifle: Patrick Ferguson in 1770
- The Lee bolt seestem as uised in the Lee–Metford an Lee–Enfield series rifles: James Paris Lee
- The Ghillie suit first uised bi the Lovat Scouts
- The percussion cap: inventit bi Scots Presbyterian clergyman Alexander Forsyth
Miscellaneous innovations
- Boys' Brigade: Sir William Alexander Smith[98]
- Bank of England devised by William Paterson
- Bank of France devised by John Law
- Grand Theft Auto: developit bi Scots game developers DMA Design (kent later on as Rockstar North)
- The industrialisation an modernisation o Japan bi Thomas Blake Glover[99]
- Colour photography: the first kent permanent colour photograph wis taen bi James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- Buick Motor Company bi David Dunbar Buick
- New York Herald newspaper bi James Gordon Bennett, Sr.
- Pinkerton National Detective Agency bi Allan Pinkerton
- Forbes magazine bi B. C. Forbes
- The estaiblishin o a staundardised botanical institute: Isaac Bayley Balfour[100]
- Lunnon Schuil o Hygiene & Tropical Medicine: fooondit bi Sir Patrick Manson in 1899
- Barr's Irn-Bru, saft drink producit bi Barr's in Cumbernauld Scotland an exportit aw aroond the warld. The drink is that widely popular in Scotland that it ootsells baith American colas Coca-Cola an Pepsi an ranks 3rd maist popular drink in the UK wi Coca-Cola an Pepsi takkin the first twa spot.[101]
References
Freemit Airtins
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
