1939–1945 global war mainly atween the Allied an Axis Pouers From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Warld War II, or the Seicont Warld War (aften abbreviatit as WWII or WW2), wis a global war that stertit in 1939 an endit in 1945. It inrowed the wappin forces o the warld's naitions—includin aw o the great pouers—at the hinner en formin twa opponin military alliances: the Feres an the Axis. It wis the braidest war in history, an directly inrowed mair nor 100 million fowk frae ower 30 kintras. In a state o "tot war", the major participants funged thair hail economic, industrial, an scienteefic cawpabilities ahint the war brash, erasin the distinction atween ceevilian an militar resoorces. Merkit bi mass daiths o ceevilians, includin the Holocaust (in whilk thareaboot 11 million fowk wis killt)[1][2] an the strategic bombin o industrial an population centres (in whilk thareaboot ane million fowk wis killt, includin the uise o twa nuclear wappens in combat),[3] it resultit in an estimate 50 million tae 85 million fatalities. Thir made Warld War II the deidliest pingle in human history.[4]
The "Scots" that wis uised in this airticle wis written bi a body that haesna a guid grip on the leid. Please mak this airticle mair better gin ye can. |
| Warld War II | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Clockwise frae tap left: Cheenese forces in the Battle o Wanjialing, Australian 25-pounder guns durin the First Battle o El Alamein, German Stuka dive bombers on the Eastren Front winter 1943–1944, US naval force in the Lingayen Gulf, Wilhelm Keitel signin the German Instrument o Surrender, Soviet troops in the Battle o Stalingrad | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Allies Client an puppet states |
Axis Co-belligerents Client and puppet states | ||||||
| Commanders an leaders | |||||||
|
...an ethers |
...an ethers | ||||||
| Casualties an losses | |||||||
|
Militar dead: Ower 16,000,000 Civilian dead: Over 45,000,000 Total dead: Over 61,000,000 (1937–45) ...further details |
Militar dead: Ower 8,000,000 Civilian dead: Over 4,000,000 Total dead: Over 12,000,000 (1937–45) ...further details | ||||||
The Empire o Japan ettilt tae dominate Asie an the Paceefic an wis awready at war wi the Republic o Cheenae in 1937,[5] but the warld war is generally said tae hae began on 1 September 1939[6] wi the invasion o Poland bi Germany an subsequent declarations o war on Germany bi Fraunce an the Unitit Kinrick. Frae late 1939 tae early 1941, in a series o campaigns an treaties, Germany vinkisht or maunt the feck o continental Europe, an formed the Axis alliance wi Italy an Japan. Follaein the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Germany an the Soviet Union pairteetioned an annexed territories o thair European neighbours, Poland, Finland, Romanie an the Baltic states. The Unitit Kinrick an the Breetish Commonweel wis the anerly Allied forces continuin the fecht agin the European Axis pouers, wi campaigns in North Africae an the Horn o Africae as weel as the lang-rinnin Battle o the Atlantic. In Juin 1941, the European Axis pouers lencht an invasion o the Soviet Union, appenin the lairgest laund war theatre in history, whilk trappit the feck o the Axis' militar forces intae a attrition war. In December 1941, Japan attackit the Unitit States an European territories in the Paceefic Ocean, an swith vinkisht a fait feck o the Wastren Paceefic.
The Axis forderin hautit in 1942 whan Japan lost the creetical Battle o Midway, near Hawaii, an Germany wis defait in the North Africae an syne, decisively, at Stalingrad in the Soviet Union. In 1943, wi a series o German defaits on the Eastren Front, the Allied invasion o Italy whilk rase Italian renooncement, an Allied owerhauns in the Paceefic, the Axis lost the initiative an taen legbail on haun on aw fronts. In 1944, the Wastren Allies invadit German-occupied Fraunce, while the Soviet Union won back aw o its territorial losses an invadit Germany an its feres. Durin 1944 an 1945 the Japanese dreed major reverses in mainland Asie in Sooth Central Cheenae an Burma, while the Allies lamed the Japanese Navy an fangt key Wastren Paceefic islands.
The war in Europe endit wi an invasion o Germany bi the Wastren Allies an the Soviet Union culminatin in the tak o Berlin bi Soviet an Pols truips an the subsequent German uncondeetional surrender on 8 Mey 1945. Follaein the Potsdam Declaration bi the Allies on the 26t Julie 1945 an Japan's refuise o tae renoonce unner its terms, the Unitit States drappit atomic bombs on the Japanese ceeties o Hiroshima an Nagasaki on the 6t August an the 9t August respectively. Wi an invasion o the Japanese airchipelago imminent, the possibility o addeetional atomic bombins, an the Soviet Union's declaration o war on Japan an invasion o Manchuria, Japan renoonced on the 15t August 1945. Sicweys endit the war in Asie, souderin the Allies' tot victory.
Warld War II chynged the warld's poleetical alignment an social structur. The Unitit Naitions (UN) wis estaiblisht fur tae forder internaitional comploutherin an fur tae prevene futur conflicks. The gree-bearin great pouers—the Unitit States, the Soviet Union, Cheenae, the Unitit Kinrick, an Fraunce—became the permanent memmers o the Unitit Naotions Security Cooncil.[7] The Soviet Union an the Unitit States ootcam as rival superpouers, settin the stage fur the Cauld War, whilk lastit fur the neist 46 year. Atween haun, the European great pouers' hank waned, while the decolonisation o Asie an Africae began. Maist kintras whase industries haed been damaged muived taewart economic betterness. Poleetical integration, inspecially in Europe, wis a war ootcome, as pairt o a ettle at endin afore-war laith an creautin a common identity.[8]
Warld War I haed radically altert the poleetical European map, wi the defeat o the Central Powers—includin Austrick-Hungary, Germany, Bulgarie an the Ottoman Empire—an the 1917 Bolshevik seizur o pouer in Roushie, that hinderly led tae the foondin o the Soviet Union. Atween haun, the veectorious Allies o Warld War I, sic as Fraunce, Belgium, Italy, Romanie an Greece, gained territory, an new naition-states wis creatit oot o the collapse o Austrick-Hungary an the Ottoman an Roushie Empires. Fur tae prevene a futur warld war, the League o Naitions wis creatit in the 1919 Paris Peace Conference.
Maugre strang pacifist sentiment efter Warld War I,[9] its eftermath still caused irredentist an revanchist naitionalism in several European states. Thir sentiments wis especially merkit in Germany acause o the signeeficant territorial, colonial, an financial losses incurred bi the Treaty o Versailles. Unner the treaty, Germany lost aroond 13 percent o its hame territory an aw o its owerseas possessions, while German annexation o ither states wis prohibitit, reparations war imposed, an leemits wis placed on the size an capability o the kintra's airmed forces.[10]
The German Empire wis dissolved in the German Revolution o 1918–1919, an a democratic govrenment, later kent as the Weimar Republic, wis creautit. The interwar period saw strife atween supporters o the new republic an hardline opponents on baith the richt an left. Italy, as an Entente ally, haed made some post-war territorial gains; houiver, Italian naitionalists wis angert that the promises made bi Breetain an Fraunce tae siccar Italian entrance intae the war wisnae fulfilt in the peace dounset. Frae 1922 tae 1925, the Fascist muivement led bi Benito Mussolini seized pouer in Italy wi a naitionalist, totalitarian, an cless collaborationist agenda that abolisht representative democracy, repressed socialist, left-weeng an leeberal forces, an pursued an aggressive expansionist foreign policy aimed at makkin Italy a warld pouer, promisin the creaution o a "New Roman Empire".[11]

Adolf Hitler, efter an unsuccessfu attempt tae owerthraw the German govrenment in 1923, eventually acame the Chancellor o Germany in 1933. He abolisht democracy, espoosin a radical, racially motivatit revision o the warld order, an suin begoud a massive reairmament campaign.[12] Meanwhile, Fraunce, tae siccar its alliance, alloued Italy a free haund in Ethiopie, that Italy desired as a colonial possession. The situation wis aggravatit in early 1935 whan the Territory o the Saar Basin wis legally reunitit wi Germany an Hitler repudiatit the Treaty o Versailles, acceleratit his reairmament programme, an introduced conscription.[13]
Hitler defee'd the Versailles an Locarno treaties bi remilitarisin the Rhineland in Mairch 1936, encoonterin little opposeetion.[14] In October 1936, Germany an Italy formed the Roum–Berlin Axis. A month later, Germany an Japan signed the Anti-Comintern Pact, that Italy wad jyne in the follaein year.
The Kuomintang (KMT) pairty in Cheenae launched a unification campaign against regional warlairds an nominally unifee'd Cheenae in the mid-1920s, but wis suin embrulyie'd in a ceevil war against its umwhile Cheenese Communist Pairty allies[15] an new regional warlairds. In 1931, an increasinly militareestic Empire o Japan, that haed lang soct influence in Cheenae[16] as the first step o whit its govrenment saw as the kintra's richt tae rule Asie, uised the Mukden Incident as a pretext tae launch an invasion o Manchurie an establish the puppet state o Manchukuo.[17]
Ower waik tae resist Japan, Cheenae appealt tae the League o Naitions fur help. Japan widrew frae the League o Naitions efter bein condemned fur its incursion intae Manchurie. The twa naitions syne focht several battles, in Shanghai, Rehe an Hebei, till the Tanggu Truce wis signed in 1933. Thareefter, Cheenese volunteer forces conteena'd the reseestance tae Japanese aggression in Manchurie, an Chahar an Suiyuan.[18] Efter the 1936 Xi'an Incident, the Kuomintang an communist forces greed on a ceasefire tae present a unitit front fur tae oppone Japan.[19]
Whan ceevil war ootbrak in Spain, Hitler an Mussolini lent militar uphaudin tae the Naitionalist rebels, led bi General Francisco Franco. The Soviet Union uphaudit the existin govrenment, the Spaingie Republic. Ower 30,000 foreign volunteers, kent as the Internaitional Brigades, forby focht agin the Naitionalists. Baith Germany an the USSR uised this proxy war as an opportunity fur tae test in combat thair maist advanced wappens an tactics. The Naitionalists wan the ceevil war in Apryle 1939; Franco, nou dictator, remeened offeecially neutral in World War II but generally favoured the Axis.[20] His greatest collaboration wi Germany wis the sendin o volunteers tae fecht on the Eastren Front.[21]
In Julie 1937, Japan capturt the umwhile Cheenese imperial caipital o Peking efter instigatin the Marco Polo Brig Incident, that culminatit in the Japanese campaign tae invade aw o Cheenae.[22] The Soviets quickly signed a non-aggression pact wi Cheenae tae lend materiel uphaudin, effectively endin Cheenae's prior comploutherin wi Germany. Frae September tae November, the Japanese attackit Taiyuan,[23][24] as weel as engagin the Kuomintang Airmy aroond Xinkou[23][24] an Communist forces in Pingxingguan.[25][26] Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek deployed his best airmy tae defend Shanghai, but, efter three month o fechtin, Shanghai fell. The Japanese conteena'd tae push the Cheenese forces back, capturin the caipital Nanking in December 1937. Efter the faw o Nanking, tens o thoosands, gif no hunders o thoosands, o Cheenese ceevilians an disairmed combatants wis murthert bi the Japanese.[27][28]
In Mairch 1938, Naitionalist Cheenese forces wan thair first major veectory at Taierzhuang but then the ceety o Xuzhou wis taken bi Japanese in Mey.[29] In Juin 1938, Cheenese forces stawed the Japanese advance bi fluidin the Yellae River; this manoeuvre bocht time fur the Cheenese tae prepare thair defences at Wuhan, but the ceety wis takken bi October.[30] Japanese militar veectories didnae bring aboot the collapse o Cheenese resistance that Japan haed howpit tae achieve; insteid the Cheenese govrenment relocatit inland tae Chongqing an conteena'd the war.[31][32]

In Europe, Germany an Italy wis becomin aggressiver. In Mairch 1938, Germany annexed Austrick, again provokin a bittock response frae ither European pouers.[33] Encouraged, Hitler begoud pressin German claims on the Sudetenland, an aurie o Czechoslovakie wi a predominantly ethnic German population; an suin Breetain an Fraunce follaed the coonsel o Breetish Prime Meenister Neville Chamberlain an concedit this territory tae Germany in the Munich Greement, that wis made agin the wishes o the Czechoslovak govrenment, in exchynge fur a promise o nae mair territorial demands.[34] Suin efterwart, Germany an Italy forced Czechoslovakie tae cede addeetional territory tae Hungary an Poland annexed Czechoslovakie's Zaolzie region.[35]
Awtho aw o Germany's statit demands haed been satisfee'd bi the greement, preevatly Hitler wis furious that Breetish interference haed preventit him frae seizin aw o Czechoslovakie in ane operation. In subsequent speeches, Hitler attackit Breetish an Jewish "war-mongers" an in Januar 1939 saicretly ordered a major big-up o the German navy tae challenge Breetish naval supremacy. In Mairch 1939, Germany invadit the remeender o Czechoslovakie an subsequently split it intae the German Pertectorate o Bohemie an Moravie an a pro-German client state, the Slovak Republic.[36] Hitler forby deleevered the 20 Mairch 1939 ultimatum tae Lithuanie, forcin the concession o the Klaipėda Region.
Greatly alairmed an wi Hitler makkin forder demands on the Free Ceety o Danzig, Breetain an Fraunce guaranteed thair uphaudin o Pols unthirldom; whan Italy conquered Albanie in Apryle 1939, the same guarantee wis extendit tae Romanie an Greece.[37] Shortly efter the Franco-Breetish pledge tae Poland, Germany an Italy formalised thair awn alliance wi the Pact o Steel.[38] Hitler accuised Breetain an Poland o tryin tae "encircle" Germany an renoonced the Anglo-German Naval Greement an the German–Pols Non-Aggression Pact.
The situation reakit a general creesis in late August as German truips conteena'd tae mobilise agin the Pols mairch. In August 23, whan tripartite negotiations aboot a militar alliance atween Fraunce, Breetain an USSR stawed[39], Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact wi Germany.[40] This pact haed a saicret protocol that defined German an Soviet "spheres o influence" (wastren Poland an Lithuanie for Germany; eastren Poland, Finland, Estonie, Latvie an Bessarabie fur the USSR), an raised the quaisten o conteenuin Pols unthirldom.[41] The pact neutralised the possibility o Soviet opposeetion tae a campaign against Poland an assured that Germany wad nae hae tae face the prospect o a twa-front war, as it haed in Warld War I. Immediately efter that, Hitler ordert the attack tae proceed on 26 August, but upon hearin that Breetain haed concludit a formal mutual assistance pact wi Poland, an that Italy wad mainteen neutrality, he decidit tae delay it.[42]
In response tae Breetish requests fur direct negotiations fur tae evit war, Germany made demands on Poland, that anerly served as a pretext tae worsen relations.[43] On 29 August, Hitler demanded that a Pols plenipotentiary immediately traivel fur tae Berlin tae negotiate the haundower o Danzig, an tae allou a plebiscite in the Pols Corridor in that the German minority wad vote on secession.[43] The Poles refuised tae complee wi the German demands, an on the nicht o 30–31 August in a veeolent meetin wi the Breetish ambassador Neville Henderson, Ribbentrop declared that Germany conseedert its claims rejectit.[44]
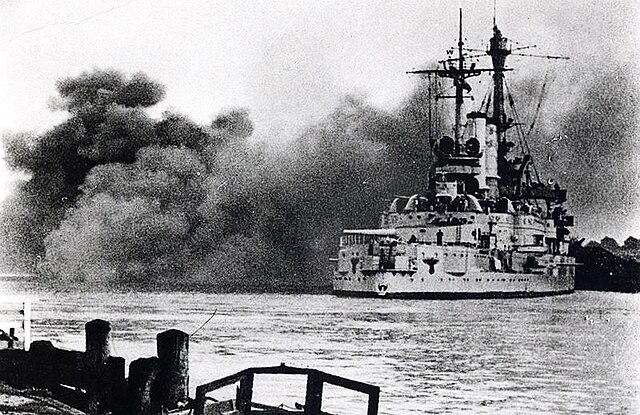
On 1 September 1939, upon haein staged several mairch incidents, Germany invadit Poland. [45] The Battle o Westerplatte is aften descrived as the first European battle o Warld War II. Breetain respondit wi an ultimatum tae Germany tae cease militar operations, an on 3 September, efter the ultimatum wis ignored, Fraunce, Breetain, Australie, an New Zealand declared a war on Germany. This alliance wis jynt bi Sooth Africae (6 September) an Canadae (10 September). The alliance providit na direct militar support tae Poland, ootside o a cautious French probe intae the Saarland.[46] The Wastren Allies forby begoud a naval blockade o Germany, that aimed tae damage the kintra's economy an war effort.[47] Germany respondit bi orderin U-boat warfare agin Allied merchand an warships, that wad later escalate intae the Battle o the Atlantic.
On 8 September, German truips reached suburbs o Warsaw. The Pols wastlin coonter offensive hautit the German advance fur several day, but it wis ootflankit an encircled bi the Wehrmacht. Remnants o the Pols airmy brak throu tae besieged Warsaw. On 17 September 1939, efter signin a cease-fire wi Japan, the Soviets invadit Eastren Poland.[48]
On 27 September, Warsaw gairison signed a cease-fire an surrendered tae the Germans, an the last lairge operational unit o the Pols Airmy surrendered on 6 October. Maugre a militar defeat, the Pols govrenment niver surrendered; the Pols resistance established an Unnergrund State an a pairtisan Hame Airmy.[49].
Germany annexed the wastren an occupied the central pairt o Poland, an the USSR annexed its eastren pairt; smaw shares o Pols territory war transferred tae Lithuanie an Slovakie. On the 6t October, Hitler made a public peace owertur tae Breetain an Fraunce, but said that the futur o Poland wis tae be determined exclusively bi Germany an the Soviet Union. The proposal wis rejectit[44], an Hitler ordered an immediate offensive agin Fraunce,[50] that wad be postponed till the ware o 1940 due tae bad wather. [51][52][53]
The Soviet Union forced the Baltic kintras—Estonie, Latvie an Lithuanie, the states that war in a Soviet sphere o influence"—tae sign "mutual assistance pacts" that stipulatit stationin Soviet truips in thir kintras. Suin efter that, signeeficant Soviet militar contingent wis muived thare.[54][55][56]. Finland refuised tae sign a seemilar pact an rejectit tae cede pairt o its territory tae the USSR, thar promptit a Soviet invasion in November 1939[57], an the USSR wis expelt frae the League o Naitions[58]. Despite owerwhelmin numerical superiority, Soviet militar sonse wis modest, an the Finno-Soviet war endit in Mairch 1940 wi meenimal Finnish concessions.[59]
In Juin 1940, the Soviet Union forcibly annexed Estonie, Latvie an Lithuanie,[55] an the disputit Romanie regions o Bessarabie, Northren Bukovina an Hertza. Meanwhile, Nazi-Soviet poleetical rapprochement an economic co-operation[60][61] gradually stawed,[62][63] an baith states begoud preparations for war.[64]

In Apryle 1940, Germany invadit Denmark an Norawa tae pertect shipments o airn ore frae Swaden, that the Allies war attemptin tae cut aff bi unilaterally minin neutral Norse watters.[65] Denmark capitulatit efter a few oors, an mauggre Allied support, in that the important herbour o Narvik temporarily wis recapturt frae the Germans, Norawa wis conquert within twa month.[66] Breetish discontent ower the Norse campaign led tae the replacement o the Breetish Prime Meenister, Neville Chamberlain, wi Winston Churchill on 10 Mey 1940.[67]
Germany launcht an offensive agin Fraunce an, adherin tae the Manstein Plan forby attackit the neutral naitions o Belgium, the Netherlands, an Luxembourg on 10 Mey 1940.[68] That same day, Breetish forces laundit in Iceland an the Faroes tae preempt a possible German invasion o the islands.[69] The US, in close co-operation wi the Dens envoy tae Washington D.C., greed tae pertect Greenland, layin the poleetical framewark for the formal establishment o bases in Apryle 1941. The Netherlands an Belgium wis owerrun uisin blitzkrieg tactics in a few days an weeks, respectively.[70] The French-fortifee'd Maginot Line an the main bouk o the Allied forces that haed muived intae Belgium wae circumventit bi a flankin muivement throu the thickly widdit Ardennes region,[71] mistakenly perceived bi Allied planners as an impenetrable naitural barrier against airmoured vehicles.[72][73] As a result, the bouk o the Allied airmies foond themsels trappit in an encirclement an war beaten. The majority war takken prisoner, whilst ower 300,000, maistly Breetish an French, war evacuated frae the continent at Dunkirk bi early Juin, awtho abandonin awmaist aw o thair equipment.[74]
On the 10t Juin, Italy invadit Fraunce, declarin war on baith Fraunce an the Unitit Kinrick.[75] Paris fell tae the Germans on the 14t Juin an aicht days later Fraunce signed an airmistice wi Germany an wis suin dividit intae German an Italian occupation zones,[76] an a wanoccupied rump state unner the Vichy Regime, that, tho offeecially neutral, wis generally aligned wi Germany. Fraunce kept its fleet but the Breetish feared the Germans wad seize it, sae on 3 Julie, the Breetish attacked it.[77]
The Battle o Breetain[78] begoud in early Julie wi Luftwaffe attacks on shippin an herbours.[79] On 19 Julie, Hitler again publicly offert tae end the war, sayin he wisna wantin tae destroy the Breetish Empire. The Unitit Kinrick rejectit this ultimatum.[80] The main German air superiority campaign stairtit in August but failed tae defeat RAF Fechter Command, an a proponed invasion wis postponed indefinitely on 17 September. The German strategic bombin offensive intensifee'd as nicht attacks on Lunnon an ither ceeties in the Blitz, but lairgely failed tae disrupt the Breetish war effort.[79]
Uisin newly capturt French ports, the German Navy enjoyed success against an ower-extendit Ryal Navy, uisin U-boats agin Breetish shippin in the Atlantic.[81] The Breetish scored a signeeficant veectory on 27 Mey 1941 bi sinkin the German battleship Bismarck.[82] Aiblins maist importantly, in the Battle o Breetain the Ryal Air Force haed successfully reseestit the Luftwaffe's assault, an the German bombin campaign lairgely endit in Mey 1941.[83]
Ootthrou this period, the neutral Unitit States teuk meisurs tae assist Cheenae an the Wastren Allies. In November 1939, the American Neutrality Act wis amendit tae allou "cash an cairy" purchases bi the Allies.[84] In 1940, follaein the German captur o Paris, the size o the Unitit States Navy wis signeeficantly increased. In September, the Unitit States forder greed tae a tred o American destroyers for Breetish bases.[85] Still, a lairge majority o the American public conteena'd tae oppone ony direct militar intervention intae the conflict weel inte 1941.[86] Awtho Roosevelt haed promised tae keep the Unitit States oot o the war, he nivertheless teuk concrete steps tae prepare for war.
At the end o September 1940, the Tripartite Pact unitit Japan, Italy an Germany tae formalise the Axis Pouers. The Tripartite Pact stipulatit that ony kintra, wi the exception o the Soviet Union, no in the war that attacked ony Axis Power wad be forced tae gae tae war agin aw three.[87] The Axis expandit in November 1940 whan Hungary, Slovakie an Romanie jynt the Tripartite Pact.[88] Romanie wad mak a major contreibution (as did Hungary) tae the Axis war agin the USSR, pairtially tae recaptur territory cedit tae the USSR, pairtially tae pursue its leader Ion Antonescu's desire tae combat communism.[89]

Italy begoud operations in the Mediterranean, ineetiatin a siege o Maltae in Juin, conquerin Breetish Somaliland in August, an makkin an incursion intae Breetish-held Egyp in September 1940. In October 1940, Italy stairtit the Greco-Italian War acause o Mussolini's jealousy o Hitler's success but within days wis repulsed wi few territorial gains an a stalemate suin occurred.[90] The Unitit Kinrick respondit tae Greek requests for assistance bi sendin truips tae Crete an providin air support tae Greece. Hitler decidit that whan the wather impruived he wad tak action against Greece tae assist the Italians an prevent the Breetish frae gaining a fithauld in the Balkans, tae strike against the Breetish naval dominance o the Mediterranean, an tae siccar his hauld on Romanie ile.[91]
Bi late Mairch 1941, follaein Bulgarie's signin o the Tripartite Pact, the Germans war in poseetion tae intervene in Greece. Plans chynged, houiver, acause o developments in neighbourin Yugoslavie. The Yugoslav govrenment haed signed the Tripartite Pact on 25 Mairch, anerly tae be owerthrawn twa day efter bi a Breetish-encouraged coup. Hitler viewed the new regime as hostile an immediately decidit tae eliminate it. On 6 Apryle Germany simultaneously invadit baith Yugoslavie an Greece, makkin rapid progress an forcin baith naitions tae surrender within the month. The Breetish war driven frae the Balkans efter Germany conquered the Greek island o Crete bi the end o Mey.[92] Awtho the Axis veectory wis swift, bitter pairtisan warfare subsequently brak oot agin the Axis occupation o Yugoslavie, whilk conteena'd till the end o the war.
Wi the situation in Europe an Asie relatively stable, Germany, Japan, an the Soviet Union made preparations. Wi the Soviets waurie o moontin tensions wi Germany an the Japanese plannin tae tak advantage o the European War bi seizin resoorce-rich European possessions in Sootheast Asie, the twa pouers signed the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact in Apryle 1941.[93] Bi contrast, the Germans war steadily makkin preparations for an attack on the Soviet Union, massin forces on the Soviet mairch.[94]
Hitler believed that Breetain's refuisal tae end the war wis based on the howp that the Unitit States an the Soviet Union wad enter the war agin Germany suiner or later.[95] He tharefore decidit tae try tae strenthen Germany's relations wi the Soviets, or failin that, tae attack an eliminate them as a factor. In November 1940, negotiations teuk place tae determine if the Soviet Union wad jyne the Tripartite Pact. The Soviets shawed some interest, but asked for concessions frae Finland, Bulgarie, Turkey, an Japan that Germany conseedert unacceptable. On 18 December 1940, Hitler issued the directive tae prepare for an invasion o the Soviet Union.
On 22 Juin 1941, Germany, supportit bi Italy an Romanie, invadit the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa, wi Germany accusin the Soviets o plottin agin them. Thay war jynt shortly bi Finland an Hungary.[96] The primar targets o this surprise offensive[97][page needit] war the Baltic region, Moscow an Ukraine, wi the ultimate goal o endin the 1941 campaign near the Arkhangelsk-Astrakhan line, frae the Caspian tae the White Seas. Hitler's objectives war tae eliminate the Soviet Union as a militar pouer, exterminate Communism, generate Lebensraum ("leevin space")[98] bi dispossessin the native population[99][page needit] an guarantee access tae the strategic resoorces needit tae defeat Germany's remeenin rivals.[100][page needit]

Awtho the Reid Airmy wis preparin for strategic coonter-offensives afore the war,[101][page needit] Barbarossa forced the Soviet supreme command tae adopt a strategic defence. In the simmer, the Axis made signeeficant gains intae Soviet territory, inflictin immense losses in baith personnel an materiel. By the middle o August, houiver, the German Airmy Heich Command decidit tae suspend the offensive o a conseederably depletit Airmy Group Centre, an tae divert the 2nt Panzer Group tae reinforce truips advancin taewart central Ukraine an Leningrad.[102][page needit] The Kiev offensive wis owerwhalminly successfu, resultin in encirclement an elimination o fower Soviet airmies, an made possible further advance intae Crimea an industrially developit Eastren Ukraine (the First Battle o Kharkov).[103]
The diversion o three quarter o the Axis truips an the majority o thair air forces frae Fraunce an the central Mediterranean tae the Eastren Front[104] promptit Breetain tae reconseeder its grand strategy.[105][page needit] In Julie, the UK an the Soviet Union formed a militar alliance against Germany[106] The Breetish an Soviets invadit neutral Iran tae siccar the Persian Corridor an Iran's ile fields.[107] In August, the Unitit Kinrick an the Unitit States jyntly issued the Atlantic Chairter.[108]
Bi October Axis operational objectives in Ukraine an the Baltic region war achieved, wi anerly the sieges o Leningrad[109][page needit] an Sevastopol conteenain.[110] A major offensive against Moscow wis renewed; efter twa month o fierce battles in increasinly hersh wather the German airmy awmaist reached the ooter suburbs o Moscow, whaur the exhaustit truips[111] war forced tae suspend thair offensive.[112] Lairge territorial gains war made bi Axis forces, but thair campaign haed failed tae achieve its main objectives: twa key ceeties remeened in Soviet haunds, the Soviet capability tae resist wis nae brak, an the Soviet Union reteened a conseederable pairt o its militar potential. The blitzkrieg phase o the war in Europe haed endit.[113][page needit]
Bi early December, freshly mobilised reserves[114][page needit] alloued the Soviets tae achieve numerical parity wi Axis truips.[115] This, as weel as intelligence data that established that a meenimal nummer o Soviet truips in the East wad be sufficient tae deter ony attack bi the Japanese Kwantung Airmy,[116][page needit] alloued the Soviets tae begin a massive coonter-offensive that stairtit on 5 December aw alang the front an pushed German truips 100–250 kilometre (62–155 mi) wast.[117]
In 1939, the Unitit States haed renoonced its tred treaty wi Japan; an, beginnin wi an aviation petrol ban in Julie 1940, Japan becam subject tae increasin economic pressur.[80] In this time, Japan launched its first attack against Changsha, a strategically important Cheenese ceety, but wis repulsed bi late September.[118] Despite several offensives bi baith sides, the war atween Cheenae an Japan wis stalematit bi 1940. Tae increase pressur on Cheenae bi blockin supply routes, an tae better poseetion Japanese forces in the event o a war wi the Wastren powers, Japan invadit an occupied northren Indocheenae.[119] Efterwart, the Unitit States embargoed airn, steel an mechanical pairts against Japan.[120] Ither sanctions suin follaed.
Syne early 1941 the Unitit States an Japan haed been engaged in negotiations in an attempt tae impruive thair streened relations an end the war in Cheenae. In thir negotiations Japan advanced a nummer o proponements that war dismissed bi the Americans as inadequate.[121] At the same time the US, Breetain, an the Netherlands engaged in saicret discussions for the jynt defence o thair territories, in the event o a Japanese attack against ony o them.[122] Roosevelt reinforced the Philippines (an American pertectorate scheduled for unthirldom in 1946) an wairned Japan that the US wad react tae Japanese attacks against ony "neebourin kintra".[122] Japan prepared for war efter failed negotiations.
On 7 December 1941 (8 December in Asie time zones), Japan attacked Breetish an American hauldins wi near-simultaneous offensives against Sootheast Asie an the Central Paceefic.[123] Thir includit an attack on the American fleet at Pearl Harbor, the Philippines, landings in Thailand an Malaya[123] an the battle o Hong Kong. Thir attacks led the Unitit States, Unitit Kinrick, Cheenae, Australie an several ither states tae formally declare war on Japan, whauras the Soviet Union, bein hivily involved in lairge-scale hostilities wi European Axis kintras, mainteened its neutrality agreement wi Japan.[124] Germany, follaed bi the ither Axis states, declared war on the Unitit States[125] in solidarity wi Japan, citin as juistification the American attacks on German war veshels that haed been ordered bi Roosevelt.[96][126]
In 1942, Allied offeecials debatit on the appropriate grand strategy tae pursue. Aw agreed that defeatin Germany wis the primar objective. The Americans favourt a straichtforrit, lairge-scale attack on Germany throu Fraunce. The Soviets wis forby demandin a seicont front. The Breetish, on the ither haund, argied that militar operations shoud target peripheral auries tae weir oot German strenth, leadin tae increasin demoralisation, an bolster resistance forces. Germany itsel wad be subject tae a hivy bombin campaign. An offensive agin Germany wad then be launched primarily bi Allied airmour withoot uisin lairge-scale airmies.[127] Eventually, the Breetish persuadit the Americans that a laundingin Fraunce wis infeasible in 1942 an thay shoud insteid focus on drivin the Axis oot o North Africae.[128]
Bi the end o Apryle 1942, Japan an its ally Thailand haed awmaist fully conquered Burma, Malaya, the Dutch East Indies, Singapore, an Rabaul, inflictin severe losses on Allied truips an takkin a lairge nummer o preesoners.[129] Despite stubborn resistance bi Filipino an US forces, the Philippine Commonweel wis eventually capturt in Mey 1942, forcin its govrenment intae exile.[130]
In airly Mey 1942, Japan ineetiatit operations tae captur Port Moresby bi amphibious assault an sicweys sever communications an supply lines atween the Unitit States an Australie. The plant invasion wis thortert whan an Allied task force, centred on twa American fleet cairiers, focht Japanese naval forces tae a draw in the Battle o the Coral Sea.[131] Japan's next plan, motivatit bi the earlier Doolittle Raid, wis tae seize Midway Atoll an wyse American cairiers intae battle tae be eliminatit; as a diversion, Japan wad forby send forces tae occupy the Aleutian Islands in Alaska.[132] In mid-Mey, Japan stairtit the Zhejiang-Jiangxi Campaign in Cheenae, wi the goal o inflictin retribution on the Cheenese that aidit the survivin American airmen in the Doolittle Raid bi destroyin air bases an fechtin against the Cheenese 23rd an 32nd Airmy Groups.[133][134] In early Juin, Japan put its operations intae action but the Americans, haein brak Japanese naval codes in late Mey, war fully awaur o plans an order o battle, an uised this knawledge tae achieve a decisive veectory at Midway ower the Imperial Japanese Navy.[135]

Maugre conseederable losses, in airly 1942 Germany an its allies stappit a major Soviet offensive in central an soothren Roushie, keepin maist territorial gains thay haed achieved in the umwhile year.[136]
Bi mid-November, the Germans haed nearly takken Stalingrad in bitter street fechtin whan the Soviets begoud thair seicont winter coonter-offensive, stairtin wi an encirclement o German forces at Stalingrad[137] an an assault on the Rzhev salient near Moscow, tho the latter failed disastrously.[138] Bi early Februar 1943, the German Airmy haed taen tremendous losses; German truips at Stalingrad haed been forced tae surrender,[139] an the front-line haed been pushed back ayont its poseetion afore the simmer offensive. In mid-Februar, efter the Soviet push haed tapered aff, the Germans launcht anither attack on Kharkov, creautin a salient in thair front line aroond the Soviet ceety o Kursk.[140]
Exploitin puir American naval command deceesions, the German navy ravaged Allied shippin aff the American Atlantic coast.[141] Bi November 1941, Commonweel forces haed launched a coonter-offensive, Operation Crusader, in North Africae, an reclaimed aw the gains the Germans an Italians haed made.[142]
In Juin 1943 the Breetish an Americans begoud a strategic bombin campaign against Germany wi a goal tae disrupt the war economy, reduce morale, an "de-hoose" the ceevilian population.[143] The firebombin o Hamburg wis amang the first attacks in this campaign, it lead tae signeeficant causalities an inflictit conseederable losses on infrastructur o this important industrial centre.[144]
On 3 September 1943, the Wastren Allies invadit the Italian mainland, follaein Italy's airmistice wi the Allies.[145] Germany wi the help o fascists respondit bi disairmin Italian forces that wis in mony places withoot superior orders, seizin militar control o Italian auries,[146] an creautin a series o defensive lines.[147] German special forces then rescued Mussolini, that then suin established a new client state in German-occupied Italy named the Italian Social Republic,[148] causin an Italian ceevil war. The Wastren Allies focht throu several lines till reachin the main German defensive line in mid-November.[149]
In November 1943, Franklin D. Roosevelt an Winston Churchill met wi Chiang Kai-shek in Cairo an then wi Joseph Stalin in Tehran.[150] The umwhile conference determined the post-war return o Japanese territory[151] an the militar plannin fur the Burma Campaign,[152] while the latter includit greement that the Wastren Allies wad invade Europe in 1944 an that the Soviet Union wad declare war on Japan within three month o Germany's defeat.[153]
Bi the end o Januar 1944, a major Soviet offensive herried oot German forces frae the Leningrad region,[154] endin the langest an maist lethal siege in history. Bi late Mey, the Soviets haed leeberatit Crimea, lairgely expelled Axis forces frae Ukraine, an made incursions intae Romanie, that war repulsed bi the Axis truips.[155] The Allied offensives in Italy haed succeedit an, at the expense o allouin several German diveesions tae retreat, on 4 Juin, Roum wis capturt.[156]

On 6 Juin 1944 (kent as D-Day), efter three year o Soviet pressur,[157] the Wastren Allies invadit northren Fraunce. Efter reassignin several Allied divisions frae Italy, thay forby attacked soothren Fraunce.[158] Thir laundins war successfu, an led tae the defeat o the German Airmy units in Fraunce. Paris wis leeberatit bi the local reseestance assistit bi the Free French Forces, baith led bi General Charles de Gaulle, on 25 August[159] an the Wastren Allies conteena'd tae push back German forces in wastren Europe in the latter pairt o the year. An attempt tae advance intae northren Germany speirheidit bi a major airborne operation in the Netherlands failed.[160] Thareefter, the Wastren Allies slawly pushed intae Germany, but failed tae cross the Ruhr river in a lairge offensive. In Italy, Allied advance forby slawed due tae the last major German defensive line.[161]
On 22 Juin, the Soviets launched a strategic offensive in Belaroushie ("Operation Bagration") that destroyed the German Airmy Group Centre awmaist completely.[162] Suin efter that anither Soviet strategic offensive forced German truips frae Wastren Ukraine an Eastren Poland. The Soviet advance promptit reseestance forces in Poland tae ineetiate several uprisins agin the German occupation. Houiver, the lairgest o thir in Warsaw, whaur German sodgers massacred 200,000 ceevilians, an a naitional uprisin in Slovakie, did nae receive Soviet support an war subsequently suppressed bi the Germans.[163] The Reid Airmy's strategic offensive in eastren Romanie cut aff an destroyed the conseederable German truips thare an triggered a successfu coup d'état in Romanie an in Bulgarie, follaed bi thae kintras' shift tae the Allied side.[164]
In September 1944, Soviet truips advanced intae Yugoslavie an forced the rapid widrawal o German Airmy Groups E an F in Greece, Albanie an Yugoslavie tae rescue them frae bein cut aff.[165] Bi this pynt, the Communist-led Pairtisans unner Marshal Josip Broz Tito, that haed led an increasinly successfu guerrilla campaign against the occupation syne 1941, controlled muckle o the territory o Yugoslavie an engaged in delayin efforts against German forces forder sooth. In northren Serbie, the Reid Airmy, wi leemitit support frae Bulgarie forces, assisted the Pairtisans in a jynt leeberation o the caipital ceety o Belgrade on 20 October. A few days later, the Soviets launched a massive assault against German-occupied Hungary that lastit till the faw o Budapest in Februar 1945.[166] Unlik impressive Soviet veectories in the Balkans, bitter Finnish reseestance tae the Soviet offensive in the Karelie Isthmus denee'd the Soviets occupation o Finland an led tae a Soviet-Finnish airmistice on relatively mild condeetions,[167][168] awtho Finland wis forced tae fecht thair umwhile allies.
In the Paceefic, US forces conteena'd tae press back the Japanese perimeter. In mid-Juin 1944, thay begoud thair offensive agin the Mariana an Palau islands, an decisively defeatit Japanese forces in the Battle o the Philippine Sea. Thir defeats led tae the resignation o the Japanese Prime Meenister, Hideki Tojo, an providit the Unitit States wi air bases tae launch intensive hivy bomber attacks on the Japanese hame islands. In late October, American forces invadit the Filipino island o Leyte; suin efter, Allied naval forces scored anither lairge veectory in the Battle o Leyte Gulf, ane o the lairgest naval battles in history.[169]
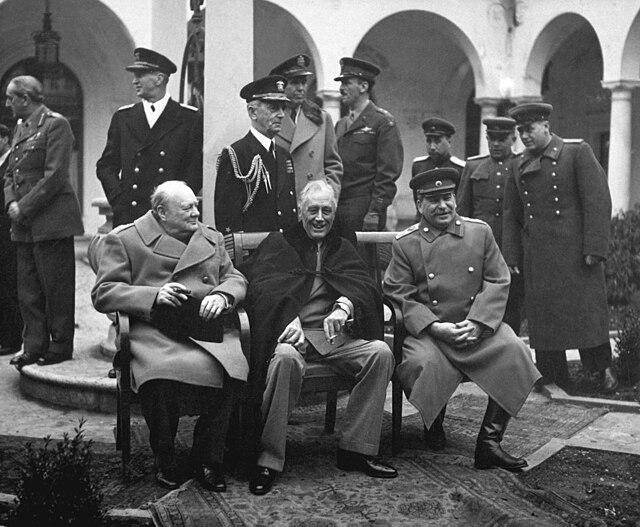

On 16 December 1944, Germany made a last attempt on the Wastren Front bi uisin maist o its remeenin reserves tae launch a massive coonter-offensive in the Ardennes an alang the French–German mairch tae split the Wastren Allies, encircle lairge portions o Wastren Allied truips an captur thair primar supply port at Antwerp tae prompt a poleetical dounset.[170] Bi Januar, the offensive haed been repulsed wi na strategic objectives fulfilled.[170] In Italy, the Wastren Allies remeened stalemated at the German defensive line. In mid-Januar 1945, the Soviets an Poles attacked in Poland, pushin frae the Vistula tae the Oder river in Germany, an overran East Proushie.[171] On 4 Februar, Soviet, Breetish an US leaders met for the Yalta Conference. Thay greed on the occupation o post-war Germany, an on whan the Soviet Union wad jyne the war against Japan.[172]
In Februar, the Soviets entered Silesie an Pomeranie, while Wastren Allies entered wastren Germany an closed tae the Rhine river. Bi Mairch, the Wastren Allies crossed the Rhine north an sooth o the Ruhr, encirclin the German Airmy Group B,[173] while the Soviets advanced tae Vienna. In early Apryle, the Wastren Allies feenally pushed forrit in Italy an soopit athort wastren Germany capturin Hamburg an Nuremberg, while Soviet an Polshforces stormed Berlin in late Apryle. American an Soviet forces met at the Elbe river on 25 Apryle. On 30 Apryle 1945, the Reichstag wis capturt, seegnallin the militar defeat o Nazi Germany.[174]
Several chynges in leadership occurred in this period. On 12 Apryle, Preses Roosevelt dee'd an wis succeedit bi Harry S. Truman. Benito Mussolini wis killt bi Italian pairtisans on 28 Apryle.[175] Twa days later, Hitler committit suicide, an wis succeedit bi Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz.[176]
German forces surrendered in Italy on 29 Apryle. Tot an uncondeetional surrender wis signed on 7 Mey, tae be effective bi the end o 8 Mey.[177] German Airmy Group Centre reseestit in Prague till 11 Mey.[178]
In the Paceefic theatre, American forces accompanied bi the forces o the Philippine Commonweel advanced in the Philippines, clearin Leyte bi the end o Apryle 1945. Thay laundit on Luzon in Januar 1945 an recapturt Manila in Mairch follaein a battle that reduced the ceety tae ruins. Fechtin conteena'd on Luzon, Mindanao, an ither islands o the Philippines till the end o the war.[179] Meanwhile, the Unitit States Airmy Air Forces (USAAF) war destroyin strategic an populatit ceeties an touns in Japan in an effort tae destroy Japanese war industrie an ceevilian morale. On the nicht o 9–10 Mairch, USAAF B-29 bombers struck Tokyo wi thoosands o incendiary bombs, that killt 100,000 ceevilians an destroyed 16 square mile (41 km2) within a few oors. Ower the next five month, the USAAF firebombed a tot o 67 Japanese ceeties, killin 393,000 ceevilians an destroyin 65% o biggit-up auries.[180]
On 11 Julie, Allied leaders met in Potsdam, Germany. Thay confirmed earlier greements aboot Germany,[181] an reiteratit the demand for uncondeetional surrender o aw Japanese forces bi Japan, speceefically statin that "the alternative for Japan is prompt an utter destruction".[182] In this conference, the Unitit Kinrick held its general election, an Clement Attlee replaced Churchill as Prime Meenister.[183]

The Allies cried for uncondeetional Japanese surrender in the Potsdam Declaration o 27 Julie, but the Japanese govrenment rejectit the cry. In early August, the USAAF drappit atomic bombs on the Japanese ceeties o Hiroshima an Nagasaki. Atween the twa bombins, the Soviets, pursuant tae the Yalta greement, invadit Japanese-held Manchurie, an quickly defeatit the Kwantung Airmy, that wis the lairgest Japanese fechtin force.[184][185] The Reid Airmy an aw capturt Sakhalin Island an the Kuril Islands. On 15 August 1945, Japan surrendered, wi the surrender documents feenally signed at Tokyo Bay on the deck o the American battleship USS Missouri on 2 September 1945, endin the war.[186]
The Allies established occupation admeenistrations in Austrick an Germany. The umwhile becam a neutral state, non-aligned wi ony poleetical bloc. The latter wis dividit intae wastren an eastren occupation zones controlled bi the Wastren Allies an the USSR, accordinly. A denazification programme in Germany led tae the prosecution o Nazi war criminals an the remuival o ex-Nazis frae power, awtho this policy muived taewart amnesty an re-integration o ex-Nazis intae Wast German society.[187]
In an effort tae mainteen warld peace,[188] the Allies formed the Unitit Naitions, that offeecially cam intae exeestence on 24 October 1945,[189] an adoptit the Universal Declaration o Human Richts in 1948, as a common staundart for aw member naitions.[190]
Post-war diveesion o the warld wis formalised bi twa internaitional militar alliances, the Unitit States-led NATO an the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact;[191] the lang period o poleetical tensions an militar competeetion atween them, the Cauld War, wad be accompanied bi an unprecedentit airms race an proxy wars.[192]
Korea, umwhile unner Japanese rule, wis dividit an occupied bi the Soviet Union in the North an the US in the Sooth atween 1945 an 1948. Separate republics emerged on baith sides o the 38t parallel in 1948, ilk claimin tae be the legitimate govrenment for aw o Korea, that led ultimately tae the Korean War.[193]
In Cheenae, naitionalist an communist forces resumed the ceevil war in Juin 1946. Communist forces war veectorious an established the Fowkrepublic o Cheenae on the mainland, while naitionalist forces retreatit tae Taiwan in 1949.[194]
Estimates fur the tot nummer o casualties in the war varies, acause mony diaths went wanrecordit. Maist suggests that some 60 million fowk dee'd in the war, includin aboot 20 million militar personnel an 40 million ceevilians.[195][196][197] Mony o the ceevilians dee'd acause o deliberate genocide, massacres, mass-bombins, disease, an stairvation.

In Asie an the Paceefic, atween 3 million an mair nor 10 million ceevilians, maistly Cheenese (estimatit at 7.5 million[198]), wis killt bi the Japanese occupation forces.[199] The best-kent Japanese atrocity wis the Nanking Massacre, in that fifty tae three hunder thoosand Cheenese ceevilians war raped an murthert.[200] Mitsuyoshi Himeta reportit that 2.7 million casualties occurred in the Sankō Sakusen. General Yasuji Okamura implementit the policy in Heipei an Shantung.[201]
The Soviet Union wis responsible for the Katyn massacre o 22,000 Pols officers,[202] an the impreesonment or execution o thoosands o poleetical preesoners bi the NKVD,[203]
The German govrenment led bi Adolf Hitler an the Nazi Pairty wis responsible for the Holocaust (killin o thareaboot 6 million Jews), as weel as fur killin o 2.7 million ethnic Poles,[204] an 4 million ithers that war deemed "unworthy o life" (includin the disabled an mentally ill, Soviet preesoners o war, homosexuals, Freemasons, Jehovah's Witnesses, an Romani) as pairt o a programme o deliberate extermination. Soviet POWs wis kept in especially unbeirable condeetion, an, awtho thair extermination wisnae an offeecial goal, 3.6 million o Soviet POWs oot o 5.7 dee'd in Nazi camps in the war.[205][206] In addeetion tae concentration camps, daith camps wis creatit in Nazi Germany fur tae exterminate fowk at an industrial scale.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.