Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Zethrene (dibenzo[de,mn]naphthacene) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of two phenalene units fused together. According to Clar's rule, the two exterior naphthalene units are truly aromatic and the two central double bonds are not aromatic at all. For this reason the compound is of some interest to academic research. Zethrene has a deep-red color and it is light sensitive - complete decomposition under a sunlight lamp occurs within 12 hours. The melting point is 262 °C.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dibenzo[de,mn]tetracene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H14 | |
| Molar mass | 302.376 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The compound was originally synthesized by Erich Clar in 1955[1] from acenaphthene in one method and from chrysene in another. Mitchell and Sondheimer prepared the compound from a benzannulated [10]annulene.[2][3]
 |
| Zethrene synthesis (Sondheimer 1968) |
|---|
A sulfur extrusion method was reported by Kemp, Storie, and Tulloch.[4] Wu et al.[5] reported the synthesis of the compound in a coupling reaction / dimerization with in-situ desilylation.
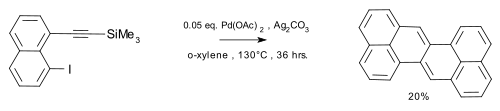 |
| Zethrene synthesis (Wu 2010) |
|---|
X-ray crystallography indicates that zethrene is a planar molecule.[5] The bond lengths in the central part of the molecule are consistent with distinct single and double bonds rather than aromatic components.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.