Vitamin D-binding protein
Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), also/originally known as gc-globulin (group-specific component), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GC gene.[5][6] DBP is genetically the oldest member of the albuminoid family and appeared early in the evolution of vertebrates.[7]
| GC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GC, DBP, DBP/GRD3, HEL-S-51, VDBG, VDBP, Gc-MAF, GcMAF, vitamin D binding protein, DBP-maf, VDB, GC vitamin D binding protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 139200; MGI: 95669; HomoloGene: 486; GeneCards: GC; OMA:GC - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Structure
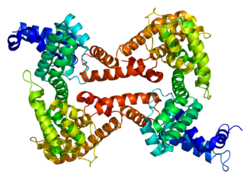
Human GC is a glycosylated alpha-globulin, ~58 kDa in size. Its 458 amino acids are coded for by 1690 nucleotides on chromosome 4 (4q11–q13). The primary structure contains 28 cysteine residues forming multiple disulfide bonds. GC contains 3 domains. Domain 1 is composed of 10 alpha helices, domain 2 of 9, and domain 3 of 4.[8]
Function
Summarize
Perspective
Vitamin D-binding protein belongs to the albumin gene family, together with human serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein. It is a multifunctional protein found in plasma, ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid and on the surface of many cell types.
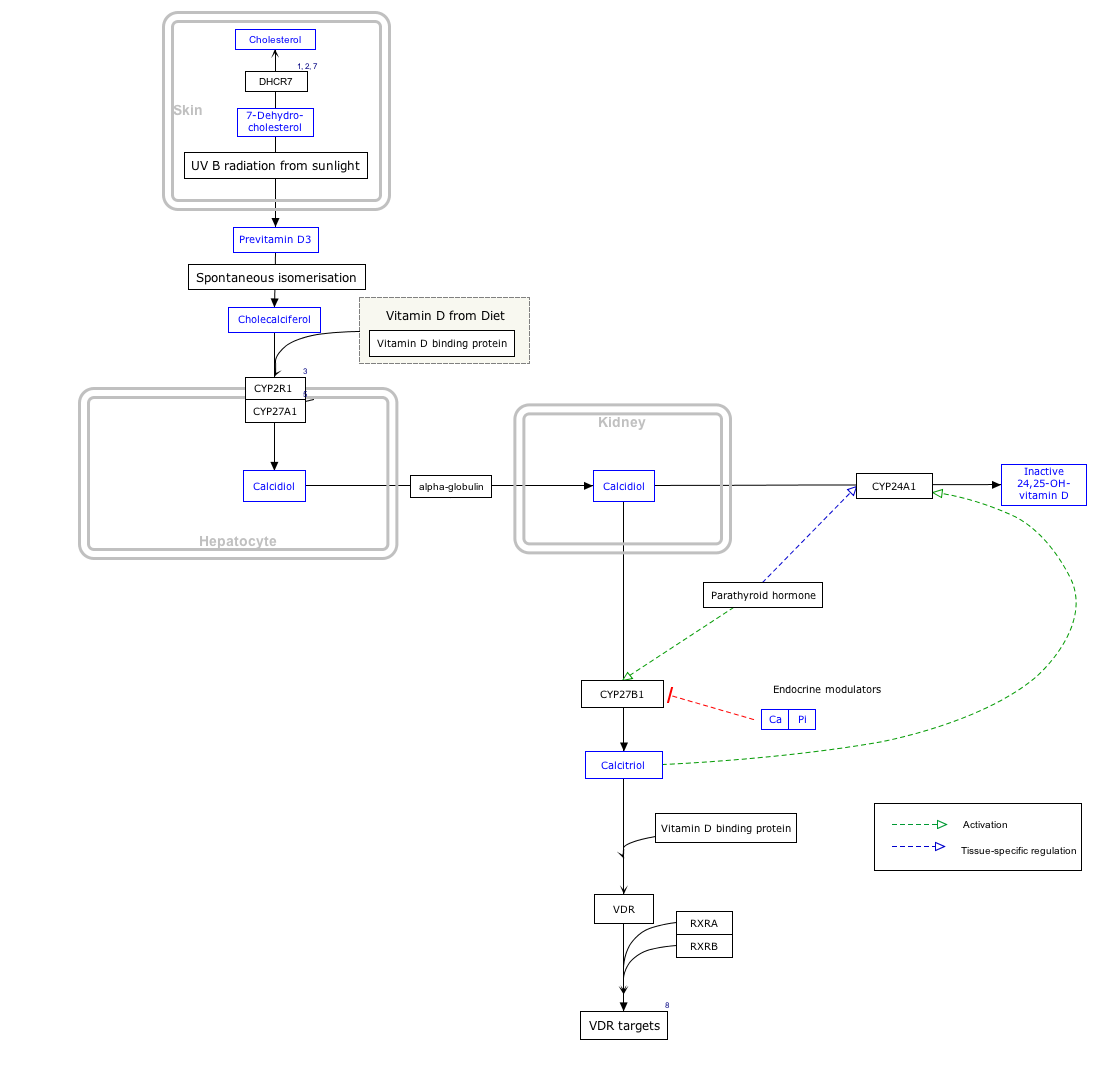
It is able to bind the various forms of vitamin D including ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), the 25-hydroxylated forms (calcifediol), and the active hormonal product, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol). The major proportion of vitamin D in blood is bound to this protein. It transports vitamin D metabolites between skin, liver and kidney, and then on to the various target tissues.[6][9]
As Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor it is a Macrophage Activating Factor (MAF) that has been tested for use as a cancer treatment that would activate macrophages against cancer cells.[10]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
Production
It is synthesized by hepatic parenchymal cells and secreted into the blood circulation.[9]
Regulation
The transcription factors HFN1α is a positive regulator while HFN1β is a dominant negative regulator of DBP expression.[11]
Variation
Many genetic variants of the GC gene are known. They produce 6 main haplotypes and 3 main protein variants (Gc1S, Gc1F and Gc2).[12] The genetic variations are associated with differences in circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.[13] They have been proposed to account for some of the differences in vitamin D status in different ethnic groups,[14] and have been found to correlate with the response to vitamin D supplementation.[12]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.