Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
USRA Heavy Mikado
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
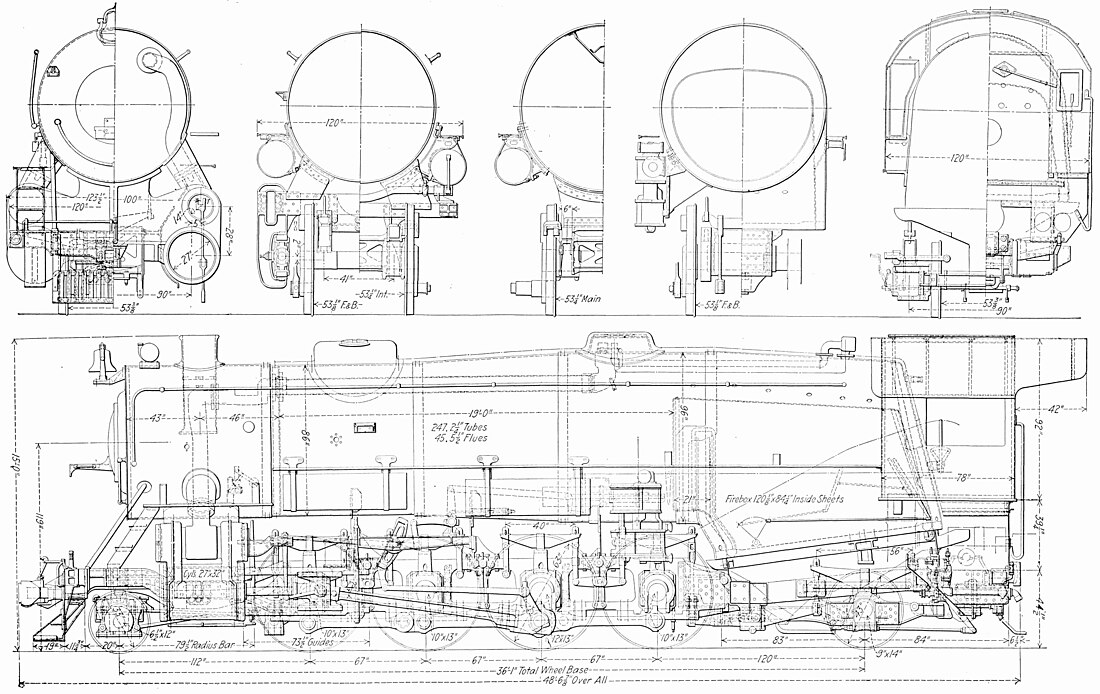
The USRA Heavy Mikado was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration (USRA), the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 1′D1′ in UIC classification. A total of 233 locomotives were built to this plan for the USRA; postwar, it became a de facto standard design, which was built to the total of 957 locomotives including the USRA originals and all subsequent copies.[2]

Heavy Mikado used the same running gear as the USRA Light Mikado but were built to a higher axle load, larger cylinders and a much larger boiler for more power and steam-generating ability. Many aspects of the PRR L1s class were carried over to the Heavy Mikado, although not that locomotive's distinctive Belpaire firebox.[1]
Remove ads
Original owners
Summarize
Perspective
USRA originals
Copies[1]
None of the originals built under USRA auspices or any of the subsequent copies were preserved.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads