| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogenetic relationships of Typhloperipatus with the tentative placement of Cretoperipatus.[9][10] |
Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Typhloperipatus
Genus and species of basal eyeless Peripatid velvet worm From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Typhloperipatus is a genus of velvet worm in the family Peripatidae, containing the sole species Typhloperipatus williamsoni.[1] This genus contains the only species in the phylum Onychophora found in South Asia.[2] This species is also striking in that this velvet worm shows no external trace of eyes,[3][4] although rudimentary optical vesicles are present internally.[5] This species is also notable for featuring males with the minimum number of legs (19 pairs) recorded in any velvet worm in the family Peripatidae.[6][7]
Remove ads
Discovery, distribution, and habitats
Summarize
Perspective
The species was discovered in the foothills of the Himalayas in northeastern India in 1911 and first described by the British biologist Stanley Kemp in 1913.[3][4] The species is named for Noel Williamson, a political officer at Sadiya who was murdered in 1911 along with his travelling companion Dr J.D. Gregorson, a physician working on a tea plantation.[3] These murders led to a punitive military expedition being organized by the British Indian government to the Abor region; Kemp, then an assistant superintendent at the Indian Museum at Calcutta was a zoologist assigned to this expedition.[3][4][8]
Kemp's assistant found the first three specimens in December 1911 near Rotung and the Dihang River gorge, where workers soon collected many more. Although the nearest known velvet worm species, from the Malay Peninsula, are typically found in dead wood, these were found mainly under large stones near the roots of trees. Subsequently some more specimens were found at the mouth of the Sireng stream and another specimen was found by the 32nd Sikh Pioneers while working between Upper Rotung and Rengin.[3] Kemp did not designate a holotype, but syntypes are deposited in the Natural History Museum of London.[1]
After the original description of this species based on specimens collected in the Siang Valley in what is now the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India, there were no records of this velvet worm for more than a century. In 2021, however, a team from the Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the Environment (ATREE) in India collected a specimen from under a small stone on a forest trail near the village of Kalek in the Siang Valley, in the East Siang district of Arunachal Pradesh, only 3 km from the type locality (Rotung). In 2023, the same team collected another specimen from under a small stone in a forest near the village of Yingku, also in the Siang Valley in the East Siang district, about 45 km from Rotung. Both of these specimens were found in subtropical evergreen forests and are deposited in the ATREE collection facility. This species is known only from the Siang Valley in Arunachal Pradesh.[9]
Remove ads
Morphology
Summarize
Perspective
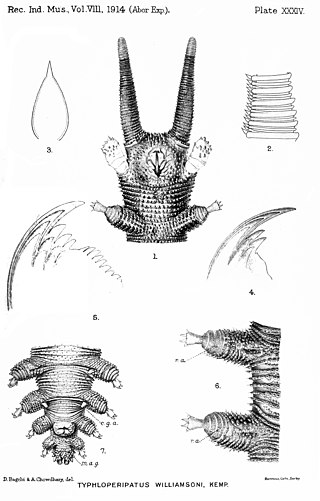
This species is blind and has no eyes, an unusual trait for a velvet worm.[4][3] The colour of the upperside is a deep umber brown with the tips of the antennae slightly paler brown. The papillae on the skin have pale tips and the underside is pale brown. Some individuals have a dark dorsal stripe. The outer blade of the jaw features two or sometimes three accessory teeth near the main tooth; the inner blade features three accessory teeth and eight to ten small denticles, with a short diastema between the accessory teeth and the denticles.[3]
Females have 20 pairs of legs; males usually have 19 leg pairs, but Kemp found one male with 20 pairs. Each leg features four complete spinous pads except for the last two leg pairs: The penultimate pair has only three pads on each leg, and the last pair has only two pads on each leg. Fine setae covers each pad. On the fourth and fifth leg pairs, the third most distal pad is divided into two parts, and near this division, the nephridial openings on each of those legs is located on the end of the longer anterior part of this pad. The feet have two distal papillae, one on each side of the claws (one anterior and one posterior). The genital opening is located between the penultimate pair of legs. The two pregenital leg pairs feature a crural gland at the base of each leg.[3]
Remove ads
Phylogeny
Summarize
Perspective
Phylogenetic analysis based on molecular evidence places Typhloperipatus in a clade with the Eoperipatus species of Southeast Asia as a sister group.[9] This analysis confirms the hypothesis that the genus Eoperipatus contains the closest extant relatives of Typhloperipatus.[11] The same molecular evidence also places these two genera on the most basal branch in a phylogenetic tree of the family Peripatidae, with all other peripatids forming a sister group. This evidence indicates that the Asian clade diverged from all other peripatids between 200 and 272 million years ago and that Typhloperipatus diverged from Eoperipatus between 179 and 257 million years ago.[9]
As Kemp noted, Typhloperipatus features a set of traits that are most similar to those found in Eoperipatus. For example, both genera feature feet with two distal papillae, one anterior and one posterior.[3] Furthermore, like Eoperipatus, Typhloperipatus exhibits lecithotrophic ovoviviparity; that is, mothers in both genera retain yolky eggs in their uteri.[12]
Several other traits, however, distinguish Typhloperipatus from Eoperipatus. For example, these genera are distinguished by not only the absence of eyes in Typhloperipatus but also the location of the nephridial openings on the fourth and fifth leg pairs.[3] These openings are located on the third pad on these legs in Typhloperipatus, but in Eoperipatus, these openings are located either on the fourth pad or between the third and fourth pad.[13] Furthermore, the anal glands in males of the genus Eoperipatus share a single opening between the last pair of legs,[13][14][15] whereas in Typhloperipatus, these male accessory glands instead have separate openings side by side close behind the last leg pair.[4]
A study of the fossil species Cretoperipatus burmiticus, embedded in Burmese amber from 100 million years ago, also finds two distal foot papillae, one anterior and one posterior, on this species. This distinctive feature places Cretoperipatus among the Asian Peripatidae (Typhloperipatus and Eoperipatus) and distinguishes this group from all other extant Peripatidae.[10] This study also identifies Typhloperipatus as the closest extant relative of Cretoperipatus.[10][2]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads