Tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III)
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
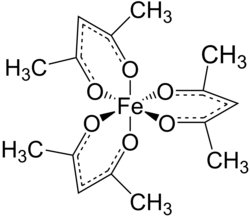
Tris(acetylacetonato) iron(III), often abbreviated Fe(acac)3, is a ferric coordination complex featuring acetylacetonate (acac) ligands, making it one of a family of metal acetylacetonates. It is a red air-stable solid that dissolves in nonpolar organic solvents.
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tris(2,4-dioxopentan-3-ido-κ2O,O′)iron | |
| Other names
Iron(III) acetylacetonate, Iron(III) tris(2,4-pentanedionato), Fe(acac)3 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.398 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Fe(C5H7O2)3 | |
| Molar mass | 353.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | Red Solid |
| Density | 1.348 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 180 to 181 °C (356 to 358 °F; 453 to 454 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| 2 g/L | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H302+H312+H332, H318 | |
| P261, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352+P312, P304+P340+P312, P305+P351+P338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Preparation
Fe(acac)3 is prepared by treating freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 with acetylacetone.[2]
- Fe(OH)3 + 3 HC5H7O2 → Fe(C5H7O2)3 + 3 H2O
Structure and properties
Fe(acac)3 is an octahedral complex with six equivalent Fe-O bonds with bond distances of about 2.00 Å. The regular geometry is consistent with a high-spin Fe3+ core with sp3d2 hybridization. As the metal orbitals are all evenly occupied the complex is not subject to Jahn-Teller distortions and thus adopts a D3 molecular symmetry. In contrast, the related metal acetylacetonate Mn(acac)3 adopts a more distorted octahedral structure.[3] The 5 unpaired d-electrons also result in the complex being paramagnetic, with a magnetic moment of 5.90 μB.
Fe(acac)3 possesses helical chirality. The Δ- and Λ-enantiomers slowly inter-convert via Bailar and Ray–Dutt twists. The rate of interconversion is sufficiently slow to allow its enantiomers to be partially resolved.[4]
Reactions
Fe(acac)3 has been examined as a precatalyst and reagent in organic chemistry, although the active iron-containing species is usually unidentified in these processes. In one instance, Fe(acac)3 was shown to promote cross-coupling a diene to an olefin.[5] Fe(acac)3 catalyzes the dimerization of isoprene to a mixture of 1,5-dimethyl-1,5-cyclooctadiene and 2,5-dimethyl-1,5-cyclooctadiene.[6]
Fe(acac)3 also catalyzes the ring-opening polymerization of 1,3-benzoxazine.[7] Beyond the area of polymerization, Fe(acac)3 has been found to catalyze the reaction of N-sulfonyl oxaziridines with olefins to form 1,3-oxazolidine products.[8]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.


