Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
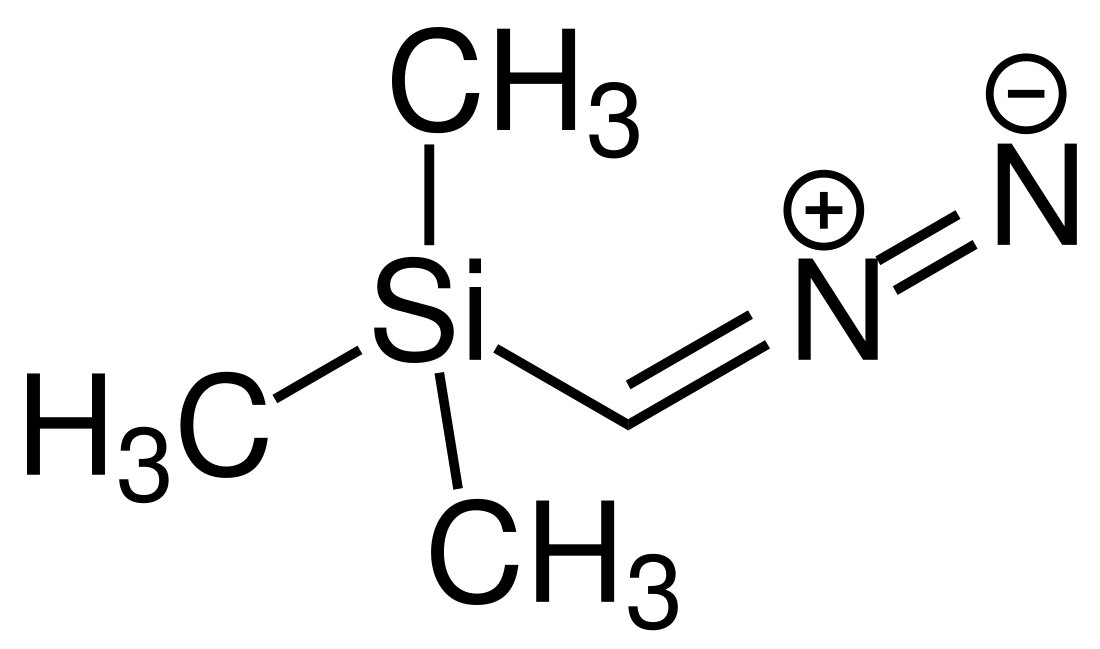
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCHN2. It is classified as a diazo compound. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is commercially available as solutions in hexanes, DCM, and ether. It is a specialized reagent used in organic chemistry as a methylating agent for carboxylic acids. It is a safer replacement for diazomethane, which is a sensitive explosive gas, whereas trimethylsilyldiazomethane is a relatively stable liquid and thus easier to handle.[4]
Remove ads
Preparation
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane can be prepared by treating (trimethylsilyl)methylmagnesium chloride with diphenyl phosphorazidate.[5] An isotopically labelled variant, with 13C at the diazomethyl carbon, is also known.[6]
Reactions
Summarize
Perspective
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is useful for conversion of carboxylic acids to their methyl esters in high yield. The typical reaction conditions for this purpose use methanol as a cosolvent. Under these conditions, diazomethane itself is generated in situ as the active methylating agent, by an acid-catalyzed reaction between trimethylsilyldiazomethane and the alcohol with trimethylsilyloxymethane as byproduct:[7]
When the methanol is omitted, substantial amounts of trimethylsilyl ester and trimethylmethyl ester products are formed as well.[7]
It also reacts with alcohols to give methyl ethers, whereas diazomethane may not.[8]
The compound is a reagent in the Doyle–Kirmse reaction with allyl sulfides and allyl amines.
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is deprotonated by butyllithium:
- (CH3)3SiCHN2 + BuLi → (CH3)3SiCLiN2 + BuH
The lithio compound is versatile. From it can be prepared other trimethylsilyldiazoalkanes:
- (CH3)3SiCLiN2 + RX → (CH3)3SiCRN2 + LiX
(CH3)3SiCLiN2 reacts with ketones and aldehydes to give, depending on the substituents, acetylenes.[9]
Remove ads
Applications
It has also been employed widely in tandem with GC-MS for the analysis of various carboxylic compounds which are ubiquitous in nature. The fact that the reaction is rapid and occurs readily makes it attractive. However, it can form artifacts which complicate spectral interpretation. Such artifacts are usually the trimethylsilylmethyl esters, RCO2CH2SiMe3, formed when insufficient methanol is present. Acid-catalysed methanolysis is necessary to achieve near-quantitative yields of the desired methyl esters, RCO2Me.[7]
Safety
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is highly toxic. It has been implicated in the death of at least two chemists, a pharmaceutical worker in Windsor, Nova Scotia and one in Pennsylvania.[10][11][12] Inhalation of diazomethane is known to cause pulmonary edema; trimethylsilyldiazomethane is suspected to behave similarly.[13]
It is possible that upon contact with water on the surface of the lung, trimethylsilyldiazomethane converts to diazomethane.[13]
Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is nonexplosive.[5]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads






![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {CH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}\mathrm {OH} \ {}+{}\mathrm {TMSCHN} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\xrightarrow {\mathrm {acid} } } {}\mathrm {CH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{3}}\mathrm {OTMS} \ {}+{}\mathrm {CH} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {N} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a9629d9d74dcb84a3d6885e549143b369e44a82c)