Trimer (chemistry)
Molecule consisting of three identical molecules bound together From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In chemistry, a trimer (/ˈtraɪmər/; from Ancient Greek tri- 'three' and -mer 'parts') is a molecule or polyatomic anion formed by combination or association of three molecules or ions of the same substance. In technical jargon, a trimer is a kind of oligomer derived from three identical precursors often in competition with polymerization.
Examples
Summarize
Perspective
Alkyne trimerization
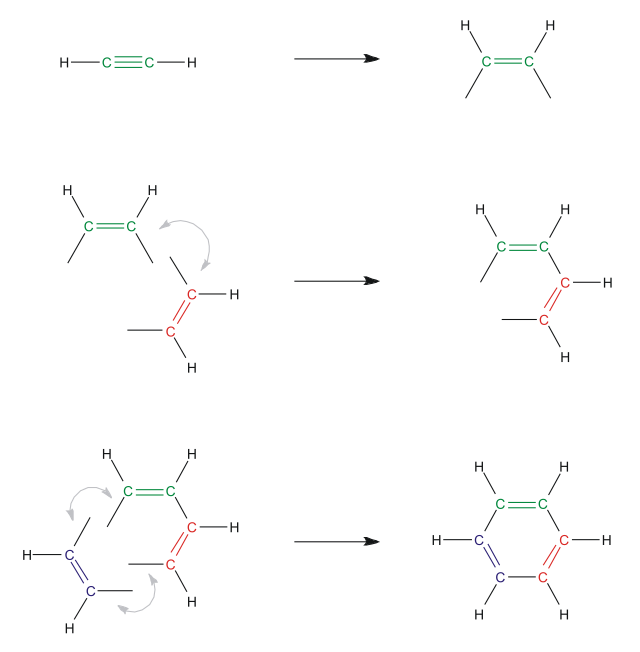
In 1866, Marcellin Berthelot reported the first example of cyclotrimerization, the conversion of acetylene to benzene.[1] This process was commercialized:
Nitrile trimerization
Symmetrical 1,3,5-triazines are prepared by trimerization of certain nitriles such as cyanogen chloride.
Cyanogen chloride and cyanogen bromide each trimerize at elevated temperatures over a carbon catalyst.[1] The chloride gives cyanuric chloride:
The bromide has an extended shelflife when refrigerated. Like the chloride, it undergoes ab exothermic trimerization to form cyanuric bromide. This reaction is catalyzed by traces of bromine, metal salts, acids and bases.[2] For this reason, experimentalists avoid brownish samples.[3]
An industrial route to cyanuric acid entails the thermal decomposition of urea, with release of ammonia. The conversion commences at approximately 175 °C:[4]
- 3 H2N−CO−NH2 → [C(O)NH]3 + 3 NH3
The endothermic synthesis of melamine can be understood in two steps.
First, urea decomposes into cyanic acid and ammonia in an endothermic reaction:
- (NH2)2CO → HOCN + NH3
Then in the second step, cyanic acid polymerizes to form cyanuric acid, which condenses with the liberated ammonia from the first step to release melamine and water.
- 3 HOCN → [C(O)NH]3
- [C(O)NH]3 + 3 NH3 → C3H6N6 + 3 H2O
This water then reacts with cyanic acid present, which helps drive the trimerization reaction, generating carbon dioxide and ammonia.
- 3 HOCN + 3 H2O → 3 CO2 + 3 NH3
In total, the second step is exothermic:
- 6 HCNO + 3 NH3 → C3H6N6 + 3 CO2 + 3 NH3
but the overall process is endothermic.
Diene trimerization
The 1,5,9-trans-trans-cis isomer of cyclododecatriene, which has some industrial importance is obtained by cyclotrimerization of butadiene with titanium tetrachloride and an organoaluminium co-catalyst:[5]
Breaking carbon-hetero double bonds forms symmetrical saturated 1,3,5-heterocycles
Cyclotrimerization of formaldehyde affords 1,3,5-Trioxane:
1,3,5-Trithiane is the cyclic trimer of the otherwise unstable species thioformaldehyde. This heterocycle consists of a six-membered ring with alternating methylene bridges and thioether groups. It is prepared by treatment of formaldehyde with hydrogen sulfide.[6]
Three molecules of acetaldehyde condense to form paraldehyde, a cyclic trimer containing C-O single bonds.
Catalyzing and dehydrating by sulfuric acid, trimerization of acetone via aldol condensation affords mesitylene[7]
Trisiloxanes
Dimethylsilanediol dehydrates to a trimer of Me2SiO as well as polydimethylsiloxane. The reaction illustrates the competition between trimerization and polymerization. The polymer and trimer are formally derived from the hypothetical sila-ketone Me2Si=O, although this species is not an intermediate.
Coordination chemistry
The dithiobenzoate complexes [M(S2CPh)2] crystallize as trimers (M = Ni, Pd).[8]

See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.





