Threonine
Amino acid From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Threonine (symbol Thr or T)[2] is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli.[3] It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG).
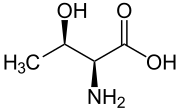 Skeletal formula of L-threonine | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Threonine | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.704 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| |||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 119.120 g·mol−1 | ||
| (H2O, g/dl) 10.6(30°),14.1(52°),19.0(61°) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.63 (carboxyl), 10.43 (amino)[1] | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Threonine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices).
Modifications
The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications.[4][5] The hydroxyl side-chain can undergo O-linked glycosylation. In addition, threonine residues undergo phosphorylation through the action of a threonine kinase. In its phosphorylated form, it can be referred to as phosphothreonine. Phosphothreonine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) and determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is important to explain the function of the phosphothreonine in biological processes.[6]
History
Threonine was the last of the 20 common proteinogenic amino acids to be discovered. It was discovered in 1935 by William Cumming Rose,[7] collaborating with Curtis Meyer. The amino acid was named threonine because it was similar in structure to threonic acid, a four-carbon monosaccharide with molecular formula C4H8O5[8]
Stereoisomers
  |
| L-threonine (2S,3R) and D-threonine (2R,3S) |
  |
| L-allothreonine (2S,3S) and D-allothreonine (2R,3R) |
Threonine is one of two proteinogenic amino acids with two stereogenic centers, the other being isoleucine. Threonine can exist in four possible stereoisomers with the following configurations: (2S,3R), (2R,3S), (2S,3S) and (2R,3R). However, the name L-threonine is used for one single stereoisomer, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. The stereoisomer (2S,3S), which is rarely present in nature, is called L-allothreonine.[9]
Biosynthesis
As an essential amino acid, threonine is not synthesized in humans, and needs to be present in proteins in the diet. Adult humans require about 20 mg/kg body weight/day.[10] In plants and microorganisms, threonine is synthesized from aspartic acid via α-aspartyl-semialdehyde and homoserine. Homoserine undergoes O-phosphorylation; this phosphate ester undergoes hydrolysis concomitant with relocation of the OH group.[11] Enzymes involved in a typical biosynthesis of threonine include:
- aspartokinase
- β-aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase
- homoserine dehydrogenase
- homoserine kinase
- threonine synthase.

Metabolism
Threonine is metabolized in at least three ways:
- In many animals it is converted to pyruvate via threonine dehydrogenase. An intermediate in this pathway can undergo thiolysis with CoA to produce acetyl-CoA and glycine.
- In humans the gene for threonine dehydrogenase is an inactive pseudogene,[12] so threonine is converted to α-ketobutyrate. The mechanism of the first step is analogous to that catalyzed by serine dehydratase, and the serine and threonine dehydratase reactions are probably catalyzed by the same enzyme.[13]
- In many organisms it is O-phosphorylated by a kinase preparatory to further metabolism. This is especially important in bacteria as part of the biosynthesis of cobalamin (Vitamin B12), as the product is converted to (R)-1-aminopropan-2-ol for incorporation into the vitamin's sidechain.[14]
- Threonine is used to synthesize glycine during the endogenous production of L-carnitine in the brain and liver of rats.[15][16]
Metabolic diseases
The degradation of threonine is impaired in the following metabolic diseases:
Research of Threonine as a Dietary Supplement in Animals
Effects of threonine dietary supplementation have been researched in broilers.[19]
An essential amino acid, threonine is involved in the metabolism of fats, the creation of proteins, the proliferation and differentiation of embryonic stem cells, and the health and function of the intestines. Animal health and illness are strongly correlated with the need for and metabolism of threonine. Intestinal inflammation and energy metabolism disorders in animals may be alleviated by appropriate amounts of dietary threonine. Nevertheless, because these effects pertain to the control of nutrition metabolism, more research is required to confirm the results in various animal models. Furthermore, more research is needed to understand how threonine controls the dynamic equilibrium of the intestinal barrier function, immunological response and gut flora.[20]
Exploration of L-Threonine for Tuberculosis
Summarize
Perspective
With multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) remaining a public health crisis with a total of 1.25 million people dead worldwide from TB in 2023 alone, new treatment strategies for TB are critical.[21] TB is an airborne infection, spread via inhalation of airborne droplets that can remain suspended in the air for several hours, and can either be killed, remain in a latent stage, or become active. One previous paper researched the inhibitory effects of the downstream product L-threonine on the homoserine kinase (HSK) pathway in Escherichia coli. They found that the HSK pathway can be successfully inhibited via L-threonine since the pathway acts as a negative feedback loop, becoming inhibited once enough of the product is formed.[22] Investigation of this pathway in TB may yield new insights into potential drug targets. Inhibiting the fatty acid synthesis pathway as well could serve as a potential drug target since this pathway is responsible for synthesizing mycolic acids, components necessary for formation of TB’s cell walls.[23] Coupling of the amino acid L-threonine with a common TB drug that inhibits fatty acid synthesis, like ethionamide, could yield a new treatment strategy for tuberculosis.
Sources
Foods high in threonine include cottage cheese, poultry, fish, meat, lentils, black turtle bean[24] and sesame seeds.[25]
Racemic threonine can be prepared from crotonic acid by alpha-functionalization using mercury(II) acetate.[26]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.


