Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Thiourea organocatalysis
Use of ureas and thioureas to accelerate and stereochemically alter organic transformations From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Within the area of organocatalysis, (thio)urea organocatalysis describes the use of ureas and thioureas to accelerate and stereochemically alter organic transformations. The effects arise through hydrogen-bonding interactions between the substrate and the (thio)urea. Unlike classical catalysts, these organocatalysts interact by non-covalent interactions, especially hydrogen bonding ("partial protonation"). The scope of these small-molecule H-bond donors termed (thio)urea organocatalysis covers both non-stereoselective and stereoselective reactions.[1]
Remove ads
Catalyst-substrate interactions
Hydrogen-bonding between thiourea derivatives and carbonyl substrates involve two hydrogen bonds provided by coplanar amino substituents in the (thio)urea.[2][3][4]
[5] Squaramide catalysts engage in double H-bonding interactions and are often superior to thioureas.[6]
Thioureas are often found to be stronger hydrogen-bond donors (i.e., more acidic) than ureas[7] because their amino groups are more positively charged. Quantum chemical analyses revealed that this counterintuitive phenomenon, which is not explainable by the relative electronegativities of O and S, results from the effective steric size of the chalcogen atoms.[8]

Remove ads
Advantages of thiourea organocatalysts
(Thio) ureas are green and sustainable catalysts. When effective, they can offer these advantages:
- absence of product inhibition due to weak enthalpic binding, but specific binding-“recognition“
- simple and inexpensive synthesis from primary amine functionalized (chiral-pool) starting materials and isothiocyanates
- easy to modulate and to handle (bench-stable), no inert gas atmosphere required
- catalysis under almost neutral conditions (pka thiourea 21.0) and mild conditions, acid-sensitive substrates are tolerated
- metal-free, nontoxic (compare traditional metal-containing Lewis-acid catalysts)
- water-tolerant, even catalytically effective in water or aqueous media.[10]
Remove ads
Substrates
H-bond accepting substrates include carbonyl compounds, imines, nitroalkenes. The Diels-Alder reaction is one process that can benefit from (thio)urea catalysts.
History
Early contributions were made by Kelly, Etter, Jorgensen, Hine, Curran, Göbel, and De Mendoza (see review articles cited below) on hydrogen bonding interactions of small, metal-free compounds with electron-rich binding sites. Peter R. Schreiner and co-workers identified and introduced electron-poor thiourea derivatives as hydrogen-bonding organocatalysts. Schreiner's thiourea, N,N'-bis3,5-bis(trifluormethyl)phenyl thiourea, combines all structural features for double H-bonding mediated organocatalysis:
- electron-poor
- rigid structure
- non-coordinating, electron withdrawing substituents in 3,4, and/or 5 position of a phenyl ring
- the 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl-group is the preferred substituent

Remove ads
Catalysts
Summarize
Perspective
A broad variety of monofunctional and bifunctional (concept of bifunctionality) chiral double hydrogen-bonding (thio)urea organocatalysts have been developed.
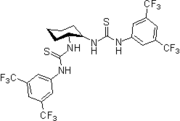
- 2003: Takemoto's bifunctional chiral thiourea derivative, catalysis of asymmetric Michael- and Aza-Henry reactions.[13]
- 2004: Nagasawa's chiral bis-thiourea organocatalyst, catalysis of asymmetric Baylis-Hillman reactions.[14]
- 2005: Nagasawa's bifunctional thiourea functionalized guanidine, asymmetric catalysis of Henry(Nitroaldol)reactions.[15]
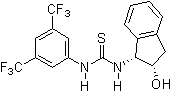
- 2005: Ricci's chiral thiourea derivative with additional hydroxy-group, enantioselective Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indols with nitroalkenes.[16]
- 2005: Wei Wang's bifunctional binaphthyl-thiourea derivative, asymmetric catalysis of Morita-Baylis-Hillman reactions.[17]
- 2005: Soós's, Connon and Dobson's bifunctional thiourea functionalized Cinchona alkaloid, asymmetric additions of nitroalkanes to chalcones [18] as well as malonates to nitroalkenes [19]
- 2006: Yong Tang's chiral bifunctional pyrrolidine-thiourea, enantioselective Michael additions of cyclohexanone to nitroolefins.[20]
- 2006: Berkessel's chiral isophoronediamine-derived bisthiourea derivative, catalysis of asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman reactions.[21]
- 2006: Takemoto's PEG-bound chiral thiourea, asymmetric catalysis of (tandem-) Michael reactions of trans"-β-nitrostyrene, aza-Henry reactions.[22]
- 2007: Kotke/Schreiner, polystyrene-bound, recoverable and reusable thiourea derivative for organocatalytic tetrahydropyranylation of alcohols.[3]
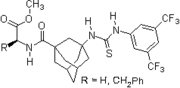
- 2007: Wanka/Schreiner, chiral peptidic adamantane-based thiourea, catalysis of Morita-Baylis-Hillman reactions.[23]
- 2007: Takemoto's chelating bifunctional hydroxy-thiourea for enantioselective Petasis-type reaction of quinolines.[24]
Remove ads
See also
Further reading
- Christian M. Kleiner, Peter R. Schreiner (2006). "Hydrophobic amplification of noncovalent organocatalysis". Chem. Commun.: 4315–4017.
- Z. Zhang and P. R. Schreiner (2007). "Thiourea-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation of Aldimines". Synlett. 2007 (9): 1455–1457. doi:10.1055/s-2007-980349.
- Wanka, Lukas; Chiara Cabrele; Maksims Vanejews; Peter R. Schreiner (2007). "γ-Aminoadamantanecarboxylic Acids Through Direct C–H Bond Amidations". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2007 (9): 1474–1490. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200600975. ISSN 1434-193X.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads