Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Thiolactic acid
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
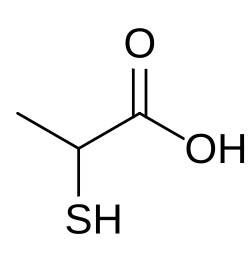
Thiolactic acid is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3CH(SH)CO2H. The molecule contains both carboxyl and thiol functional groups, −C(=O)−OH and −SH respectively. It is structurally related to lactic acid by the interchange of −SH for −OH. It is a colorless oil.
Thiolactic acid was once widely used in hair permanent waving formulations, but has been displaced by formulations based on thioglycolic acid. Instead of using the acid itself, its salts (2-sulfanylpropanoates) are used. It is now mainly used for depilation.[1]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads