Terrestrial Planet Finder
NASA concept study of an array of space telescopes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF) was a proposed project by NASA to construct a system of space telescopes for detecting extrasolar terrestrial planets. TPF was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2011.[1][2] There were two telescope systems under consideration, the TPF-I, which had several small telescopes, and TPF-C, which used one large telescope.

History
Summarize
Perspective
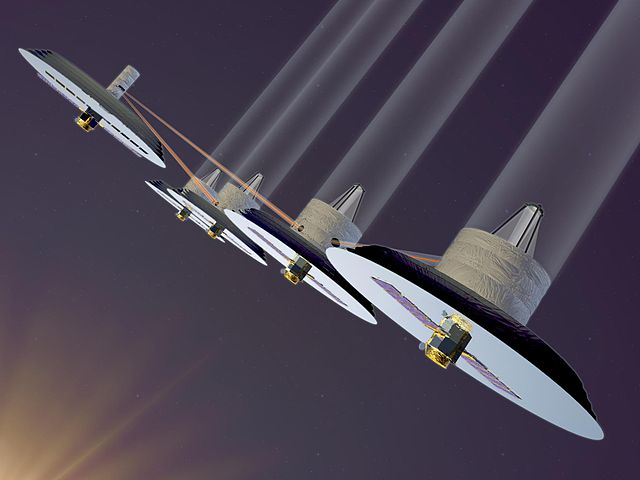
In May 2002, NASA chose two TPF mission architecture concepts for further study and technology development. Each would use a different means to achieve the same goal—to block the light from a parent star in order to see its much smaller, dimmer planets. The technological challenge of imaging planets near their much brighter star has been likened to finding a firefly near the beam of a distant searchlight. Additional goals of the mission would include the characterization of the surfaces and atmospheres of newfound planets, and looking for the chemical signatures of life.
The two planned architectures were:
- Infrared astronomical interferometer (TPF-I): Multiple small telescopes on a fixed structure or on separated spacecraft floating in precision formation would simulate a much larger, very powerful telescope. The interferometer would use a technique called nulling to reduce the starlight by a factor of one million, thus enabling the detection of the very dim infrared emission from the planets.
- Visible Light Coronagraph (TPF-C): A large optical telescope, with a mirror three to four times bigger and at least 100 times more precise than the Hubble Space Telescope, would collect starlight and the very dim reflected light from the planets. The telescope would have special optics to reduce the starlight by a factor of one billion, thus enabling astronomers to detect faint planets.
NASA and Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) were to issue calls for proposals seeking input on the development and demonstration of technologies to implement the two architectures, and on scientific research relevant to planet finding. Launch of TPF-C had been anticipated to occur around 2014, and TPF-I possibly by 2020.
According to NASA's 2007 budget documentation, released on 6 February 2006,[3] the project was deferred indefinitely.[4]
In June 2006, a House of Representatives subcommittee voted to provide funding for the TPF along with the long-sought mission to Europa, a moon of Jupiter that might harbor extraterrestrial life.[5] Congressional spending limits under House Resolution 20 passed on 31 January 2007, by the United States House of Representatives and 14 February by the U.S. Senate postponed the program indefinitely. Actual funding has not materialized, and TPF remains a concept.[6] In June 2011, the TPF (and SIM) programs were reported as "cancelled".[1]
Top 10 target stars
| Rank [7] | Target star | Constellation | Distance (light-years) |
Spectral type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alpha Centauri A | Centaurus | 4.3 | G2V |
| 2 | Alpha Centauri B | Centaurus | 4.3 | K1V |
| 3 | Tau Ceti | Cetus | 12 | G8V |
| 4 | Eta Cassiopeiae | Cassiopeia | 19 | G3V |
| 5 | Beta Hydri | Hydrus | 24 | G2IV |
| 6 | Delta Pavonis | Pavo | 20 | G8V |
| 7 | Pi3 Orionis | Orion | 26 | F6V |
| 8 | Gamma Leporis | Lepus | 29 | F7V |
| 9 | Epsilon Eridani | Eridanus | 10 | K2V |
| 10 | 40 Eridani | Eridanus | 16 | K1V |
See also
- Automated Planet Finder – Robotic optical telescope searching for extrasolar planets
- CoRoT – European space telescope that operated between 2006 - 2014
- Darwin – 2007 European study concept of an array of space observatories
- High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher – Instrument for detecting planets
- James Webb Space Telescope – NASA/ESA/CSA space telescope launched in 2021
- Kepler space telescope – NASA space telescope for exoplanetology (2009–2018)
- List of NASA cancellations
- Navigator Program – NASA project
- Space Interferometry Mission – Cancelled NASA space telescope
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
