Tau Herculis
Variable star in the constellation Hercules From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Tau Herculis, a name Latinized from τ Herculis, is a variable star in the northern constellation of Hercules. It has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye at night with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 3.91.[2] The star is located at a distance of approximately 307 light years from the Sun based on parallax,[1] but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −16 km/s.[2]

| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Hercules |
| Right ascension | 16h 19m 44.43666s[1] |
| Declination | 46° 18′ 48.1123″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.91[2] 3.83 to 3.86[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence[4] |
| Spectral type | B5 IV[5] |
| U−B color index | −0.569[2] |
| B−V color index | −0.151±0.009[2] |
| Variable type | SPB[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −15.5±0.5[2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −13.33[1] mas/yr Dec.: 38.48[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.61±0.11 mas[1] |
| Distance | 307 ± 3 ly (94.3 ± 1.0 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.96[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 4.01[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.55±0.19 R☉[7] 3.80±0.25[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 574[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.02±0.05[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 15,615±301[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.15[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 32[6] km/s |
| Age | 26[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Rukbalgethi Shemali, τ Her, 22 Her, BD+46°2169, FK5 608, GC 21987, HD 147394, HIP 79992, HR 6092, SAO 46028, CCDM J16197+4619A[10] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV,[5] and it serves as a standard spectrum in the modern Morgan–Keenan (MK) classification.[12] It is estimated to be just 26 million years old with a relatively low projected rotational velocity of 32 km/s.[6] Slowly rotating B-type stars are often chemically peculiar, so the mostly normal spectra of this star suggests we may be viewing it from near pole-on.[13] The abundance of most heavier elements in this star are about 85% of those in the Sun.[14] The star has four times the mass of the Sun[6] and around 3.8[8] times the Sun's radius. On average, it is radiating 574[2] times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 15,615 K.[7]
During the Hipparcos mission,[4] Tau Hercules was discovered to be a variable star of the slowly pulsating B-type. These are mid-B main sequence stars that vary with a period of about a day;[4] the brightness of Tau Hercules varies by 0.03 magnitude[3] over a period of 1.24970±0.00008 days. The radial velocity of the star varies at a different rate than the photometric period, with the object showing both radial and non-radial pulsation modes.[4][15]
Historical significance and etymology
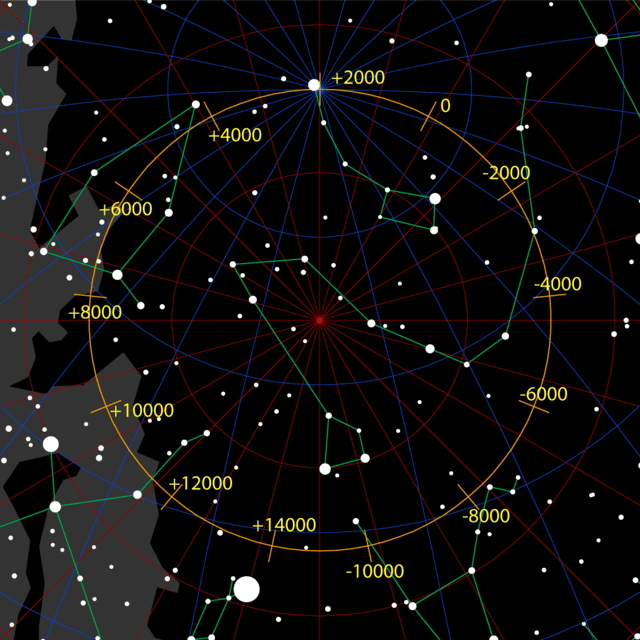
Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's North pole. It could have served the northern pole star around the year 7400 BCE, a phenomenon which is expected to reoccur in the year 18,400 due to precession.[13]
| Preceded by | Pole Star | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| Iota Herculis | 18,400 AD | Alpha Draconis |
Its traditional name, Rukbalgethi Shemali, is of Arabic origin and shares certain etymological characteristics with the stars Ruchbah and Zubeneschamali, signifying Hercules' "northern knee".[16][better source needed]
In Chinese, 七公 (Qī Gōng), meaning Seven Excellencies, refers to an asterism consisting of τ Herculis, 42 Herculis, φ Herculis, χ Herculis, ν1 Boötis, μ1 Boötis and δ Boötis.[17] Consequently, the Chinese name for τ Herculis itself is 七公二 (Qī Gōng èr, English: the Second Star of Seven Excellencies.)[18]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

