Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Sustainable Development Goal 13
UN goal to combat climate change From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13 or Global Goal 13) is the United Nations Global Goal to limit and adapt to climate change. It is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The official mission statement of this goal is to "Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts".[1] SDG 13 and SDG 7 on clean energy are closely related and complementary.[2]: 101
SDG 13 has five targets which are to be achieved by 2030. They cover a wide range of issues surrounding climate action. The first three targets are outcome targets. The first target is to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity towards climate change-related disasters. The second target is to integrate climate change measures into policies and planning. The third target is to build knowledge and capacity. The remaining two targets are means of implementation targets.[3] These include implementing the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), and to promote mechanisms to raise capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management. Along with each target, there are indicators that provide a method to review the overall progress of each target. The UNFCCC is the main intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change.
Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2°C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.7 °C (4.9 °F) by the end of the century.[4]
As of 2020, many countries are now implementing their national climate change adaptation plans which is to be achieved by 2030.[5]: 15
Remove ads
Context
Summarize
Perspective


Some effects of climate change, clockwise from top left: Wildfire intensified by heat and drought, worsening droughts compromising water supplies, and bleaching of coral caused by marine heatwaves
SDG 13 intends to take urgent action in order to combat climate change and its impacts.[9] Many climate change impacts are already felt at the current 1.2 °C (2.2 °F) level of warming. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet.[10] Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.7 °C (4.9 °F) by the end of the century.[4]
Reducing emissions requires generating electricity from low-carbon sources rather than burning fossil fuels. This change includes phasing out coal and natural gas fired power plants, vastly increasing use of wind, solar, and other types of renewable energy, and reducing energy use.[11]
Remove ads
Targets, indicators and progress
Summarize
Perspective
SDG 13 has five targets. The targets include to strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters (Target 13.1), integrate climate change measures into policies and planning (Target 13.2), build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change (Target 13.3), implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (Target 13.a), and promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management (Target 13.b).[12]
Each target includes one or more indicators that help to measure and monitor the progress. Some of the indicators are number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population (13.1.1) or total greenhouse emissions generated by year (13.2.2). [12]


Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters
The full text of Target 13.1 is: "Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries".[1]
This target has 3 indicators.[13]
- Indicator 13.1.1: "Number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population"
- Indicator 13.1.2: "Number of countries that adopt and implement national disaster risk reduction strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030"
- Indicator 13.1.3: "Proportion of local governments that adopt and implement local disaster risk reduction strategies in line with national disaster risk reduction strategies"[14]
Indicator 13.1.2 serves as a bridge between the Sustainable Development Goals and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.[15]
In April 2020, the number of countries and territories that adopted national disaster risk reduction strategies increased to 118 compared to 48 from the first year of the Sendai Framework.[16]

Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policy and planning
The full text of Target 13.2 is: "Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning".[1]
This target has two indicators:
- Indicator 13.2.1: "Number of countries with nationally determined contributions, long-term strategies, national adaptation plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications".[13]
- Indicator 13.2.2: "Total greenhouse gas emissions per year"[14]
In order to stay under 1.5 °C of global warming, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from G20 countries need to decline by about 45% by 2030 and attain net zero in 2050.[18] To be able to meet the 1.5 °C or even 2 °C, which is the maximum set by the Paris Agreement, greenhouse gas emissions must start to fall by 7.6% per year starting on 2020.[19] However, there is a large gap between these overall temperature targets and the nationally determined contributions set by individual countries.[19] Between 2000 and 2018, greenhouse gas emissions of transition economies and developed countries have declined by 6.5%. In contrast, developing countries saw their emissions go up by 43% between 2000 and 2013.[19]
As of 2015, 170 countries are a part of at least one multilateral environmental agreement,[20] with each year having an increase in the number of countries signing onto environmental agreements.

Target 13.3: Build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change
The full text of Target 13.3 is: "Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning".[1]
This target has two indicators:[13]
- Indicator 13.3.1: "The extent to which (i) global citizenship education and (ii) education for sustainable development are mainstreamed in (a) national education policies; (b) curricula; (c) teacher education; and (d) student assessment"
- Indicator 13.3.2: "Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation and technology transfer, and development actions"[14]
The indicator 13.3.1 measures the extent to which countries mainstream Global Citizenship Education (GCED) and Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) in their education systems and educational policies.[21]
The indicator 13.3.2 identifies countries who have and have not adopted and implemented disaster risk management strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. The goal by 2030 is to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.[13]
To explain the concept of "Education for Sustainable Development and Global Citizenship seeks to equip learners with the knowledge of how their choices impact others and their immediate environment.[22]
There is currently no data available for this indicator as of September 2020.[13]
Target 13.a: Implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change
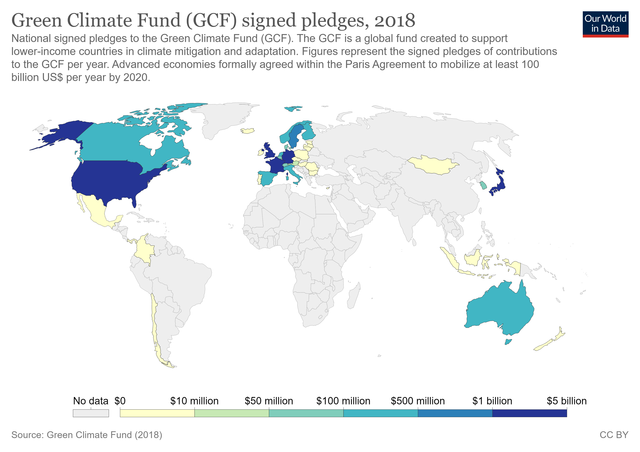
The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible."[1]
This target only has one indicator: Indicator 13.a is the "Amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the $100 billion commitment through to 2025".[23]
Previously, the indicator was worded as "Mobilized amount of United States dollars per year between 2020 and 2025 accountable towards the $100 billion commitment".[23]
This indicator measures the current pledged commitments from countries to the Green Climate Fund (GCF), the amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars (USD) per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the US$100 billion commitment to 2025.[13]
A report by the UN stated in 2020 that the financial flows for global climate finance as well as for renewable energy are "relatively small in relation to the scale of annual investment needed for a low-carbon, climate-resilient transition".[5]: 15
Target 13.b: Promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management

The full text of Target 13.b is: "Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities acknowledging that the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is the primary international, intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change."[1]
This target has one indicator: Indicator 13.b.1 is the "Number of least developed countries and small island developing states with nationally determined contributions, long-term strategies, national adaptation plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications".
A previous version of this indicator was: "Indicator 13.b.1: Number of least developed countries and small island developing states that are receiving specialized support, and amount of support, including finance, technology and capacity building, for mechanisms for raising capacities for effective climate change-related planning and management, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities."[23] This indicator's previous focus on women, youth and local and marginalized communities is not included anymore in the latest version of the indicator.
Annual UN reports are monitoring how many countries are implementing national adaptation plans.[5]: 15
Custodian agencies
Custodian agencies are in charge of reporting on the following indicators:[25]
- Indicators 13.1.1, 13.1.2 and 13.1.3: UN International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR).
- Indicator 13.2.1: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), UN Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization-Institute for Statistics (UNESCO-UIS).
- Indicators 13.3.1, 13.a.1 and 13.b.1: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Remove ads
Monitoring
High-level progress reports for all the SDGs are published in the form of reports by the United Nations Secretary General.[5] Updates and progress can also be found on the SDG website that is managed by the United Nations[26] and at Our World in Data.[27]
Challenges
Summarize
Perspective
Climate migration
SDG 13 does not directly address the link between nations most vulnerable to climate change and increased migration flows (climate migration). It therefore misses the chance to recognize migration as an adaptive response of mobile populations.[28] Weather-related disasters displace millions of people, but the goal's focus on national policies overlooks the role of migration. SDG 13 could instead track government policies on relocating communities, a practice likely to grow in the future.[28]
Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic
During the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a reduction in economic activity.[19][29] This resulted in a 6% drop in greenhouse gas emissions from what was initially projected for 2020, however these improvements were only temporary.[30] Greenhouse gas emissions rebounded later in the pandemic as many countries began lifting restrictions, with the direct impact of pandemic policies having a negligible long-term impact on climate change.[31] A rebound in transport pollution has occurred since restrictions of government lockdown policies have been lifted.[32] Transport pollution accounts for roughly 21% of global carbon emissions due to it being still 95% dependent on oil.[33]
Post pandemic, there is a rush for governments globally to stimulate local economies by putting money towards fossil fuel production and in turn economic stimulation.[34] Funding for economic policies will likely divert the emergency funds usually afforded to climate funding like The Green Climate Fund and other sustainable policies, unless an emphasis is put on green deals in the redirection of monetary funds.[35][36][37]
A 2022 publication reported that the COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted progress on SDG 13 and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) processes. Travel restrictions and reduced in-person meetings disrupted climate-related work, delaying actions and some planned deliverables. Scientists in developing countries faced greater challenges than their colleagues in higher-income countries due to weaker communication infrastructure and higher work demands in developing countries.[38]
Russian invasion of Ukraine
The Russian invasion of Ukraine and the resulting trade sanctions had a further adverse effect on SDG 13, as some countries responded to the crisis by increasing domestic oil production.[39]
Remove ads
Links with other SDGs
Sustainable Development Goal 13 connects with the other 16 SDGs. For example, increasing access to sustainable energy (SDG 7) will reduce greenhouse gas emissions.[2]: 101 Combating climate change can improve agricultural yield which will lead to zero hunger (SDG 2).[40]
Organizations
United Nations organizations
- Climate target
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)[41]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)[42]
- Conferences of the Parties (COP)[43]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO)[44]
- UN-Habitat[45]
- United Nations Environment Program (UNEP)[46]
- Green Climate Fund (GCF)[47]
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) [48]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




