Stria vascularis of cochlear duct
Capillary in the outer wall of the cochlear duct From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
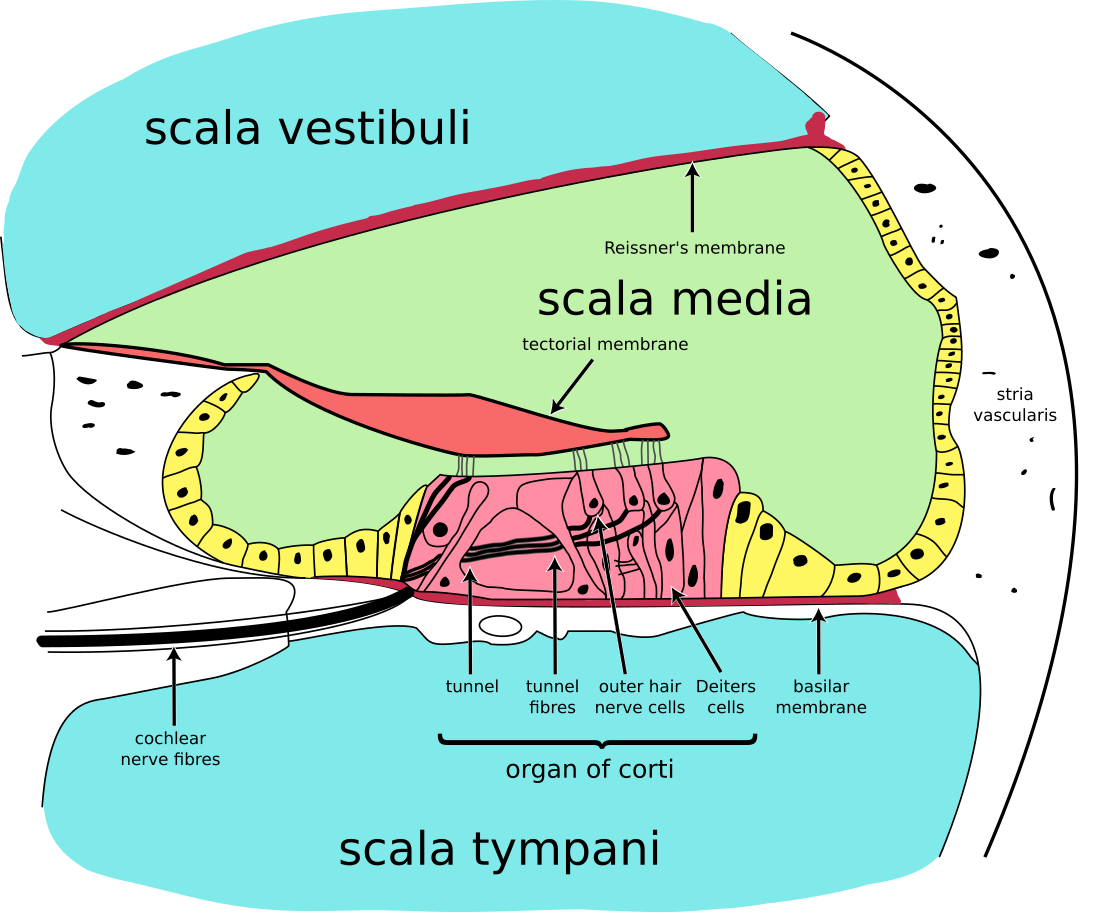
The stria vascularis of the cochlear duct is a capillary loop in the upper portion of the spiral ligament (the outer wall of the cochlear duct or scala media). It produces endolymph for the scala media in the cochlea.
| Stria vascularis of cochlear duct | |
|---|---|
 Cross section of the cochlea. | |
| Details | |
| System | Cochlea |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | stria vascularis ductus cochlearis |
| MeSH | D013316 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2525 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.096 |
| TA2 | 7028 |
| FMA | 77832 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The stria vascularis is part of the lateral wall of the cochlear duct.[1] It is a somewhat stratified epithelium containing primarily three cell types:
- marginal cells,[1] which are involved in K+ transport, and line the endolymphatic space of the scala media.
- intermediate cells,[1] which are pigment-containing cells scattered among capillaries.
- basal cells,[1] which separate the stria vascularis from the underlying spiral ligament.[2] They are connected to basal cells with gap junctions.[1]
The stria vascularis also contains pericytes, melanocytes, and endothelial cells.[3]: 2380 It also contains intraepithelial capillaries - it is the only epithelial tissue that is not avascular (completely lacking blood vessels and lymphatic vessels).[citation needed]
Function
The stria vascularis produces endolymph for the scala media, one of the three fluid-filled compartments of the cochlea.[4] This maintains the ion balance of the endolymph that surround inner hair cells and outer hair cells of the organ of Corti.[4] It secretes lots of K+,[1][4] and may also secrete H+.[1]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.