Srubnaya culture
Archaeological culture in Eastern Europe From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Srubnaya culture (Russian: Срубная культура, romanized: Srubnaya kul'tura, Ukrainian: Зрубна культура, romanized: Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1900–1200 BC culture[1][2][3] in the eastern part of the Pontic–Caspian steppe. It is a successor of the Yamna culture, the Catacomb culture and the Poltavka culture. It is co-ordinate and probably closely related to the Andronovo culture, its eastern neighbor.[3] Whether the Srubnaya culture originated in the east, west, or was a local development, is disputed among archaeologists.[3]
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (November 2018) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
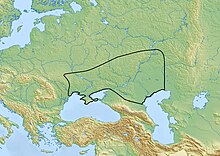 | |
| Geographical range | Pontic steppe |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | ca. 1900 BC – 1200 BC |
| Preceded by | Abashevo culture, Multi-cordoned ware culture, Sintashta culture, Lola culture |
| Followed by | Noua-Sabatinovka culture, Trzciniec culture, Belozerka culture, Bondarikha culture, Scythians, Sauromatians |
The Srubnaya culture is generally associated with archaic Iranian-speakers.[3][4] The name comes from Russian сруб (srub), "timber framework", from the way graves were constructed.
Distribution


The Srubnaya culture occupied the area along and above the north shore of the Black Sea from the Dnieper eastwards along the northern base of the Caucasus to the area abutting the north shore of the Caspian Sea, west of the Ural Mountains.[3] Historical testimony indicate that the Srubnaya culture was succeeded by the Scythians.[3]
In the early 2nd millennium BC, the Lola culture in the North Caucasus came under increasing pressure from the Srubnaya culture, who were advancing from the Middle Volga region. By 1800 BC, the Srubnaya replaced the Lola population. The Lola culture had previously replaced the local variants of the Catacomb culture.[5] The physical type of the Lola population was very different from that of the Srubnaya and Catacomb populations.[6]
Characteristics
The Srubnaya culture is named for its use of timber constructions within its burial pits. Its cemeteries consisted of five to ten kurgans. Burials included the skulls and forelegs of animals and ritual hearths. Stone cists were occasionally employed.[3] Srubnaya settlements consisted of semi-subterranean and two-roomed houses. The presence of bronze sickles, grinding stones, domestic cattle, sheep and pigs indicate that the Srubnaya engaged in both agriculture and stockbreeding.[3]
The use of chariots in the Srubnaya culture is indicated by finds of studded antler cheek-pieces (for controlling chariot horses), burials of paired domesticated horses, and ceramic vessels with images of two-wheeled vehicles on them.[7][8] The predecessor of the Srubnaya culture, a variant of the Abashevo culture known as the Pokrovka type, is considered to be an important part of the early ‘chariot horizon’, representing the rapid spread of the 'chariot complex'.[9][10]
Language
The Srubnaya culture is generally considered to have been Iranian.[3][4] Its area, which coincides with the presence of Iranian hydronyms,[4] has been suggested as a staging region from which the Iranian peoples migrated across the Caucasus into the Iranian Plateau.[3]
Genetics
Summarize
Perspective

Mathieson et al. (2015)[12] surveyed 14 individuals of the Srubnaya culture. Six men from 5 different cemeteries belonged to the Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a1. Extractions of mtDNA from fourteen individuals were determined to represent five samples of haplogroup H, four samples of haplogroup U5, two samples of T1, one sample of T2, one sample of K1b, one of J2b and one of I1a.
A 2017 genetic study published in Scientific Reports found that the Scythians shared similar mitochondrial lineages with the Srubnaya culture. The authors of the study suggested that the Srubnaya culture was ancestral to the Scythians.[13]
In 2018, a genetic study of the earlier Srubnaya culture, and later peoples of the Scythian cultures, including the Cimmerians, Scythians, Sarmatians, was published in Science Advances. Six males from two sites ascribed to the Srubnaya culture were analysed, and were all found to possess haplogroup R1a1a1. Cimmerian, Sarmatian and Scythian males were however found have mostly haplogroup R1b1a1a2, although one Sarmatian male carried haplogroup R1a1a1. The authors of the study suggested that rather than being ancestral to the Scythians, the Srubnaya shared with them a common origin from the earlier Yamnaya culture.[14]
In a genetic study published in Science in 2018, the remains of twelve individuals ascribed to the Srubnaya culture was analyzed. Of the six samples of Y-DNA extracted, three belonged to R1a1a1b2 or subclades of it, one belonged to R1, one belonged to R1a1, and one belonged to R1a1a. With regards to mtDNA, five samples belonged to subclades of U, five belonged to subclades of H, and two belonged to subclades of T. People of the Srubnaya culture were found to be closely related to people of the Corded Ware culture, the Sintashta culture, Potapovka culture and the Andronovo culture.[a][b] These were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the Yamnaya culture and peoples of the Central European Middle Neolithic.[15] The genetic data suggested that these cultures were ultimately derived of a remigration of Central European peoples with steppe ancestry back into the steppe.[c]
In a 2023 study, one sample from the site Nepluyevsky, belonging to Srubnaya-Alakul culture and located in Southern Urals, (c. 1877 to 1642 calBC), (2-sigma, 95.4%), featured Y-haplogroup R1a1a1b2a (R1a-Z94), and other not dated sample featured R1a1a1b2 (R1a-Z93).[16]
Gallery
- Ceramic sherd
- Bronze axes
- Horse bridle items
- Reconstructed Srubnaya hut
- Timber grave and tumulus
- Dispersion of double-horse burials ca. 2000-1400/1300 BCE.[17] Horses were domesticated on the Pontic-Caspian steppe.[18]
See also
Notes
- "We observed a main cluster of Sintashta individuals that was similar to Srubnaya, Potapovka, and Andronovo in being well modeled as a mixture of Yamnaya-related and Anatolian Neolithic (European agriculturalist-related) ancestry."[15]
- "Genetic analysis indicates that the individuals in our study classified as falling within the Andronovo complex are genetically similar to the main clusters of Potapovka, Sintashta, and Srubnaya in being well modeled as a mixture of Yamnaya-related and early European agriculturalist-related or Anatolian agriculturalist-related ancestry."[15]
- "Corded Ware, Srubnaya, Petrovka, Sintashta and Andronovo complexes, all of which harbored a mixture of Steppe_EMBA ancestry and ancestry from European Middle Neolithic agriculturalists (Europe_MN). This is consistent with previous findings showing that following westward movement of eastern European populations and mixture with local European agriculturalists, there was an eastward reflux back beyond the Urals."[15]
References
Bibliography
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.