Inferior orbital fissure
Gap between bones of the human eye socket From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The inferior orbital fissure is a gap between the greater wing of sphenoid bone, and the maxilla. It connects the orbit (anteriorly) with the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (posteriorly).[1]: 397
| Inferior orbital fissure | |
|---|---|
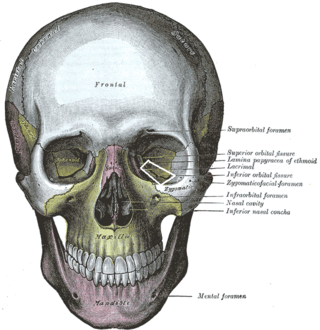
 The skull from the front. (Label for inferior orbital fissure is at center right.) | |
 1 Foramen ethmoidale, 2 Canalis opticus, 3 Fissura orbitalis superior, 4 Fossa sacci lacrimalis, 5 Sulcus infraorbitalis, 6 Fissura orbitalis inferior, 7 Foramen infraorbitale | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fissura orbitalis inferior |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.084 |
| TA2 | 489 |
| FMA | 54802 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomy
The medial end of the inferior orbital fissure diverges laterally from the medial end of the superior orbital fissure. It is situated between the lateral wall of the orbit and the floor of the orbit.[1]: 397
Contents
The fissure gives passage to multiple structures, including:
- Infraorbital nerve,[1]: 402 artery[1]: 364 and vein[citation needed]
- Inferior ophthalmic vein[1]: 364, 403
- Zygomatic nerve[1]: 496
- Orbital branches of the pharyngeal nerve[1]: 370
- Maxillary nerve
Additional images
- Left infratemporal fossa.
- Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities.
- Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
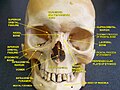
- Inferior orbital fissure.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.