Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of foramina of the human body
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This article lists foramina that occur in the human body.
Skull
Summarize
Perspective
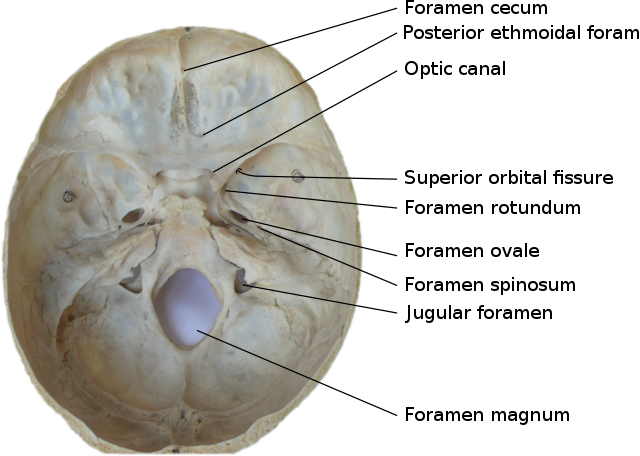
The human skull has numerous openings (foramina), through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. These foramina vary in size and number, with age.[1][2]
- Base of the skull, upper surface
- Base of the skull, inferior surface, attachment of muscles marked in red
Spine
Within the vertebral column (spine) of vertebrates, including the human spine, each bone has an opening at both its top and bottom to allow nerves, arteries, veins, etc. to pass through.
Other
- Apical foramen, the opening at the tip of the root of a tooth
- Foramen ovale (heart), an opening between the venous and arterial sides of the fetal heart
- Foramen transversarium, one of a pair of openings in each cervical vertebra, in which the vertebral artery travels
- Greater sciatic foramen, a major foramen of the pelvis
- Interventricular foramen, channels connecting ventricles in the brain
- Intervertebral foramen, foramina formed between vertebrae
- Lesser sciatic foramen, an opening between the pelvis and the posterior thigh
- Obturator foramen, the opening created by the ischium and pubis bones of the pelvis
- Vertebral foramen, the foramen formed by the anterior segment (the body), and the posterior part, the vertebral arch
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


