Solar analog
Star that is particularly similar to the Sun From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Solar-type stars, solar analogs (also analogues), and solar twins are stars that are particularly similar to the Sun. The stellar classification is a hierarchy with solar twin being most like the Sun followed by solar analog and then solar-type.[1] Observations of these stars are important for understanding better the properties of the Sun in relation to other stars and the habitability of planets.[2]
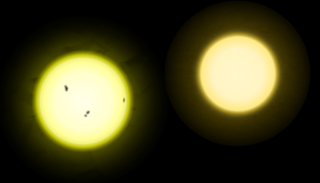
By similarity to the Sun
Summarize
Perspective
Defining the three categories by their similarity to the Sun reflects the evolution of astronomical observational techniques. Originally, solar-type was the closest that similarity to the Sun could be defined. Later, more precise measurement techniques and improved observatories allowed for greater precision of key details like temperature, enabling the creation of a solar analog category for stars that were particularly similar to the Sun. Later still, continued improvements in precision allowed for the creation of a solar-twin category for near-perfect matches.[citation needed]
Similarity to the Sun allows for checking derived quantities—such as temperature, which is derived from the color index—against the Sun, the only star whose temperature is confidently known. For stars that are not similar to the Sun, this cross-checking cannot be done.[1]
Solar-type
These stars are broadly similar to the Sun. They are main-sequence stars with a B−V color between 0.48 and 0.80, the Sun having a B−V color of 0.65. Alternatively, a definition based on spectral type can be used, such as F8V through K2V, which would correspond to B−V color of 0.50 to 1.00.[1] This definition fits approximately 10% of stars, so a list of solar-type stars would be quite extensive.[3]
Solar-type stars show highly correlated behavior between their rotation rates and their chromospheric activity (e.g. Calcium H & K line emission) and coronal activity (e.g. X-ray emission)[4] Because solar-type stars spin down during their main-sequence lifetimes due to magnetic braking, these correlations allow rough ages to be derived. Mamajek & Hillenbrand (2008)[5] have estimated the ages for the 108 solar-type (F8V–K2V) main-sequence stars within 52 light-years (16 parsecs) of the Sun based on their chromospheric activity (as measured via Ca, H, and K emission lines).[citation needed]
The following table shows a sample of solar-type stars within 50 light years that nearly satisfy the criteria for solar analogs (B−V color between 0.48 and 0.80), based on current measurements (the Sun is listed for comparison):
| Identifier | J2000 coordinates[6] | Distance[6] (ly) |
Stellar class[6] |
Temperature (K) |
Metallicity (dex) |
Age (Gyr) |
Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right ascension | Declination | |||||||
| Sun | — | — | 0.0000158 | G2V | 5778 | +0.00 | 4.6 | [7] |
| Rigil Kentaurus [8] | 15h 49m 36.49400s | −60° 50′ 02.3737″ | 4.37 | G2V | 5790 | +0.20 | 4.4 | [9][10][11][12] |
| Toliman | 4.37 | K0V | 5260 | 4.4 | ||||
| Epsilon Eridani [13] | -09h 27m 29.7s | 03° 32′ 55.8″ | 10.4 | K2V | 5084 | -0.13 | 0.4-0.8 | |
| Tau Ceti [14] | 01h 44m 04.1s | −15° 56′ 15″ | 11.9 | G8V | 5344 | –0.52 | 5.8 | [15] |
| 82 Eridani [16] | 03h 19m 55.7s | −43° 04′ 11.2″ | 19.8 | G8V | 5338 | –0.54 | 6.1 | [17] |
| Delta Pavonis [18] | 20h 08m 43.6s | −66° 10′ 55″ | 19.9 | G8IV | 5604 | +0.33 | ~7 | [19] |
| V538 Aurigae [20] | 05h 41m 20.3s | +53° 28′ 51.8″ | 39.9 | K1V | 5257 | −0.20 | 3.7 | [17] |
| HD 14412 [21] | 02h 18m 58.5s | −25° 56′ 45″ | 41.3 | G5V | 5432 | −0.46 | 9.6 | [17] |
| HR 4587 [22] | 12h 00m 44.3s | −10° 26′ 45.7″ | 42.1 | G8IV | 5538 | +0.18 | 8.5 | [17] |
| HD 172051 [23] | 18h 38m 53.4s | −21° 03′ 07″ | 42.7 | G5V | 5610 | −0.32 | 4.3 | [17] |
| 72 Herculis [24] | 17h 20m 39.6s | +32° 28′ 04″ | 46.9 | G0V | 5662 | −0.37 | 5 | [17] |
| HD 196761 [25] | 20h 40m 11.8s | −23° 46′ 26″ | 46.9 | G8V | 5415 | −0.31 | 6.6 | [19] |
| Nu² Lupi [26] | 15h 21m 48.1s | −48° 19′ 03″ | 47.5 | G4V | 5664 | −0.34 | 10.3 | [19] |
Solar analog
These stars are photometrically similar to the Sun, having the following qualities:[1]
- Temperature within 500 K from that of the Sun (5278 to 6278 K)
- Metallicity of 50–200% (± 0.3 dex) of that of the Sun, meaning the star's protoplanetary disk would have had similar amounts of dust from which planets could form
- No close companion (orbital period of ten days or less), because such a companion stimulates stellar activity
Solar analogs not meeting the stricter solar twin criteria include, within 50 light years and in order of increasing distance (The Sun is listed for comparison.):
| Identifier | J2000 coordinates[6] | Distance[6] (ly) |
Stellar class[6] |
Temperature (K) |
Metallicity (dex) |
Age (Gyr) |
Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right ascension | Declination | |||||||
| Sun | — | — | 0.0000158 | G2V | 5,778 | +0.00 | 4.6 | [7] |
| Sigma Draconis [27] | 19h 32m 21.6s | +69° 39′ 40″ | 18.8 | G9–K0 V | 5,297 | −0.20 | 4.7 | [28] |
| Beta Canum Venaticorum [29] | 12h 33m 44.5s | +41° 21′ 27″ | 27.4 | G0V | 5,930 | −0.30 | 6.0 | [17] |
| 61 Virginis [30] | 13h 18m 24.3s | −18° 18′ 40″ | 27.8 | G5V | 5,558 | −0.02 | 6.3 | [19] |
| Zeta Tucanae [31] | 00h 20m 04.3s | –64° 52′ 29″ | 28.0 | F9.5V | 5,956 | −0.14 | 2.5 | [15] |
| Beta Comae Berenices [32] | 13h 11m 52.4s | +27° 52′ 41″ | 29.8 | G0V | 5,970 | −0.06 | 2.0 | [17] |
| 61 Ursae Majoris [33] | 11h 41m 03.0s | +34° 12′ 06″ | 31.1 | G8V | 5,483 | −0.12 | 1.0 | [17] |
| HR 511 [34] | 01h 47m 44.8s | +63° 51′ 09″ | 32.8 | K0V | 5,333 | +0.05 | 3.0 | [17] |
| Alpha Mensae [35] | 06h 10m 14.5s | –74° 45′ 11″ | 33.1 | G5V | 5,594 | +0.10 | 5.4 | [15] |
| HD 69830 [36] | 08h 18m 23.9s | −12° 37′ 56″ | 40.6 | K0V | 5,410 | −0.03 | 10.6 | [15] |
| HD 10307 [37] | 01h 41m 47.1s | +42° 36′ 48″ | 41.2 | G1.5V | 5,848 | −0.05 | 7.0 | [17] |
| HD 147513 [38] | 16h 24m 01.3s | −39° 11′ 35″ | 42.0 | G1V | 5,858 | +0.03 | 0.4 | [19] |
| 58 Eridani [39] | 04h 47m 36.3s | −16° 56′ 04″ | 43.3 | G3V | 5,868 | +0.02 | 0.6 | [15] |
| 47 Ursae Majoris [40] | 10h 59m 28.0s | +40° 25′ 49″ | 45.9 | G1V | 5,954 | +0.06 | 6.0 | [15] |
| Psi Serpentis [41] | 15h 44m 01.8s | +02° 30′ 54.6″ | 47.8 | G5V | 5,683 | 0.04 | 3.2 | [42] |
| HD 84117 [43] | 09h 42m 14.4s | –23° 54′ 56″ | 48.5 | F8V | 6,167 | −0.03 | 3.1 | [15] |
| HD 4391 [44] | 00h 45m 45.6s | –47° 33′ 07″ | 48.6 | G3V | 5,878 | −0.03 | 1.2 | [15] |
| 20 Leonis Minoris [45] | 10h 01m 00.7s | +31° 55′ 25″ | 49.1 | G3V | 5,741 | +0.20 | 6.5 | [17] |
| Nu Phoenicis [46] | 01h 15m 11.1s | –45° 31′ 54″ | 49.3 | F8V | 6,140 | +0.18 | 5.7 | [15] |
| Helvetios [47] | 22h 57m 28.0s | +20° 46′ 08″ | 50.9 | G2.5IVa | 5,804 | +0.20 | 7.0 | [15] |
Solar twin
To date no solar twin that exactly matches the Sun has been found.[48] However, there are some stars that come very close to being identical to the Sun, and are such considered solar twins by members of the astronomical community. An exact solar twin would be a G2V star with a 5,778 K surface temperature, be 4.6 billion years old, with the correct metallicity and a 0.1% solar luminosity variation.[48] Stars with an age of 4.6 billion years are at the most stable state. Proper metallicity, radius, chemical composition, rotation, magnetic activity, and size are also very important to low luminosity variation.[49][50][51][52]
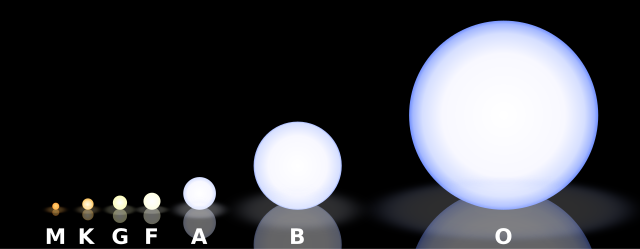
The stars below are more similar to the Sun and having the following qualities:[1]
- Temperature within 50 K from that of the Sun (5728 to 5828 K)[a] (within 10 K of sun (5768–5788 K)).
- Metallicity of 89–112% (± 0.05 dex) of that of the Sun, meaning the star's proplyd would have had almost exactly the same amount of dust for planetary formation
- No stellar companion, because the Sun itself is a solitary star
- An age within 1 billion years from that of the Sun (3.6 to 5.6 Ga)
Other Sun parameters:[53]
- Sun rotates on its axis once in about 27 days or 1.997 kilometres per second (1.241 mi/s)
- Sun radius is 700,000 kilometres (430,000 mi)
- Sun chemical composition by mass: hydrogen (73.4%); helium (25%); carbon (0.2%); nitrogen (0.09%);oxygen (0.80%); neon (0.16%); magnesium (0.06%); silicon (0.09&); sulfur (0.05%); iron (0.003%).[54]
The following are the known stars that come closest to satisfying the criteria for a solar twin. The Sun is listed for comparison. Highlighted boxes are out of range for a solar twin. The star may have been noted as solar twin in the past, but are more of a solar analog.
| Identifier | J2000 coordinates[6] | Distance[6] (ly) |
Stellar class[6] |
Temperature (K) |
Metallicity (dex) |
Age (Gyr) |
Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right ascension | Declination | |||||||
| Sun | — | — | 0.0000158 | G2V | 5,778 | +0.00 | 4.6 | [7] |
| 18 Scorpii [55] | 16h 15m 37.3s | –08° 22′ 06″ | 45.1 | G2Va | 5,433 | −0.03 | 2.9 | [56][57] |
| HD 150248 [58] | 16h 41m 49.8s | –45° 22′ 07″ | 88 | G2 | 5,750 | −0.04 | 6.2 | [57] |
| HD 164595 [59] | 18h 00m 38.9s | +29° 34′ 19″ | 91 | G2 | 5,810 | −0.06 | 4.5 | [57] |
| HD 195034 [60] | 20h 28m 11.8s | +22° 07′ 44″ | 92 | G5 | 5,760 | −0.04 | 2.9 | [61] |
| HD 117939 [62] | 13h 34m 32.6s | –38° 54′ 26″ | 98 | G3 | 5,730 | −0.10 | 6.1 | [57] |
| HD 138573 [63] | 15h 32m 43.7s | +10° 58′ 06″ | 99 | G5IV–V | 5,757 | +0.00 | 7.1 | [64] |
| HD 71334 [65] | 08h 25m 49.5s | −29° 55′ 50″ | 124 | G2 | 5,701 | −0.075 | 8.1 | [66] |
| HD 98649 [67] | 11h 20m 51.769s | –23° 13′ 02″ | 135 | G4V | 5,759 | −0.02 | 2.3 | [57] |
| HD 143436 [68] | 16h 00m 18.8s | +00° 08′ 13″ | 141 | G0 | 5,768 | +0.00 | 3.8 (±2.9) | [69] |
| HD 129357 [70] | 14h 41m 22.4s | +29° 03′ 32″ | 154 | G2V | 5,749 | −0.02 | 8.2 | [69] |
| HD 133600 [71] | 15h 05m 13.2s | +06° 17′ 24″ | 171 | G0 | 5,808 | +0.02 | 6.3 | [56] |
| HD 186302 [72] | 19h 49m 6.43s | −70° 11′ 16.7″ | 184 | G3 | 5,675 | +0.00 | 4.5 | [73] |
| HIP 11915 [74] | 02h 33m 49.02s | −19° 36′ 42.5″ | 190 | G5V | 5,760 | –0.059 | 4.1 | [75] |
| HD 101364 [76] | 11h 40m 28.5s | +69° 00′ 31″ | 208 | G5V | 5,795 | +0.02 | 7.1 | [56][77] |
| HD 197027 [78] | 20h 41m 54.6s | –27° 12′ 57″ | 250 | G3V | 5,723 | −0.013 | 8.2 | [79] |
| Kepler-452 [80] | 19h 44m 00.89s | +44° 16′ 39.2″ | 1400 | G2V | 5,757 | +0.21 | 6.0 | [81] |
| YBP 1194 [82] | 08h 51m 00.8s | +11° 48′ 53″ | 2934 | G5V | 5,780 | +0.023 | ~ 4.2 (± 1.6) | [83] |
Some other stars are sometimes mentioned as solar-twin candidates such as: Beta Canum Venaticorum; however it has too low metallicities (−0.21) for solar twin. 16 Cygni B is sometimes noted as twin, but is part of a triple star system and is very old for a solar twin at 6.8 Ga.
By potential habitability
Summarize
Perspective
Another way of defining solar twin is as a "habstar"—a star with qualities believed to be particularly hospitable to a life-hosting planet. Qualities considered include variability, mass, age, metallicity, and close companions.[84][b]
- At least 0.5–1 billion years old
- On the main sequence
- Non-variable
- Capable of harboring terrestrial planets
- Support a dynamically stable habitable zone
- 0–1 non-wide stellar companion stars.
The requirement that the star remain on the main sequence for at least 0.5–1 Ga sets an upper limit of approximately 2.2–3.4 solar masses, corresponding to a hottest spectral type of A0-B7V. Such stars can be 100x as bright as the Sun.[84][87] Tardigrade-like life (due to the UV flux) could potentially survive on planets orbiting stars as hot as B1V, with a mass of 10 M☉, and a temperature of 25,000 K, a main-sequence lifetime of about 20 million years.[c]
Non-variability is ideally defined as variability of less than 1%, but 3% is the practical limit due to limits in available data. Variation in irradiance in a star's habitable zone due to a companion star with an eccentric orbit is also a concern.[50][51][84][52]
Terrestrial planets in multiple star systems, those containing three or more stars, are not likely to have stable orbits in the long term. Stable orbits in binary systems take one of two forms: S-Type (satellite or circumstellar) orbits around one of the stars, and P-Type (planetary or circumbinary) orbits around the entire binary pair. Eccentric Jupiters may also disrupt the orbits of planets in habitable zones.[84]
Metallicity of at least 40% solar ([Fe/H] = −0.4) is required for the formation of an Earth-like terrestrial planet. High metallicity strongly correlates to the formation of hot Jupiters, but these are not absolute bars to life, as some gas giants end up orbiting within the habitable zone themselves, and could potentially host Earth-like moons.[84]
One example of such a star is HD 70642 [88], a G5V, at temperature of 5533 K, but is much younger than the Sun, at 1.9 billion years old.[89]
Another such example would be HIP 11915, which has a planetary system containing a Jupiter-like planet orbiting at a similar distance that the planet Jupiter does in the Solar System.[90] To strengthen the similarities, the star is class G5V, has a temperature of 5750 K, has a Sun-like mass and radius, and is only 500 million years younger than the Sun. As such, the habitable zone would extend in the same area as the zone in the Solar System, around 1 AU. This would allow an Earth-like planet to exist around 1 AU.[91]
See also
Footnotes
- A true solar twins as noted by the Lowell Observatory should have a temperature within ~10 K of the Sun. Space Telescope Science Institute, Lowell Observatory, noted in 1996 that temperature precision of ~10 K can be measured. A temperature of ~10 K reduces the solar twin list to near zero, so ±50 K is used for the chart.[2]
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
