Silylene
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
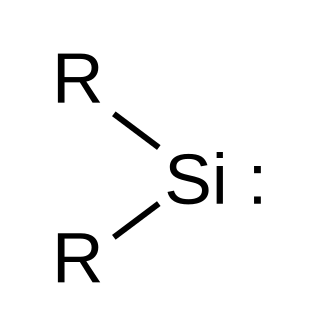
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon analog of carbene. Silylene rapidly when condensed.
 Simplest silylene has R=Hydrogen | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silylene | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Silylidene[1] | |
| Other names
Hydrogen silicide(−II) Silicene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H2Si | |
| Molar mass | 30.101 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents.[2] Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups.[3][4]
Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs.[5]
Synthesis and properties
Silylenes have been generated by thermolysis or photolysis of polysilanes, by silicon atom reactions (insertion, addition or abstraction), by pyrolysis of silanes, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane. It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates:
- Si + Cl2 → SiCl2
- SiCl2 + Cl2 → SiCl4
Similar considerations apply to the direct process, the reaction of methyl chloride and bulk silicon.
Early observations of silylenes involved generation of dimethylsilylene by dechlorination of dimethyldichlorosilane:[6]
- SiCl2(CH3)2 + 2 K → Si(CH3)2 + 2 KCl
The formation of dimethylsilylene was demonstrated by conducting the dechlorination in the presence of trimethylsilane: the trapped product being pentamethyldisilane:
- Si(CH3)2 + HSi(CH3)3 → (CH3)2Si(H)−Si(CH3)3
A room-temperature isolable N-heterocyclic silylene is N,N′-di-tert-butyl-1,3-diaza-2-silacyclopent-4-en-2-ylidene:[7]

The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.[8]
Related reactions

In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis of a trisilane:[9]
In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two microseconds. Added methanol acts as a chemical trap with a second order rate constant of 1.3×1010 mol−1 s−1 which is close to diffusion control.
See also
- Carbene analogs
- N-heterocyclic silylene
- Silenes, R2Si=SiR2
- Silylium ions, protonated silylenes
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.