Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Rigging (material handling)
Equipment and procedure in material handling From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Remove ads
Rigging is both a noun, the equipment, and verb, the action of designing and installing the equipment, in the preparation to move objects. A team of riggers design and install the lifting or rolling equipment needed to raise, roll, slide or lift objects such as heavy machinery, structural components, building materials, or large-scale fixtures with a crane, hoist or block and tackle.
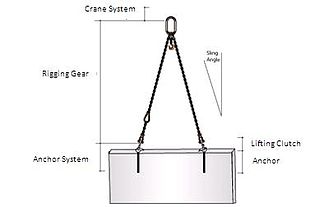
Rigging comes from rig, to set up or prepare. Rigging is the equipment such as wire rope, turnbuckles, clevis, jacks used with cranes and other lifting equipment[1] in material handling and structure relocation. Rigging systems commonly include shackles, master links and slings, and lifting bags in underwater lifting.
In the United States the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulates workplace safety including rigging in CFR 1926.251.[2]
The Health and Safety Executive is responsible for the matters in the United Kingdom.
Remove ads
Equipment
- Block (sailing) – Sailing term; single or multiple pulley
- Cargo net – Net used to secure or transfer cargo
- Cargo strap
- Chain – Series of connected links which are typically made of metal
- Chain hoist – Device used for lifting or lowering a load
- Chain stopper
- Come-along – Lever operated, portable ratchet winch
- Crane (machine) – Type of machine
- Crawler (rigging)
- Hook – Tool used to grab onto, connect, or attach to something
- Hoist (device) – Device used for lifting or lowering a load
- Jack (device) – Mechanical lifting device
- Knot – Method of fastening or securing linear material
- Lever – Simple machine consisting of a beam pivoted at a fixed hinge
- Lifting bag – Airtight bag used for underwater buoyant lifting when filled with air
- Lifting beam
- Link (chain) – Basic component of a chain
- Pry bar – Type of lever tool
- Rope – Length of braided strands
- Shackle – Metal assembly which functions as a removable connecting link
- Sheave – Grooved wheel used to support a moving belt, wire or rope
- Sheer legs
- Sling (rigging) – Rope, webbing, wire or chain used to support a load for lifting
- Rope splicing – Semi-permanent joint between two ropes
- Tackle – System of two or more pulleys and a rope or cable
- Tirfor – Device for pulling cable
- Tugger (rigging)
- Turnbuckle – Device for adjusting the tension or length of ropes or cables
- Turning block
- Wire rope – Metal rope
- Winch
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2022) |
Remove ads
Procedures
In order to rig, there are several standard steps that should be followed, in order to ensure safety and efficiency in the rigging process:
Planning - First, one must determine the mass, dimensions and center of gravity of the load being rigged. Based off this information, and the environment the load is present in, one must then determine the appropriate lifting gear needed to move the load.
Inspection - Check slings, hooks, shackles, and lifting appliances for wear, damage, or expiry of certification.
Setting Up Rigging – Rig lifting gear properly to load anchor points utilizing proper rigging methods such as vertical, basket, or choker hitches.
Communication – Notify all the members present on hand signals or radio communication before initiating the lift.
Conducting the Lift – Execute the lift slowly and gradually while balancing and stabilizing. Use taglines in the control of load movement.
Post-lift Inspection – Lower the load safely, remove rigging, and check gear prior to storage. [3]
Remove ads
Safety
Safety should be a top priority whilst rigging, as extremely heavy loads are usually involved, and handling heavy material has its hazards. Dropped loads, equipment failure, and pinch trauma are all potential risks present when rigging. Usual safety measures include:
Training and Certification – Only trained riggers and signalmen should carry out or supervise rigging operations.
PPE Usage – People who are rigging should wear hard hats, gloves, steel-toed boots, and high-visibility vests.
Load Limits – Never exceed the Working Load Limit (WLL) of rigging equipment.
Load Path Awareness – Never stand under a suspended load.
Weather Considerations – Never rig in windy or low-visibility weather conditions.
Taglines – Use taglines to prevent uncontrolled load swinging.[3][4]
Gallery
- A Humvee is rigged for being airdropped at the Heavy Drop Rigging Facility near Pope Field at Fort Bragg, N.C.
- The rigging is the two frameworks, spreaders, wire ropes and related fittings used by the crane to pick up this submarine.
- An advanced rigging challenge assembling a wind turbine.
- An adjustable spreader bar with webbing slings.
See also
- Entertainment rigging – Setting up equipment for shows
- Boat rigging – Setting up a rowing boat to accommodate the crew for rowing
- Parachute rigger – Person who is trained or licensed to pack, maintain or repair parachutes
- High lead logging – Method of cable logging using a spar, yarder and loader
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




