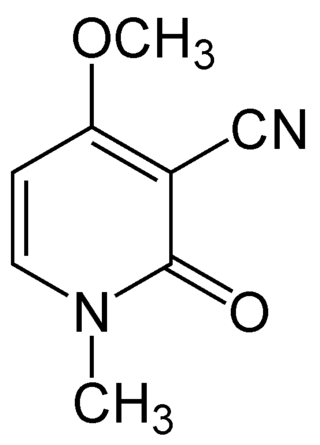
Ricinine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Ricinine is a toxic alkaloid found in the castor plant.[2] It can serve as a biomarker of ricin poisoning.[3][4] It was first isolated from the castor seeds by Tuson in 1864.[5][6]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Methoxy-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile | |
| Other names
3-cyano-4-methoxy-N-methyl-2-pyridone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.601 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 164.164 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
340 mg/kg[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ricinine has insecticidal effects.[7]
It sublimes between 170 and 180 °C at 20 mmHg. It does not form salts, and is precipitated in iodine or mercuric chloride solutions, but not in Mayer's reagent.[5]
It can be hydrolyzed to methanol and ricininic acid by alkali.[5]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.