Rhynia
Extinct species of vascular plant From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Rhynia is a single-species genus of Devonian vascular plants. Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii was the sporophyte[2] generation of a vascular, axial, free-sporing diplohaplontic embryophytic land plant of the Early Devonian that had anatomical features more advanced than those of the bryophytes. Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii was a member of a sister group to all other eutracheophytes, including modern vascular plants.
| Rhynia Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
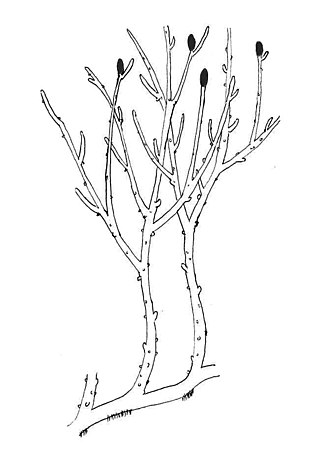
| Reconstruction of Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii, redrawn after Kenrick & Crane (1997:101)[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Subdivision: | †Rhyniophytina |
| Class: | †Rhyniopsida |
| Order: | †Rhyniales |
| Family: | †Rhyniaceae |
| Genus: | †Rhynia Kidst. & W.H.Lang (1917) |
| Type species | |
| R. gwynne-vaughanii Kidst. & W.H.Lang (1917) | |
| Species | |
| |
Description
Summarize
Perspective
Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii was first described as a new species by Robert Kidston and William H. Lang in 1917.[3] The species is known only from the Rhynie chert in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, where it grew in the vicinity of a silica-rich hot spring. Rhynia was a vascular plant, and grew in association with other vascular plants such as Asteroxylon mackei, a probable ancestor of modern clubmosses (Lycopsida), and with pre-vascular plants such as Aglaophyton major, which is interpreted as basal to true vascular plants.[4]

Rhynia is thought to have had deciduous lateral branches, which it used to disperse laterally over the substrate[5][6] and stands of the plant may therefore have been clonal populations.
Evidence of the gametophyte generation of Rhynia has been described in the form of crowded tufts of diminutive stems only a few mm in height, with the form genus name Remyophyton delicatum.[7] Like those of Aglaophyton major,[8][9] Horneophyton lignieri[10] and Nothia aphylla[11] the gametophytes of Rhynia were dioicous, bearing male and female gametangia (antheridia and archegonia) on different axes. A significant finding is that the axes of the gametophytes were vascular, unlike almost all of the gametophytes of modern pteridophytes except for that of Psilotum.[12]
Taxonomy
Two species of Rhynia were initially described by R. Kidston and W. H. Lang from the Rhynie chert bed: R. gwynne-vaughnii in 1917,[3] and R. major in 1920.[13] R. gwynne-vaughanii was named by Kidston and Lang in honour of their late friend and colleague, the botanist David Thomas Gwynne-Vaughan.[3]
A study of the vascular tissue of the two by David S. Edwards in 1986 lead to the conclusion that the cell walls of the water-conducting cells of R. major lacked the secondary thickening bars seen in the xylem of R. gwynne-vaughanii, and were more like the water-conducting hydroids of moss sporophytes. His conclusion was that R. gwynne-vaughanii belongs in the vascular plants, while R. major belongs among the bryophytes. Accordingly, he transferred it to a new genus Aglaophyton, leaving R. gwynne-vaughnii as the only known species of Rhynia.[14] Rhynia is the type genus for the rhyniophytes, established as the subdivision Rhyniophytina by Banks,[15] but since treated at various ranks.
Phylogeny
In 2004, Crane et al. published a cladogram for the polysporangiophytes, in which Rhynia and the other Rhyniaceae are placed as basal vascular plants (tracheophyes).[16]
| polysporangiophytes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.