Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Trinidad and Tobago is divided into seven regions, five boroughs, two cities and one ward.
Trinidad
Summarize
Perspective
The following are the municipalities and regions created after the amendment of Act No. 8 of 1992:[1][2]
The following regions were merged after the amendment of Act No. 8 of 1992:[2]
Before 1990, Trinidad was divided into eight counties.
Remove ads
Tobago
Summarize
Perspective
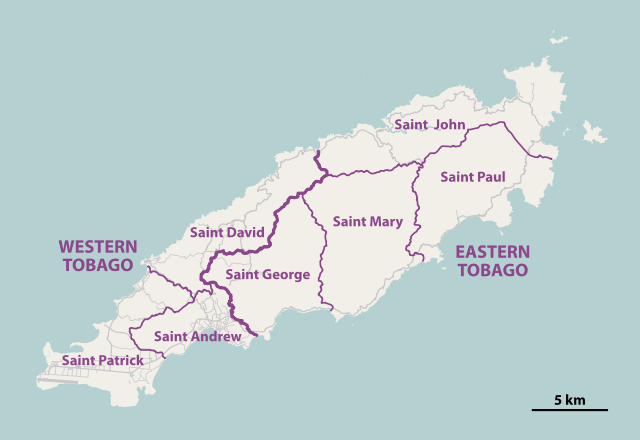
Tobago is a ward of Trinidad and Tobago and is governed locally by the Tobago House of Assembly.
Historically, Tobago was divided into seven parishes (Saint Andrew, Saint David, Saint George, Saint John, Saint Mary, Saint Patrick and Saint Paul). In 1768 each parish of Tobago had nominated representatives to the Tobago House of Assembly. On 20 October 1889 the British crown implemented a Royal Order in Council constituting Tobago as a ward of Trinidad, thus terminating local government on Tobago and formed a unified colony government.
In 1945 when the county council system was first introduced, Tobago was administered as a single county of Trinidad.
In 1980 provisions were made for the Tobago House of Assembly to be revived as an entity providing local government in Tobago. Under the revived system, Tobago is made up of 15 local electoral districts since 2021, previously 12 districts, with each district electing one Assemblyman to the THA.
Remove ads
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

