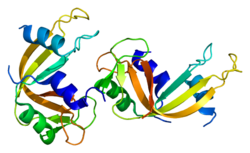According to the US National Library of Medicine, "This gene encodes a member of the pancreatic-type of secretory ribonucleases, a subset of the ribonuclease A super-family. The encoded endonuclease cleaves internal phosphodiester RNA bonds on the 3'-side of pyrimidine bases. It prefers poly(C) as a substrate and hydrolyses 2',3'-cyclic nucleotides, with a pH optimum near 8.0. The encoded protein is monomeric and more commonly acts to degrade ss-RNA over ds-RNA." Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and four transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.[6]