Pullulan
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
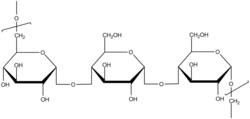
Pullulan is a polysaccharide consisting of maltotriose units, also known as α-1,4- ;α-1,6-glucan'. Three glucose units in maltotriose are connected by an α-1,4 glycosidic bond, whereas consecutive maltotriose units are connected to each other by an α-1,6 glycosidic bond. Pullulan is produced from starch by the fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. Pullulan is mainly used by the cell to resist desiccation and predation. The presence of this polysaccharide also facilitates diffusion of molecules both into and out of the cell.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
E1204 | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.938 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E1204 (additional chemicals) |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (C6H10O5)n | |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
As an edible, mostly tasteless polymer, the chief commercial use of pullulan is in the manufacture of edible films that are used in various breath freshener or oral hygiene products such as Listerine Cool Mint of Johnson and Johnson (USA) and Meltz Super Thin Mints of Avery Bio-Tech Private Ltd. (India). Pullulan and HPMC can also be used as a vegetarian substitute for drug capsules, rather than gelatine. As a food additive, it is known by the E number E1204.
Pullulan has also be explored as natural polymeric biomaterials used to fabricate injectable scaffolding for bone tissue engineering,[2] cartilage tissue engineering,[3] and intervertebral disc regeneration.[4]
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
