Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Politics of South Korea
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
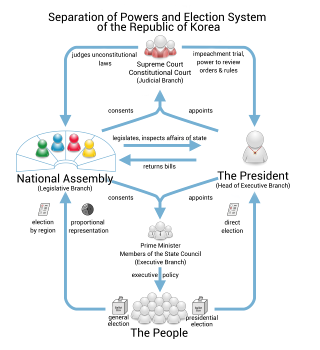
The politics of South Korea take place in the framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the president is the head of state, and of a multi-party system. To ensure a separation of powers, the Republic of Korea Government is made up of three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The government exercises executive power, and legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature and comprises a Supreme Court, appellate courts, and a Constitutional Court.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2014) |
Remove ads

Since 1948, the constitution has undergone five major revisions, each signifying a new republic. The current Sixth Republic began with the last major constitutional revision that took effect in 1988. From its founding until the June Democratic Struggle, the South Korean political system operated under a military authoritarian regime, with the freedom of assembly, association, expression, press and religion as well as civil society activism being tightly restricted. During that period, there were no freely elected national leaders, political opposition was suppressed, dissent was not permitted and civil rights were curtailed.
The Economist Intelligence Unit rated South Korea a "full democracy" in 2022.[2][needs update] According to the V-Dem Democracy indices in 2023, South Korea was the third most electoral democratic country in Asia.[3] South Korea is often cited as a model of democracy due to its relatively peaceful and internally-driven democratic transition.[4][5][6][7][8]
The period from the mid-2000s to mid-2010s are often considered South Korea's backsliding period. Although, some have argued South Korea has hit a democratic ceiling and changes are more characteristic of democratic stagnation, rather than outright regression. This took the form of more state involvement (particularly through the Korea Communications Commission or KCC) in media control and less editorial independence among journalists with conservative media owners.[9][10]
Overall, political expression lagged behind comparable democracies.[11][12] Additionally, South Korea has very strict election and campaign finance regulations, that includes no door-to-door canvassing and, consequently, some have cited these regulations as barriers to political expression and free and fair elections.[13][14] These changes have largely attributed to South Korea's weak political party structure that emphasizes leaders and, consequently, hyper-presidentialism. Moreover, a right-left ideological divide has been more deeply entrenched into South Korean political society.[15][16][17] However, South Korea is considered to have a strong civil society or simin sahoe manifested through a large number of civic organizations that prevented further backsliding via the 2016-2017 Candlelight Demonstrations.[18][15] South Korea was also plagued by strong regionalism, dating back to the Silla-Baekje rivalry.[19]
Under more recent administrations such as President Yoon Suk Yeol, South Korea has taken a stance as a "Global Pivotal State," which involves a greater role in East Asia as a democratic power. Despite its own democratic struggles, South Korea has taken an active role on democracy on the global stage, having hosted the 2024 Summit for Democracy and committing to "strengthen coordination on promoting democracy and protecting human rights" at the 2023 Camp David Summit with the U.S. and Japan, bolstering their trilateral relationship.[20]
Remove ads
National government
Summarize
Perspective
Executive branch
The head of state is the president, who is elected by direct popular vote for a single five-year[21] term. The president is Commander-in-Chief of the Republic of Korea Armed Forces and enjoys considerable executive powers.
The president appoints the prime minister with approval of the National Assembly, as well as appointing and presiding over the State Council of chief ministers as the head of government. On 12 March 2004, the executive power of then President Roh Moo-hyun was suspended when the Assembly voted to impeach him and Prime Minister Goh Kun became an Acting President. On 14 May 2004, the Constitutional Court overturned the impeachment decision made by the Assembly and Roh was reinstated.
On 10 May 2022, Yoon Suk Yeol succeeded Moon Jae-in as president of South Korea.[22]
Legislative branch

The National Assembly (Korean: 국회; Hanja: 國會; RR: gukhoe) has 300 members, elected for a four-year term, 253 members in single-seat constituencies and 47 members by proportional representation. The ruling Democratic Party of Korea is the largest party in the Assembly.
Judicial branch
The South Korean judiciary is independent of the other two branches of government, and is composed of two different highest courts. Inferior ordinary courts are under the Supreme Court, whose justices are appointed by the president of South Korea with the consent of the National Assembly. In addition, the Constitutional Court oversees questions of constitutionality, as single and the only court whose justices are appointed by the president of South Korea by equal portion of nomination from the president, the National Assembly, and the Supreme Court Chief justice. South Korea has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction.
Remove ads
Political parties and elections
Summarize
Perspective
South Korea elects on national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The National Assembly (Gukhoe) has 300 members, elected for a four-year term, 253 members in single-seat constituencies and 47 members by proportional representation.
The main two political parties in South Korea are the centrist or centre-left Democratic Party of Korea (lit. 'Together Democratic Party' or DPK) and the conservative People Power Party (PPP), formerly the United Future Party (UFP). These are the dominant forces of South Korean politics at present.
Political nature
South Korea's political history has always been prone to splits from and merges with other parties. One reason is that there is a greater emphasis around the 'politics of the individual' rather than the party; therefore, party loyalty is not strong when disagreements occur. The graph below illustrates the extent of the political volatility within the last 10 years alone. These splits were intensified after the 2016 South Korean political scandal.

Latest elections
Presidential election
In March 2022, Yoon Suk-yeol, the candidate of the conservative opposition People Power Party, won a close election over Democratic Party candidate Lee Jae-myung by the narrowest margin ever. On 10 May 2022, Yoon was sworn in as South Korea's new president.[23]
Legislative election
Remove ads
Political pressure groups and leaders
- Federation of Korean Industries
- Federation of Korean Trade Unions
- Korean Confederation of Trade Unions
- Korean National Council of Churches
- Korean Traders Association
- Korean Veterans' Association
- National Council of Labor Unions
- National Democratic Alliance of Korea
- National Federation of Farmers' Associations
- National Federation of Student Associations
Administrative divisions
One Special City (Teukbyeolsi, Capital City), six Metropolitan Cities (Gwangyeoksi, singular and plural), nine Provinces (Do, singular and plural) and one Special Autonomous City (Sejong City).
- Seoul Teukbyeolsi (서울특별시)
- Busan Gwangyeoksi (부산광역시)
- Daegu Gwangyeoksi (대구광역시)
- Incheon Gwangyeoksi (인천광역시)
- Daejeon Gwangyeoksi (대전광역시)
- Gwangju Gwangyeoksi (광주광역시)
- Ulsan Gwangyeoksi (울산광역시)
- Gyeonggi-do (경기도)
- Gangwon-do (강원도)
- Chungcheongbuk-do (충청북도)
- Chungcheongnam-do (충청남도)
- Jeollabuk-do (전라북도)
- Jeollanam-do (전라남도)
- Gyeongsangbuk-do (경상북도)
- Gyeongsangnam-do (경상남도)
- Jeju Teukbyeoljachi-do (제주특별자치도)
- Sejong Teukbyeol-jachisi (세종특별자치시)
Remove ads
Foreign relations
Summarize
Perspective
South Korea is a member of the
- African Development Bank
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
- Asian Development Bank
- Bank for International Settlements
- Colombo Plan
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
- Food and Agriculture Organization
- Group of 77
- International Atomic Energy Agency
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- International Civil Aviation Organization
- International Criminal Court
- International Chamber of Commerce
- International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement
- International Development Association
- International Energy Agency (observer)
- International Fund for Agricultural Development
- International Finance Corporation
- International Hydrographic Organization
- International Labour Organization
- International Monetary Fund
- International Maritime Organization
- International Mobile Satellite Organization
- Intelsat
- Interpol
- International Olympic Committee
- International Organization for Migration
- International Organization for Standardization
- International Telecommunication Union
- International Trade Union Confederation
- United Nations Mission for the Referendum in Western Sahara
- Non-Aligned Movement (guest)
- Nuclear Suppliers Group
- Organization of American States (observer)
- OECD
- Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (partner)
- United Nations
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- UNESCO
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization
- UN mediation of the Kashmir dispute
- United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia
- United Nations University
- Universal Postal Union
- World Customs Organization
- World Health Organization
- World Intellectual Property Organization
- World Meteorological Organization
- World Tourism Organization
- World Trade Organization
- Zangger Committee
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads