Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tire
Ring-shaped covering that fits around a wheel's rim From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A tire (North American English) or tyre (Commonwealth English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, designed to match the vehicle's weight and the bearing on the surface that it rolls over by exerting a pressure that will avoid deforming the surface.



The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber,[1] natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tread and a body. The tread provides traction while the body provides containment for a quantity of compressed air. Before rubber was developed, tires were metal bands fitted around wooden wheels to hold the wheel together under load and to prevent wear and tear. Early rubber tires were solid (not pneumatic). Pneumatic tires are used on many vehicles, including cars, bicycles, motorcycles, buses, trucks, heavy equipment, and aircraft. Metal tires are used on locomotives and railcars, and solid rubber (or other polymers) tires are also used in various non-automotive applications, such as casters, carts, lawnmowers, and wheelbarrows.
Unmaintained tires can lead to severe hazards for vehicles and people, ranging from flat tires making the vehicle inoperable to blowouts, where tires explode during operation and possibly damage vehicles and injure people. The manufacture of tires is often highly regulated for this reason. Because of the widespread use of tires for motor vehicles, tire waste is a substantial portion of global waste. There is a need for tire recycling through mechanical recycling and reuse, such as for crumb rubber and other tire-derived aggregate, and pyrolysis for chemical reuse, such as for tire-derived fuel. If not recycled properly or burned, waste tires release toxic chemicals into the environment. Moreover, the regular use of tires produces micro-plastic particles that contain these chemicals that both enter the environment and affect human health.[2]
Remove ads
Etymology and spelling
The word tire is a short form of attire, from the idea that a wheel with a tire is a dressed wheel.[3][4]
Tyre is the oldest spelling,[5] and both tyre and tire were used during the 15th and 16th centuries. During the 17th and 18th centuries, tire became more common in print. The spelling tyre did not reappear until the 1840s when the English began shrink-fitting railway car wheels with malleable iron. Nevertheless, many publishers continued using tire. The Times newspaper in London was still using tire as late as 1905.[6] The spelling tyre began to be commonly used in the 19th century for pneumatic tires in the UK. The 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica states that "The spelling 'tyre' is not now accepted by the best English authorities, and is unrecognized in the US",[7] while Fowler's Modern English Usage of 1926 describes that "there is nothing to be said for 'tyre', which is etymologically wrong, as well as needlessly divergent from our own [sc. British] older & the present American usage".[8] However, over the 20th century, tyre became established as the standard British spelling.[4]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective


The earliest tires were bands of leather in Sumer,[9] then iron (later steel) placed on wooden wheels used on carts and wagons. A skilled worker, known as a wheelwright, would cause the tire to expand by heating it in a forge fire, placing it over the wheel, and quenching it, causing the metal to contract back to its original size to fit tightly on the wheel.
The first patent for what appears to be a standard pneumatic tire appeared in 1847 and was lodged by Scottish inventor Robert William Thomson.[10] However, this idea never went into production. The first practical pneumatic tire was made in 1888 on May Street, Belfast, by Scots-born John Boyd Dunlop, owner of one of Ireland's most prosperous veterinary practices. It was an effort to prevent the headaches of his 10-year-old son Johnnie while riding his tricycle on rough pavements. His doctor Sir John Fagan, had prescribed cycling as an exercise for the boy and was a regular visitor. Fagan participated in designing the first pneumatic tires. Cyclist Willie Hume demonstrated the supremacy of Dunlop's tires in 1889, winning the tire's first-ever races in Ireland and then England.[11][12] In Dunlop's tire patent specification dated 31 October 1888, his interest is only in its use in cycles and light vehicles. In September 1890, he was made aware of an earlier development, but the company kept the information to itself.[13] In 1892, Dunlop's patent was declared invalid because of the prior art by forgotten fellow Scot Robert William Thomson of London (patents London 1845, France 1846, USA 1847). However, Dunlop is credited with "realizing rubber could withstand the wear and tear of being a tire while retaining its resilience".[14] John Boyd Dunlop and Harvey du Cros worked through the ensuing considerable difficulties. They employed inventor Charles Kingston Welch and acquired other rights and patents, which allowed them some limited protection of their Pneumatic Tyre business's position. Pneumatic Tyre would become Dunlop Rubber and Dunlop Tyres. The development of this technology hinged on myriad engineering advances, including the vulcanization of natural rubber using sulfur, as well as the development of the "clincher" rim for holding the tire in place laterally on the wheel rim.
Synthetic rubbers were invented in the laboratories of Bayer in the 1920s.[15] Rubber shortages in the United Kingdom during WWII prompted research on alternatives to rubber tires with suggestions including leather, compressed asbestos, rayon, felt, bristles, and paper.[16]
In 1946, Michelin developed the radial tire method of construction. Michelin had bought the bankrupt Citroën automobile company in 1934 to utilize this new technology. Because of its superiority in handling and fuel economy,[17] use of this technology quickly spread throughout Europe and Asia.[18] In the US, the outdated bias-ply tire construction persisted until the Ford Motor Company adopted radial tires in the early 1970s,[19] following a 1968 article in an influential American magazine, Consumer Reports, highlighting the superiority of radial construction.[20][21] The US tire industry lost its market share to Japanese and European manufacturers,[22] which bought out US companies.[23]
Remove ads
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
Tires may be classified according to the type of vehicle they serve. They may be distinguished by the load they carry and by their application, e.g. to a motor vehicle, aircraft, or bicycle.
Automotive
Light–medium duty
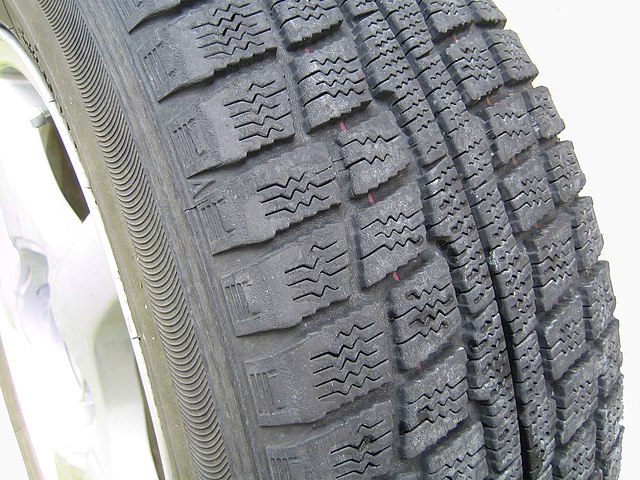



Light-duty tires for passenger vehicles carry loads in the range of 250 to 500 kilograms (550 to 1,100 lb) on the drive wheel. Light-to-medium duty trucks and vans carry loads in the range of 500 to 1,500 kilograms (1,100 to 3,300 lb) on the drive wheel.[25] They are differentiated by speed rating for different vehicles, including (starting from the lowest speed to the highest): winter tires, light truck tires, entry-level car tires, sedans and vans, sport sedans, and high-performance cars.[26] Apart from road tires, there are special categories:
- Snow tires are designed for use on snow and ice. They have a tread design with larger gaps than those on summer tires, increasing traction on snow and ice. Such tires that have passed a specific winter traction performance test are entitled to display a "Three-Peak Mountain Snow Flake" symbol on their sidewalls. Tires designed for winter conditions are optimized to drive at temperatures below 7 °C (45 °F). Some snow tires have metal or ceramic studs that protrude from the tire to increase traction on hard-packed snow or ice. Studs abrade dry pavement, causing dust and creating wear in the wheel path.[27] Regulations that require the use of snow tires or permit the use of studs vary by country in Asia and Europe, and by state or province in North America.
- All-season tires are typically rated for mud and snow (M+S). These tires have tread gaps that are smaller than snow tires and larger than conventional tires. They are quieter than snow tires on clear roads, but less capable on snow or ice.[28]
- All-terrain tires are designed to have adequate traction off-road, yet have benign handling and noise characteristics for highway driving.[29] Such tires are rated better on snow and rain than street tires and "good" on ice, rock, and sand.[30]
- Mud-terrain tires have a deeper, more open tread for good grip in mud, than all-terrain tires, but perform less well on pavement.[31]
- High-performance tires are rated for speeds up to 270 kilometres per hour (168 mph) and ultra-high-performance tires are rated for speeds up to 299 kilometres per hour (186 mph), but have harsher ride characteristics and durability.[32]
- Electric vehicles have unique demands on tires due to the combination of weight (resulting in new load index), higher torque, and requirements for lower rolling resistance.[33]
Other types of light-duty automotive tires include run-flat tires and race car tires:
- Run-flat tires eliminates the need for a spare tire because they can be traveled on at a reduced speed in the event of a puncture, using a stiff sidewall to prevent damage to the tire rim.[34] Vehicles without run-flat tires rely on a spare tire, which may be a compact tire, to replace a damaged tire.[34]
- Race car tires come in three main categories, DOT (street-legal), slick, and rain. Race car tires are designed to maximize cornering and acceleration friction at the expense of longevity. Racing slicks have no tread to maximize contact with the pavement and rain tires have channels to eject water to avoid hydroplaning.[35]
Heavy duty

Heavy-duty tires for large trucks and buses come in a variety of profiles and carry loads in the range of 1,800 to 2,500 kilograms (4,000 to 5,500 lb) on the drive wheel.[25] These are typically mounted in tandem on the drive axle.[34]
- Truck tires come in a variety of profiles that include "low profile" with a section height that is 70 to 45% of the tread width, "wide-base" for heavy vehicles, and a "super-single" tire that has the same total contact pressure as a dual-mounted tire combination.[34]
- Off-road tires are used on construction vehicles, agricultural and forestry equipment, and other applications that take place on soft terrain. The category also includes machinery that travels over hardened surfaces at industrial sites, ports, and airports.[36] Tires designed for soft terrain have a deep, wide tread to provide traction in loose dirt, mud, sand, or gravel.[37]
Other
Aircraft, bicycles, and a variety of industrial applications have distinct design requirements.
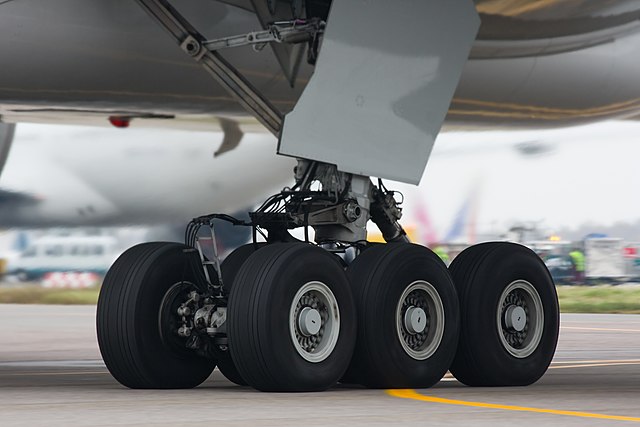

- Aircraft tires are designed for landing on paved surfaces and rely on their landing gear to absorb the shock of landing. To conserve the weight and space required, they are typically small in proportion to the vehicle that they support. Most are radial-ply construction. They are designed for a peak load when the aircraft is stationary, although side loads upon landing are an important factor.[38] Although hydroplaning is a concern for aircraft tires, they typically have radial grooves and no lateral grooves or sipes.[39] Some light aircraft employ large-diameter, low-pressure tundra tires for landing on unprepared surfaces in wilderness areas.[40]
- Bicycle tires may be designed for riding on roads or over unimproved terrain and may be mounted on vehicles with more than two wheels. There are three main types: clincher, wired and tubular.[41] Most bicycle tires are clincher and have a bead that presses against the wheel rim. An inner tube provides the air pressure and the contact pressure between the bead and wheel rim.[42]
- Industrial tires support such vehicles as forklifts, tractors, excavators, road rollers, and bucket loaders. Those used on smooth surfaces have a smooth tread, whereas those used on soft surfaces typically have large tread features.[43] Some industrial tires are solid or filled with foam.[44]
- Motorcycle tires provide traction, resisting wear, absorbing surface irregularities, and allow the motorcycle to turn via countersteering. The two tires' contact with the ground affects safety, braking, fuel economy, noise, and rider comfort.[45][self-published source?]
Remove ads
Construction types
Summarize
Perspective
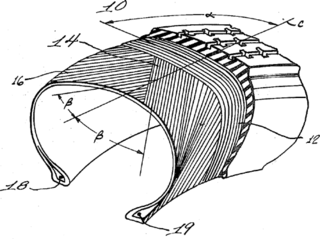
Tire construction spans pneumatic tires used on cars, trucks, and aircraft, but also includes non-automotive applications with slow-moving, light-duty, or railroad applications, which may have non-pneumatic tires.
Automotive
Following the 1968 Consumer Reports announcement of the superiority of the radial design, radial tires began an inexorable climb in market share, reaching 100% of the North American market in the 1980s.[20] Radial tire technology is now the standard design for essentially all automotive tires, but other methods have been used.[26]
Radial (or radial-ply) tire construction utilizes body ply cords extending straight across the tread from bead to bead—so that the cords are laid at approximately right angles to the centerline of the tread, and parallel to one another—as well as stabilizer belts directly beneath the tread. The plies are generally made of nylon, polyester, or steel, and the belts of steel, fiberglass, or Kevlar.[46][47] The tire's footprint, wider than a bias tire's, and flexible sidewalls provide a better grip in turns, and its circumferential belts stabilize it. The advantages of this construction over that of a bias tire are many, including longer tread life, better steering control, lower rolling resistance, improved fuel economy, more uniform wear, higher heat resistance, fewer blowouts, and a steadier, more comfortable ride at speed. Disadvantages, besides a higher cost than that of bias tires, are a harder ride at low speeds and generally worse performance on rough terrain.[48][49][26] Radial tires are also seldom seen in diameters of greater than 42 inches, as such tires are difficult to make.[50]
Bias tire (bias-ply, or cross-ply) construction utilizes body ply cords that extend diagonally from bead to bead, usually at angles in the range of 30 to 40 degrees from the direction of travel.[51] Successive plies are laid at opposing angles, forming a crisscross pattern to which the tread is applied. Such a design is resistant to sidewall deformation and punctures (and to punctures’ expansion, or "torque splitting") and therefore durable in severe use.[52] Since the tread and sidewalls share their casing plies, the tire body flexes as a whole, providing the main advantage of this construction, better traction and smoother motion on uneven surfaces, with a greater tendency to conform to rocky ground and throw off mud and clay, especially because the rubber is usually of a softer compound than that used on radial tires. However, this conformity increases a bias tire's rolling resistance, and its stiffness allows less control, traction, and comfort at higher speeds, while shear between its overlapping plies causes friction that generates heat.[48][53][54][26] Still, bias tires benefit from simpler structure and so cost less than like-size radials, and they remain in use on heavy equipment and off-road vehicles, although the earthmoving market has shifted to radials.[26][55]
A belted bias tire starts with two or more bias plies to which stabilizer belts are bonded directly beneath the tread. This construction provides a smoother ride that is similar to the bias tire, while lessening rolling resistance because the belts increase tread stiffness. The design was introduced by Armstrong, while Goodyear made it popular with the "Polyglas" trademark tire featuring a polyester carcass with belts of fiberglass.[56] The "belted" tire starts two main plies of polyester, rayon, or nylon annealed as in conventional tires, and then placed on top are circumferential belts at different angles that improve performance compared to non-belted bias tires. The belts may be fiberglass or steel.[56]
Other
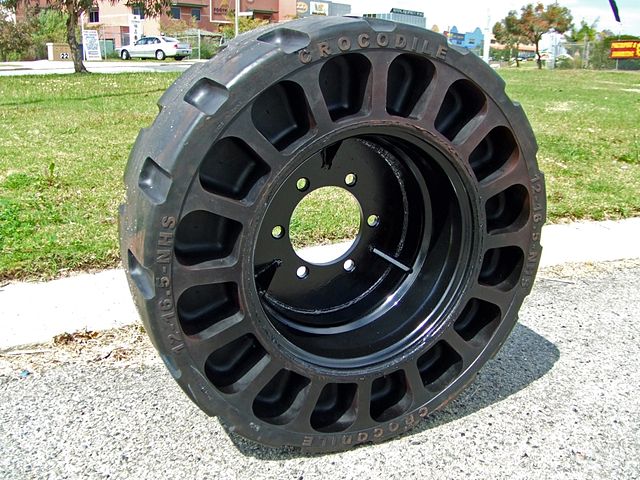

Tubeless tires are pneumatic tires that do not require a separate inner tube.
Semi-pneumatic tires have a hollow center, but they are not pressurized. They are lightweight, low-cost, puncture-proof, and provide cushioning.[57] These tires often come as a complete assembly with the wheel and even integral ball bearings. They are used on lawn mowers, wheelchairs, and wheelbarrows. They can also be rugged, typically used in industrial applications,[58] and are designed to not pull off their rim under use.
An airless tire is a non-pneumatic tire that is not supported by air pressure. They are most commonly used on small vehicles, such as golf carts, and on utility vehicles in situations where the risk of puncture is high, such as on construction equipment. Many tires used in industrial and commercial applications are non-pneumatic, and are manufactured from solid rubber and plastic compounds via molding operations. Solid tires include those used for lawnmowers, skateboards, golf carts, scooters, and many types of light industrial vehicles, carts, and trailers. One of the most common applications for solid tires is for material handling equipment (forklifts). Such tires are installed utilizing a hydraulic tire press.
Wooden wheels for horse-drawn vehicles usually have a wrought iron tire. This construction was extended to wagons on horse-drawn tramways, rolling on granite setts or cast iron rails.
The wheels of some railway engines and older types of rolling stock are fitted with railway tires to prevent the need to replace the entirety of a wheel. The tire, usually made of steel, surrounds the wheel and is primarily held in place by interference fit.
Aircraft tires may operate at pressures that exceed 1,400 kilopascals (14 bar; 200 psi).[59] Some aircraft tires are inflated with nitrogen to "eliminate the possibility of a chemical reaction between atmospheric oxygen and volatile gases from the tire inner liner producing a tire explosion".[60]
Remove ads
Manufacturing
Summarize
Perspective
Pneumatic tires are manufactured in about 450 tire factories around the world. Tire production starts with bulk raw materials such as rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produces numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured. Many kinds of rubber are used, the most common being styrene-butadiene copolymer.[61]
Forecasts for the global automotive tire market indicate continued growth through 2027. Estimates put the value of worldwide sales volume around $126 billion in 2022, it is expected to reach the value of over $176 billion by 2027.[62] Production of tires is also experiencing growth. In 2015, the US manufactured almost 170 million tires.[63] Over 2.5 billion tires are manufactured annually, making the tire industry a major consumer of natural rubber. It was estimated that for 2019 onwards, at least 3 billion tires would be sold globally every year.[64] However, other estimates put worldwide tire production of 2,268 million in 2021 and is predicted to reach 2,665 million tires by 2027.[65]
As of 2011, the top three tire manufacturing companies by revenue were Bridgestone (manufacturing 190 million tires), Michelin (184 million), Goodyear (181 million); they were followed by Continental, and Pirelli.[66][67] The Lego group produced over 318 million toy tires in 2011 and was recognized by Guinness World Records as having the highest annual production of tires by any manufacturer.[68][69]
Components
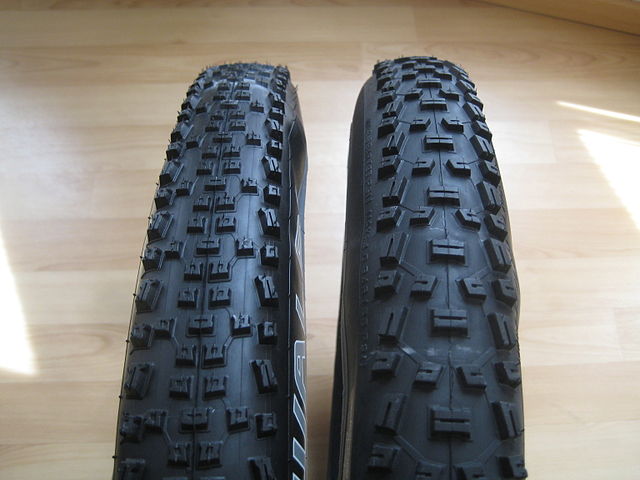



A tire comprises several components: the tread, bead, sidewall, shoulder, and ply.
Tread
The tread is the part of the tire that comes in contact with the road surface. The portion that is in contact with the road at a given instant in time is the contact patch. The tread is a thick rubber, or rubber/composite compound formulated to provide an appropriate level of traction that does not wear away too quickly.[70]
The tread pattern is characterized by a system of circumferential grooves, lateral sipes, and slots for road tires[26] or a system of lugs and voids for tires designed for soft terrain or snow. Grooves run circumferentially around the tire and are needed to channel away water. Lugs are that portion of the tread design that contacts the road surface. Grooves, sipes, and slots allow tires to evacuate water.
The design of treads and the interaction of specific tire types with the roadway surface affects roadway noise, a source of noise pollution emanating from moving vehicles. These sound intensities increase with higher vehicle speeds.[71] Tires treads may incorporate a variety of distances between slots (pitch lengths) to minimize noise levels at discrete frequencies. Sipes are slits cut across the tire, usually perpendicular to the grooves, which allow the water from the grooves to escape sideways and mitigate hydroplaning.[26]
Different tread designs address a variety of driving conditions. As the ratio of tire tread area to groove area increases, so does tire friction on dry pavement, as seen on Formula One tires, some of which have no grooves. High-performance tires often have smaller void areas to provide more rubber in contact with the road for higher traction, but may be compounded with softer rubber that provides better traction, but wears quickly.[72] Mud and snow (M&S) tires employ larger and deeper slots to engage mud and snow.[26] Snow tires have still larger and deeper slots that compact snow and create shear strength within the compacted snow to improve braking and cornering performance.[73]
Wear bars (or wear indicators) are raised features located at the bottom of the tread grooves that indicate the tire has reached its wear limit. When the tread lugs are worn to the point that the wear bars connect across the lugs, the tires are fully worn and should be taken out of service, typically at a remaining tread depth of 1.6 millimetres (0.063 in).[74]
Other
The tire bead is the part of the tire that contacts the rim on the wheel. This essential component is constructed with robust steel cables encased in durable, specially formulated rubber designed to resist stretching. The precision of the bead's fit is crucial, as it seals the tire against the wheel, maintaining air pressure integrity and preventing any loss of air. The bead's design ensures a secure, non-slip connection, preventing the tire from rotating independently from the wheel during vehicle motion. Additionally, the interplay between the bead's dimensions and the wheel's width significantly influences the vehicle's steering responsiveness and stability, as it helps to maintain the tire's intended shape and contact with the road.
The sidewall is that part of the tire, or bicycle tire, that bridges between the tread and bead. The sidewall is largely rubber but reinforced with fabric or steel cords that provide for tensile strength and flexibility. The sidewall contains air pressure and transmits the torque applied by the drive axle to the tread to create traction but supports little of the weight of the vehicle, as is clear from the total collapse of the tire when punctured.
Sidewalls are molded with manufacturer-specific detail, government-mandated warning labels, and other consumer information.[75][76]
Sidewall may also have sometimes decorative ornamentation that includes whitewall or red-line inserts as well as tire lettering.[77]
The shoulder is that part of the tire at the edge of the tread as it makes the transition to the sidewall.[78]
Plies are layers of relatively inextensible cords embedded in the rubber[79] to hold its shape by preventing the rubber from stretching in response to the internal pressure. The orientations of the plies play a large role in the performance of the tire and are one of the main ways that tires are categorized.[80]
Blems
Blem (short for "blemished") is a term used for a tire that failed inspection during manufacturing - but only for superficial/cosmetic/aesthetic reasons. For example, a tire with white painted lettering which is smudged or incomplete might be classified as a "blem". Blem tires are fully functional and generally carry the same warranty as flawless tires - but are sold at a discount.[81]
Materials
The materials of modern pneumatic tires can be divided into two groups, the cords that make up the ply and the elastomer which encases them.
Cords
The cords, which form the ply and bead and provide the tensile strength necessary to contain the inflation pressure, can be composed of steel, natural fibers such as cotton or silk, or synthetic fibers such as nylon or kevlar. Good adhesion between the cords and the rubber is important. To achieve this the steel cords are coated in a thin layer of brass,[82] various additives will also be added to the rubber to improve binding, such as resorcinol/HMMM mixtures.
Elastomer

The elastomer, which forms the tread and encases the cords to protect them from abrasion and hold them in place, is a key component of pneumatic tire design. It can be composed of various composites of rubber material – the most common being styrene-butadiene copolymer – with other chemical compounds such as silica and carbon black.
Optimizing rolling resistance in the elastomer material is a key challenge for reducing fuel consumption in the transportation sector. It is estimated that passenger vehicles consume approximately 5%–15% of their fuel to overcome rolling resistance, while the estimate is understood to be higher for heavy trucks.[83] However, there can be a trade-off between rolling resistance and wet traction and grip, based on the viscoelastic properties of the rubber compound. A low dissipation factor, which is often written as the tangent of the phase angle delta (tan(δ)), reduces rolling resistance, whereas a high tan(δ) can improve wet traction and grip. Fortunately, this tradeoff is not inherent: rolling resistance is affected by tan(δ) at low frequencies (on the order of 100 Hz) whereas the improvement in traction comes from high tan(δ) at much higher frequencies. Historically, direct measurement of tan(δ) at high frequencies was difficult, and it became common to instead use measured low-frequency tan(δ) at a low temperature (0 °C) as a predictor of wet traction because of its correlation to high-frequency tan(δ). For rolling resistance, tan(δ) value at 60 °C is directly relevant and often used as a predictor of low rolling resistance. [84] [31]
Designing an elastomer material that can achieve both high wet traction and low rolling resistance is key in achieving safety and fuel efficiency in the transportation sector. More recent research has found that compounds using dual-phase fillers exhibit a poor correlation between low-temperature tan(δ) and wet traction, indicating an opportunity to circumvent the tradeoff assumed in the traditional approach. New approaches to understanding wet traction incorporate consideration of the effect of water lubrication on the interactions between surfaces and have pointed the way to developing compounds that can provide high wet traction and low rolling resistance.[85]
The most common elastomer material used today is a styrene-butadiene copolymer. It combines the properties of polybutadiene, which is a highly rubbery polymer (Tg = −100 °C) having high hysteresis and thus offering good wet grip properties, with the properties of polystyrene, which is a glassy polymer (Tg = 100 °C) having low hysteresis and thus offering low rolling resistance in addition to wear resistance. Therefore, the ratio of the two monomers in the styrene-butadiene copolymer is considered key in determining the glass transition temperature of the material, which is correlated to its grip and resistance properties.[86]
Non-exhaust emissions of particulate matter, generated by the wearing down of brakes, clutches, tires, and road surfaces, as well as by the suspension of road dust, constitute a little-known but rising share of emissions from road traffic and significantly harm public health.[87]
Remove ads
On the wheel
Summarize
Perspective

Associated components of tires include the wheel on which it is mounted, the valve stem through which air is introduced, and, for some tires, an inner tube that provides the airtight means for maintaining tire pressure.
- Wheel: Pneumatic tires are mounted onto wheels that most often have integral rims on their outer edges to hold the tire. Automotive wheels are typically made from pressed and welded steel, or a composite of lightweight metal alloys, such as aluminum or magnesium. There are two aspects to how pneumatic tires support the rim of the wheel on which they are mounted.[88] First, the tension in the cords pull on the bead uniformly around the wheel, except where it is reduced above the contact patch.[89] Second, the bead transfers that net force to the rim.[90][89] Tires are mounted on the wheel by forcing its beads into the channel formed by the wheel's inner and outer rims.[91][92]
- Valve stem: Pneumatic tires receive their air through a valve stem—a tube made of metal or rubber, with a check valve, typically a Schrader valve on automobiles and most bicycle tires, or a Presta valve on high-performance bicycles. They mount directly to the rim, in the case of tubeless tires, or are an integral part of the inner tube. Most modern passenger vehicles are now required to have a tire pressure monitoring system which usually consists of a valve stem attached to an electronic module.[34]
- Inner tube: Most bicycle tires, many motorcycle tires, and many tires for large vehicles such as buses, heavy trucks, and tractors are designed for use with inner tubes. Inner tubes are torus-shaped balloons made from an impermeable material, such as soft, elastic synthetic rubber, to prevent air leakage. The inner tubes are inserted into the tire and inflated to retain air pressure. Large inner tubes can be reused for other purposes, such as swimming and rafting (see swim ring), tubing (recreation), sledding, and skitching. Purpose-built inflatable tori are also manufactured for these uses, offering a choice of colors, fabric covering, handles, decks, and other accessories, and eliminating the protruding valve stem.
Remove ads
Performance characteristics
Summarize
Perspective

The interactions of a tire with the pavement are complex. A commonly used (empirical) model of tire properties is Pacejka's "Magic Formula".[93] Some are explained below, alphabetically, by section.
Dynamics
- Balance: Wheel-tire combinations require an even distribution of mass around their circumferences to maintain tire balance, while turning at speed. Tires are checked at the point of manufacture for excessive static imbalance and dynamic imbalance using automatic tire balance machines. Tires are checked again in the auto assembly plant or tire retail shop after mounting the tire to the wheel. Assemblies that exhibit excessive imbalance are corrected by applying balance weights to the wheels to counteract the tire/wheel imbalance. An alternative method to tire balancing is the use of internal tire balancing agents. These agents take advantage of centrifugal force and inertia to counteract the tire imbalance.[94] To facilitate proper balancing, most high-performance tire manufacturers place red and yellow marks on the sidewalls to enable the best possible match-mounting of the tire/wheel assembly. There are two methods of match-mounting high-performance tire-to-wheel assemblies using these red (uniformity) or yellow (weight) marks.[95]
- Centrifugal growth: A tire rotating at higher speeds tends to develop a larger diameter, due to centrifugal forces that force the tread rubber away from the axis of rotation. This may cause speedometer error. As the tire diameter grows, the tire width decreases. This centrifugal growth can cause rubbing of the tire against the vehicle at high speeds. Motorcycle tires are often designed with reinforcements aimed at minimizing centrifugal growth.[26]
- Pneumatic trail: Pneumatic trail of a tire is the trail-like effect generated by compliant tires rolling on a hard surface and subject to side loads, as in a turn. More technically, it is the distance that the resultant force of side-slip occurs behind the geometric center of the contact patch.[96]
- Slip angle: Slip angle or sideslip angle is the angle between a rolling wheel's actual direction of travel and the direction towards which it is pointing (i.e., the angle of the vector sum of wheel translational velocity and sideslip velocity ).[26]
- Relaxation length: Relaxation length is the delay between when a slip angle is introduced and when the cornering force reaches its steady-state value.[26]
- Spring rate: Vertical stiffness, or spring rate, is the ratio of vertical force to vertical deflection of the tire, and it contributes to the overall suspension performance of the vehicle. In general, the spring rate increases with inflation pressure.[97]
- Stopping distance: Performance-oriented tires have a tread pattern and rubber compounds designed to grip the road surface, and so usually have a slightly shorter stopping distance. However, specific braking tests are necessary for data beyond generalizations.[26]
Forces
- Camber thrust: Camber thrust and camber force are the force generated perpendicular to the direction of travel of a rolling tire due to its camber angle and finite contact patch.[26]
- Circle of forces: The circle of forces, traction circle, friction circle, or friction ellipse is a useful way to think about the dynamic interaction between a vehicle's tire and the road surface.[98]
- Contact patch: The contact patch, or footprint, of the tire, is the area of the tread that is in contact with the road surface. This area transmits forces between the tire and the road via friction. The length-to-width ratio of the contact patch affects steering and cornering behavior.[26]
- Cornering force: Cornering force or side force is the lateral (i.e. parallel to the road surface) force produced by a vehicle tire during cornering.[26]
- Dry traction: Dry traction is the measure of the tire's ability to deliver traction, or grip, under dry conditions. Dry traction is a function of the tackiness of the rubber compound.[26]
- Force variation: The tire tread and sidewall elements undergo deformation and recovery as they enter and exit the footprint. Since the rubber is elastomeric, it is deformed during this cycle. As the rubber deforms and recovers, it imparts cyclical forces into the vehicle. These variations are collectively referred to as tire uniformity. Tire uniformity is characterized by radial force variation (RFV), lateral force variation (LFV), and tangential force variation. Radial and lateral force variation is measured on a force variation machine at the end of the manufacturing process. Tires outside the specified limits for RFV and LFV are rejected. Geometric parameters, including radial runout, lateral runout, and sidewall bulge, are measured using a tire uniformity machine at the tire factory at the end of the manufacturing process as a quality check.[26]
- Rolling resistance: Rolling resistance is the resistance to rolling caused by deformation of the tire in contact with the road surface. As the tire rolls, the tread enters the contact area and is deformed flat to conform to the roadway. The energy required to make the deformation depends on the inflation pressure, rotating speed, and numerous physical properties of the tire structure, such as spring force and stiffness. Tire makers seek lower rolling resistance tire constructions to improve fuel economy in cars and especially trucks, where rolling resistance accounts for a high proportion of fuel consumption. Pneumatic tires also have a much lower rolling resistance than solid tires. Because the internal air pressure acts in all directions, a pneumatic tire is able to "absorb" bumps in the road as it rolls over them without experiencing a reaction force opposite to the direction of travel, as is the case with a solid (or foam-filled) tire.[26]
- Self aligning torque: Self-aligning torque, also known as the aligning torque, SAT or Mz, is the torque that a tire creates as it rolls along that tends to steer it, i.e. rotate it around its vertical axis.[26]
- Wet traction: Wet traction is the tire's traction, or grip, under wet conditions. Wet traction is improved by the tread design's ability to channel water out of the tire footprint and reduce hydroplaning. However, tires with a circular cross-section, such as those found on racing bicycles, when properly inflated have a sufficiently small footprint to not be susceptible to hydroplaning. For such tires, it is observed that fully slick tires will give superior traction on both wet and dry pavement.[99]
Load
- Load sensitivity: Load sensitivity is the behavior of tires under load. Conventional pneumatic tires do not behave as classical friction theory would suggest. Namely, the load sensitivity of most real tires in their typical operating range is such that the coefficient of friction decreases as the vertical load, Fz, increases.[26]
- Work load: The work load of a tire is monitored so that it is not put under undue stress, which may lead to its premature failure.[100] Work load is measured in Ton Kilometer Per Hour (TKPH). The measurement's appellation and units are the same. The recent shortage and increasing cost of tires for heavy equipment has made TKPH an important parameter in tire selection and equipment maintenance for the mining industry. For this reason, manufacturers of tires for large earth-moving and mining vehicles assign TKPH ratings to their tires based on their size, construction, tread type, and rubber compound.[101][102] The rating is based on the weight and speed that the tire can handle without overheating and causing it to deteriorate prematurely. The equivalent measure used in the United States is Ton Mile Per Hour (TMPH).
Wear
Tire wear is a major source of rubber pollution. A concern hereby is that vehicle tire wear pollution is unregulated, unlike exhaust emissions.[103]

- Tread wear
- This occurs through normal contact with roads or terrain; there are several types of abnormal tread wear. Poor wheel alignment can cause excessive wear of the innermost or outermost ribs. Gravel roads, rocky terrain, and other rough terrain cause accelerated wear. Over-inflation above the sidewall maximum can cause excessive wear to the center of the tread. Modern tires have steel belts built in to prevent this. Under-inflation causes excessive wear to the outer ribs. Unbalanced wheels can cause uneven tire wear, as the rotation may not be perfectly circular. Tire manufacturers and car companies have mutually established standards for tread wear testing that include measurement parameters for tread loss profile, lug count, and heel-toe wear.[26]

- Tread wear indicators (T.W.I.)
- Raised bars in the tread channels, which indicate that the tread is becoming worn and therefore unsafe. Indicators have been required on all new tires since 1968 in the US.[104] In many countries the Highway Code forbids driving on public roads when the contact surface is flush with any of these bars - this is often defined when the groove depth is approximately 1.5 or 1.6 mm (2/32 inch). TWI can also be used to refer to small arrows or icons on the tire sidewall, indicating the location of the raised wear bars.
- Damage by aging
- Tire aging or "thermo-oxidative degradation" can be caused by time, ambient and operating temperatures, partial pressure of O2 in a tire, flex fatigue, or construction and compounding characteristics. For example, prolonged UV exposure leads to rubber's chemicals warping, potentially causing dry rot. Various storage methods may slow the aging process, but will not eliminate tire degradation.[105]
Remove ads
Sizes, codes, standards, and regulatory agencies
Summarize
Perspective

Automotive tires have a variety of identifying markings molded onto the sidewall as a tire code. They denote size, rating, and other information pertinent to that individual tire.
Americas
The National Highway and Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is a U.S. government body within the Department of Transportation (DOT) tasked with regulating automotive safety in the United States.[106] NHTSA established the Uniform Tire Quality Grading System (UTQG), is a system for comparing the performance of tires according to the Code of Federal Regulations 49 CFR 575.104; it requires labeling of tires for tread wear, traction, and temperature. The DOT Code is an alphanumeric character sequence molded into the sidewall of the tire and allows the identification of the tire and its age. The code is mandated by the U.S. Department of Transportation[106] but is used worldwide.[107] The DOT Code is also useful in identifying tires subject to product recall[108] or at end of life due to age. The Tire and Rim Association (T&RA) is a voluntary U.S. standards organization that promotes the interchangeability of tires, rims, and allied parts. Of particular interest, they publish key tire dimensions, rim contour dimensions, tire valve dimension standards, and load/inflation standards.
The National Institute of Metrology Standardization and Industrial Quality (INMETRO) is the Brazilian federal body responsible for automotive wheel and tire certification.[109]
Europe
The European Tyre and Rim Technical Organisation (ETRTO) is the European standards organization "to establish engineering dimensions, load/pressure characteristics and operating guidelines".[110] All tires sold for road use in Europe after July 1997 must carry an E-mark. The mark itself is either an upper case "E" or lower case "e" – followed by a number in a circle or rectangle, followed by a further number. An (upper case) "E" indicates that the tire is certified to comply with the dimensional, performance, and marking requirements of ECE regulation 30. A (lowercase) "e" indicates that the tire is certified to comply with the dimensional, performance, and marking requirements of Directive 92/23/EEC. The number in the circle or rectangle denotes the country code of the government that granted the type approval. The last number outside the circle or rectangle is the number of the type approval certificate issued for that particular tire size and type.[111]
The British Rubber Manufacturers Association (BRMA) recommended practice, issued June 2001, states, "BRMA members strongly recommend that unused tires should not be put into service if they are over six years old and that all tires should be replaced ten years from the date of their manufacture."[112]
Asia
The Japanese Automobile Tire Manufacturers Association (JATMA) is the Japanese standards organization for tires, rims, and valves.[113] It performs similar functions as the T&RA and ETRTO.
The China Compulsory Certification (CCC) is a mandatory certification system concerning product safety in China that went into effect in August 2002. The CCC certification system is operated by the State General Administration for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China (AQSIQ) and the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA).[114]
Remove ads
Maintenance
Summarize
Perspective

To maintain tire health, several actions are appropriate, tire rotation, wheel alignment, and, sometimes, retreading the tire.
- Rotation: Tires may exhibit irregular wear patterns once installed on a vehicle and partially worn. Front-wheel drive vehicles tend to wear the front tires at a greater rate compared to the rear tires. Tire rotation is moving the tires to different car positions, such as front-to-rear, in order to even out the wear, with the objective of extending the life of the tire.[115]
- Alignment: Wheel alignment helps prevent wear due to rotation in a direction other than the path of the vehicle. When mounted on the vehicle, the wheel and tire may not be perfectly aligned to the direction of travel, and therefore may exhibit irregular wear. If the discrepancy in alignment is large, then the irregular wear will become substantial if left uncorrected. Wheel alignment is the procedure for checking and correcting this condition through adjustment of camber, caster, and toe angles. The adjustment of the angles should be done as per the OEM specifications.[116]
Inflation

Inflation is key to proper wear and rolling resistance of pneumatic tires. Many vehicles have monitoring systems to assure proper inflation. Most passenger cars are advised to maintain a tire pressure within the range of 220 to 240 kilopascals (32 to 35 psi) when the tires are not warmed by driving.[117][118]
- Specification— Vehicle manufacturers provide tire specifications, including a recommended cold inflation pressure, to ensure safe operation within the designated load rating and vehicle loading capacity. While many tires feature a maximum pressure rating stamped on them, passenger vehicles and light trucks typically include inflation guidance on a decal located just inside the driver's door and in the vehicle owner's handbook.[119]
- Ground contact: The tire contact patch is readily changed by both over- and underinflation. Overinflation may increase the wear on the center contact patch, and underinflation will cause a concave tread, resulting in less center contact, though the overall contact patch will still be larger.[120] Most modern tires will wear evenly at high tire pressures, but will degrade prematurely if underinflated. Increased tire pressure may decrease rolling resistance, and may also result in shorter stopping distances[121] If tire pressure is too low, the tire contact patch is greatly increased. This increases rolling resistance, tire flexing, and friction between the road and the tire. Under-inflation can lead to tire overheating, premature tread wear, and tread separation in severe cases.[122]
- Monitoring: Tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are electronic systems that monitor the tire pressures on individual wheels on a vehicle and alert the driver when the pressure goes below a warning limit. There are several types of designs to monitor tire pressure. Some actually measure the air pressure, and some make indirect measurements, such as gauging when the relative size of the tire changes due to lower air pressure.
Remove ads
Hazards
Summarize
Perspective



Tire hazards may occur from failure of the tire, itself, or from loss of traction on the surface over which it is rolling. Structural failures of a tire can result in flat tires or more dangerous blowouts. Some of these failures can be caused by manufacture error and may lead to recalls, such as the widespread Firestone tire failures on Ford vehicles that lead to the Firestone and Ford tire controversy in the 1990s.
Tire failure
Tires may fail for any of a variety of reasons, including:[123]
- Belt separation which may be belt-to-belt, tread and belt, or separation of the edge of the belt. Belt-to-belt separation may occur having the tire deflect too much, from high pavement temperatures, road hazard impacts, or other causes that have to do with maintenance and storage.
- Non-belt separations include those at the tire tread, in the bead area, in the lower sidewall, between reinforcing plies, and of the reinforcing steel or fabric materials.
- Other types of failure include run-flat damage, chemical degradation, cracking, indentations and bulges.
Vehicle operation failures
- Melting rubber: As tire rubber compounds heat, owing to the friction of stopping, cornering, or accelerating, they may begin to melt, lubricate the tire-road contact area, and become deposited on the pavement. This effect is stronger with increased ambient temperature.[26]
- Hydroplaning: Motor vehicles or aircraft tires passing over a wet pavement may lose contact with sufficient speed or water depth for a given tread design. In this case, the tire contact area is riding on a film of water and loses the friction needed for braking or cornering and begins to hydroplane (or aquaplane). Hydroplaning may occur as dynamic hydroplaning where standing water is present with a depth of at least 3 millimetres (0.12 in) above the texture of the pavement and speed is sustained above a threshold level. It may also occur as viscous hydroplaning whereby tire rubber melts for a brief interval and causes slippage. This may leave deposits of rubber on a runway as airplanes land.[124] Dynamic hydroplaning causes decreased friction and contact with increased tire speed.[125]
- Snow: The degree to which a tire can maintain traction in snow depends on its ability to compact snow, which material then develops strength against slippage along a shear plane parallel to the contact area of the tire on the ground.[126] At the same time, the bottom of the tire treads compress the snow on which they are bearing, also creating friction. The process of compacting snow within the treads requires it to be expelled in time for the tread to compact snow anew on the next rotation. The compaction/contact process works both in the direction of travel for propulsion and braking, but also laterally for cornering.[73]
- Ice: Ice is typically close to its melting point when a tire travels over it. This, combined with a smooth texture, promotes a low coefficient of friction and reduced traction during braking, cornering or acceleration.[26]
- Soft ground: Soil can become lubricated with water, which reduces its ability to maintain shear strength when a tire tries to apply force in acceleration, braking, or cornering. Dry sand also has low shear strength, owing to poor cohesiveness among sand particles.[127]
Remove ads
Health impacts
Tires contain a number of trace toxic chemicals including heavy metals and chemical agents used to increase the durability of the tires.[2] These typically include polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, benzothiazoles, isoprene and heavy metals such as zinc and lead.[2]
As tires are used for vehicle operations, the natural wear of the tire leaves microfine particles equivalent to PM0.1, PM2.5, and PM10 as tire residue.[2] This residue accumulates near roadways and vehicle use areas, but also will travel into the environment through surface runoff.[2] Both humans and animals are exposed to these chemicals at the sites of accumulation (i.e. walking on the road surface) and through bioaccumulation in natural environments and foodchains.[2] A 2023 literature review from Imperial College London, warned of both the toxic chemicals and microplastics produced from tire wear as having potential widespread serious environmental and health consequences.[2]
Moreover, burning of tires releases these chemicals as air pollutants that can harm first responders and leaves toxic residues that endanger local communities.[128]
Remove ads
End of use
Summarize
Perspective

Once tires are discarded, they are considered scrap tires. Scrap tires are often re-used for things from bumper car barriers to weights to hold down tarps. Tires are not desired at landfills, due to their large volumes and 75% void space, which quickly consumes valuable space. Rubber tires are likely to contain some traces of heavy metals or other serious pollutants, but these are tightly bonded within the actual rubber compound so they are unlikely to be hazardous unless the tire structure is seriously damaged by fire or strong chemicals.[129] Some facilities are permitted to recycle scrap tires by chipping and processing them into new products or selling the material to licensed power plants for fuel. Some tires may also be retreaded for re-use.
Environmental issues

Americans generate about 285 million scrap tires per year.[130] Many states regulate the number of scrap tires that can be held at any site out of concern with dumping, fire hazards, and mosquitoes. In the past, millions of tires were simply discarded into open fields. Outdoor tire heaps create breeding grounds for mosquitoes, which are a nuisance and may spread disease, since the tires often hold water inside and remain warm enough for mosquito breeding. It also creates a fire hazard. Tires very seldom catch fire inadvertently, requiring a temperature of 400 °C (752 °F) to combust,[131] but once burning are hard to extinguish, for a large tire pile has ample fuel and water used to douse fires does not adequately penetrate or cool them. Some tire fires have burned for months, sometimes liquefying and releasing hydrocarbons and other contaminants to the ground and even groundwater, and black smoke, an air pollutant that is a hazard to downwind properties, to the air.
The use of scrap tire chips for landscaping has become controversial because of the leaching of metals and other contaminants from the tire pieces. Zinc is concentrated (up to 2% by weight) to levels high enough to be highly toxic to aquatic life and plants.[132] Of particular concern is evidence that some of the compounds that leach from tires into the water contain hormone disruptors and cause liver lesions.[133]
Tires are a major source of microplastic pollution, found in a 2020 study to contribute 78% of the total mass of microplastics found in the ocean.[134][135] The commonly used compound 6PPD-quinone, found entering stormwater runoff via tire-wear particles, has been identified as toxic to coho salmon, brook trout, and rainbow trout.[136]
Retreading
Tires that are fully worn can be retreaded, re-manufactured to replace the worn tread.[137] This is known as retreading or recapping, a process of buffing away the worn tread and applying a new tread.[138] There are two main processes used for retreading tires, called mold-cure and pre-cure methods. Both processes start with the inspection of the tire, followed by non-destructive inspection method such as shearography[139] to locate non-visible damage and embedded debris and nails. Some casings are repaired and some are discarded. Tires can be retreaded multiple times if the casing is in usable condition. Tires used for short delivery vehicles are retreaded more than long haul tires over the life of the tire body. Casings fit for retreading have the old tread buffed away to prepare for retreading.[140]
During the retreading process, retread technicians must ensure the casing is in the best condition possible to minimize the possibility of a casing failure. Casings with problems such as capped tread, tread separation, irreparable cuts, corroded belts or sidewall damage, or any run-flat or skidded tires, will be rejected. The mold cure method involves the application of raw rubber on the previously buffed and prepared casing, which is later cured in matrices. During the curing period, vulcanization takes place, and the raw rubber bonds to the casing, taking the tread shape of the matrix. On the other hand, the pre-cure method involves the application of a ready-made tread band on the buffed and prepared casing, which later is cured in an autoclave so that vulcanization can occur.[140]
Recycling
Tires can be recycled into, among other things, the hot melt asphalt, typically as crumb rubber modifier—recycled asphalt pavement (CRM—RAP),[141][142] and as an aggregate in portland cement concrete.[143] Shredded tires can create rubber mulch on playgrounds to diminish fall injuries.[144] There are some "green" buildings that are being made both private and public buildings that are made from old tires.[145]
The tire pyrolysis method for recycling used tires is a technique that heats whole or shredded tires in a reactor vessel containing an oxygen-free atmosphere and a heat source. In the reactor, the rubber is softened after which the rubber polymers continuously break down into smaller molecules.
Other uses
Other downstream uses have been developed for worn-out tires, including:
- Building elements: Tires filled with earth have been used as garden containers[146] house foundations,[147] bullet-proof walls[148] and to prevent soil erosion in flood plains.[149] Tire walls are a common feature of motor racing circuits for safety.
- Recreational equipment: Used tires are employed as exercise equipment for athletic programs such as American football.[150] One classic conditioning drill that hones players' speed and agility is the "Tire Run" where tires are laid out side by side, with each tire on the left a few inches ahead of the tire on the right in a zigzag pattern. Athletes then run through the tire pattern by stepping in the center of each tire. The drill forces athletes to lift their feet above the ground higher than normal to avoid tripping on the tires.[151] Old tires are sometimes converted into a swing for play.[152]
- Burning tires as protest: Protestors, worldwide, have burned tires to create black smoke.[153][154]
- Necklacing is the use of tires to kill people, typically by lynch mobs. A tire is soaked in gasoline, placed around the victim's neck, and set on fire.
- Children on a tire swing
- Burning tires in protest
See also
- Dry steering – Act of steering a stationary vehicle
- List of auto parts
- List of inflatable manufactured goods
- Off-road tire – Category of vehicle tire with deep tread
- Rubber-tyred metro – Form of rapid transit
- Rubber-tyred trams – Development of the guided bus
- Shinosaur – Street-art object in Moscow
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




