Pax Gupta
Historiographical term From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
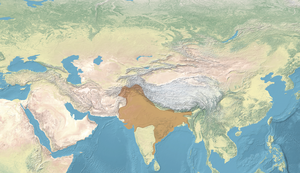
Pax Gupta or Pax Guptana (Latin for "Gupta Peace", modelled after Pax Romana) is a historiographical term sometimes used to describe the social and economic peace in the regions under the Gupta Empire between 4th and 5th centuries CE, notably in the Indus Valley and Northern India.[1]
Background
This period ushered an unprecedented growth and development of scientific knowledge in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in the fields of art, mathematics and astrology and is called the golden age of India.[2] Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as the Mahabharata and Ramayana, were canonised during this period.[3] The Gupta period produced the scholars Kalidasa,[4] Aryabhata, Varahamihira, and Vatsyayana who made great advancements in many academic fields.[5][6] The game of chess developed during this period.[7]
See also
- Pax Kushana, a period of relative peace in the preceding Kushan Empire
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.