Paralimbic cortex
Area of three-layered cortex From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The paralimbic cortex is an area of three-layered cortex that includes the following regions: the piriform cortex, entorhinal cortex, the parahippocampal cortex on the medial surface of the temporal lobe, and the cingulate cortex just above the corpus callosum.[1][2]
| Paralimbic cortex | |
|---|---|
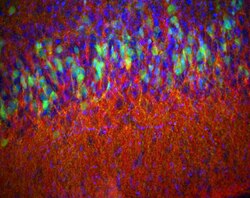 Piriform cortex from a 14-day-old mouse, stained for D2-eGFP (green), enkephalin (red) and DAPI (blue) to show nuclei. Epifluorescence. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cortex paralimbicus |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The paralimbic cortex lies close to, and is directly connected with, the structures of the limbic system.[1] (The prefix para meaning beside or adjacent to.) The paralimbic cortex, also referred to as the mesocortex, or juxtallocortex, is interposed between the neocortex and the allocortex.[3] The paralimbic cortex provides a gradual transition from primary limbic regions, including the septal region, substantia innominata, and the amygdala nuclei, to higher neocortical regions.[4]
There are dense connections between the paralimbic cortex and core limbic structures, in particular the amygdala. The amygdaloid complex comprises both nuclear and cortical layers. These cortical features of the amygdala often extend into the paralimbic areas, blurring the boundaries between limbic and paralimbic regions.[5] Thus, these regions may collectively be termed the ‘paralimbic system’.
It is cytoarchitecturally defined: it has three layers, where layers 2, 3 and 4 are merged, and is intermediate in form between the allocortex (less than six layers) and the neocortex (six distinct layers). It is found within the limbic system, representing the border between neocortical and allocortical parts.[6][7] It has been hypothesized that the cortex should be viewed as concentric rings of allocortex, mesocortex (paralimbic cortex), and isocortex (neocortex).[8]
Functions
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
The paralimbic cortex serves as a transitional region between the neocortex and the allocortex incorporating a region of proisocortex, as a subdivision of the neocortex, and a region of periallocortex, as a subdivision of the allocortex.[9]
It constitutes a group of interconnecting brain structures that are involved in the functions of emotion processing, goal setting, motivation and self-control.
- The paralimbic cortex integrates external sensory information with internal emotional and motivational states, serving as an interface between higher-order cognition and basic emotional/behavioral processes.[10]
- The olfactocentric paralimbic cortex critically regulates emotional and autonomic functions, overseeing the regulation of emotional and neurovegetative functions.
- Specific paralimbic regions like Brodmann area 10 are activated during more complex working memory and cognitive tasks, indicating their involvement in episodic and working memory tasks, as well as abstract cognitive function.[11]
- The perirhinal cortex, a paralimbic region, integrates item information with spatial/temporal data and transmits this to the hippocampus, contributing significantly to declarative memory processing and item identification.[12]
- The orbitofrontal cortex, a paralimbic area, plays a key role in the evaluation of rewards and punishment, as well as in self-regulation and behavioral inhibition.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
