Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
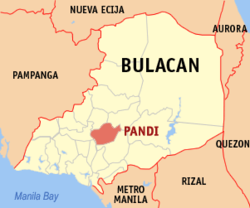
Pandi, Bulacan
Municipality in Bulacan, Philippines From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Pandi [pɐnˈde], officially the Municipality of Pandi (Tagalog: Bayan ng Pandi), is a municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2024 census, it has a population of 162,725 people.[5]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2011) |
Pandi is one of the youngest towns in Bulacan. During the Spanish Regime, Pandi was a part of the political jurisdiction of the town of Meycauayan City including the towns of San Jose del Monte, Bocaue, Marilao, Valenzuela, Obando, Santa Maria, Balagtas, it also formed part of the vast Hacienda Santa Maria de Pandi, which included the towns of Santa Maria and Balagtas and parts of Angat and Bustos. Pandi was then a part of the town Balagtas (then Bigaa) until its formal separation and independence on April 17, 1946.
Remove ads
Etymology
Pandi was derived from pande, Kapampangan word of "blacksmith," cognate of Tagalog word "panday."
History
Summarize
Perspective
Early history
Pandi was originally part of Hacienda of Dominicans named Hacienda which belongs to the Town Santa Maria de Pandi (now Santa Maria, Bulacan). In 1874 it was turn over to the town of Bigaa as one of its Barrio and the religious activity belongs to Convento de Bigaa under the auspices of Augustinian order established a chapel under the advocacy of Immaculate Concepcion.
Spanish colonial era
The Republic of Kakarong de Sili

During the Philippine Revolution, Pandi played a vital and historical role in the fight for Philippine independence, Pandi is historically known for the Real de Kakarong de Sili Shrine - Inang Filipina Shrine, the site where the bloodiest revolution in Bulacan took place, where more than 3,000 Katipunero revolutionaries died. Likewise, it is on this site where the 'Republic of Real de Kakarong de Sili' of 1896, one of the first Philippine revolutionary republics was established.
It was in Kakarong de Sili where about 6,000 Katipuneros from various towns of Bulacan headed by Brigadier General Eusebio Roque, a mysticist (albolaryo) better known as "Maestrong Sebio or Dimabungo"[6] that the Kakarong Republic was organized shortly after the Cry of Pugad Lawin referred to as 'The Cry of Balintawak' - Andres Bonifacio a Filipino nationalist and revolutionalist who led in 'The Cry of Balintawak'. The 'Kakarong Republic' was the first revolutionary government established in Bulacan to overthrow the Spaniards. These significant event shave been included as of one of the attributes in the seal of the province of Bulacan.
According to available records including the biography of General Gregorio del Pilar entitled "Life and Death of a Boy General" written by Teodoro Kalaw, former director of the National Library of the Philippines, an improvised fort was constructed at 'Kakarong de Sili'. It had streets, an independent police force, a band, a factory of falconets, bolos and repair shops for rifles and cartridges. The 'Kakarong Republic' had a complete set of officials with Canuto Villanueva as Supreme Chief and 'Maestrong Sebio'- Eusebio Roque, who was Brigadier General. The fort was attacked and totally destroyed on January 1, 1897, by a large Spanish force headed by General Olaguer-Feliu.[7] Gen. Gregorio del Pilar was only a lieutenant at that time and 'The Battle of Kakarong de Sili' was his first "baptism of fire". This was where he was first wounded and escaped to nearby barangay 'Manatal'. After the Battle of Kakarong de Sili mysticist Eusebio Roque were arrested and transferred to Bulakan town where the seat of Alcaldia Mayor located and he was sentenced to death.
The Kakarong Lodge No. 168 of the 'Legionarios del Trabajo' in memory of the 1,200 Katipuneros who perished in the battle erected a monument of the Inang Filipina Shrine - Mother Philippines Shrine in 1924 in the barrio of Kakarong. The actual site of the 'Battle of Kakarong de Sili' belongs to the administrative and geographical jurisdiction of Town of Bigaa and it was given to Pandi in 1946. The site is now a part of the barangay of 'Real de Kakarong'. No less than one of the greatest generals in the Philippines' history, General Emilio Aguinaldo who became first Philippine president visited this sacred ground in the late fifties.
The birth of the town of Pandi
The independence of Pandi as a new town of Bulacan was through the efforts of Mamerto Carpio Bernardo - (The Father of Pandi, Bulacan). During his term as mayor of Balagtas, he worked for the independence of Pandi as a town. Matias B. Salvador become the first mayor after the town gained independence in 1946 from its mother town Balagtas formerly named Bigaa, under the Presidential Decree of President Sergio Osmeña the 4th president of the country.
Remove ads
Geography
Summarize
Perspective
Pandi is located at the center of four adjoining towns of Bulacan Province: Santa Maria; Bustos; Angat; and Balagtas. The land area is composed mostly of rice fields devoted for planting crops and agriculture. Some barrios of the town are covered by irrigation system coming from Angat Dam on the Angat River.
There are many streams that branch out from this river that become estuaries. Some of these provide livelihood by fanning gold. The biggest river is Bunsuran River that empties itself to the Philippine Sea. Along the side of the rivers are banana plantations thriving naturally and many taro plants.
Pandi is rich in many natural brooks coming from the mainland itself. In some remote areas the lands are still covered by bamboo trees that naturally thrive and multiplies. Some lands privately owned have mango plantations. In some areas that are privately owned are rock deposits being used for housing materials. The eastern area of Poblacion is gifted by the natural panoramic beauty of the scenery of Sierra Madre Mountains in Luzon. Owing to this the morning climate is always cloudy and cool in some areas of the town proper of Pandi, Bulacan. Some of the natural variations in topography of Pandi land areas have been evened out due to the urbanization of the town. The town's central area has been altered substantially by commercial establishments. Pandi was part of 2nd congressional district from 1987 to 2022. It was moved to 5th district along with Balagtas, Bocaue, and Guiguinto.
Pandi lies 31 kilometres (19 mi) north-east of Manila and 22 kilometres (14 mi) from Malolos City; it is located at the eastern portion of Bulacan Province. With the continuous expansion of Metro Manila, Pandi is now included in the Greater Manila's built-up area which reaches San Ildefonso, Bulacan at its northernmost part.
Climate
The prevailing climatic conditions in the municipality is categorized into two types: wet season and dry season.
- Wet season (Rainy Season or Monsoon Season)
- Dry season (Summer Season)
Barangays
Pandi is subdivided into 22 barangays, as shown in the matrix below. Each barangay consists of puroks and some have sitios.
Remove ads
Demographics
Summarize
Perspective

In the 2020 census, the population of Pandi, Bulacan, was 155,115 people,[15] with a density of 5,000 inhabitants per square kilometre or 13,000 inhabitants per square mile.
Language and ethnicity
Majority of the population of 'Pandienos' are native to Pandi whose roots can be traced back from the neighboring towns of Balagtas, Bulacan, Bocaue, Bulacan and Santa Maria, Bulacan. Some families are intermarriage between immigrants from Ilocos Region and as far as Nueva Ecija during earlier periods. The most recent immigrants are from Luzon and Visayas islands, and Bicol. The population speaks Tagalog and it is the medium of instruction in schools, as well as Kapampangan and English.
Religion
The majority of the population are Christians. Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion in the municipality and has two parishes: Immaculate Conception Parish in Poblacion town proper and Santo Cristo Parish in baranggay 'Siling Bata'. Other religious groups with strong presence in the municipality are the following: Members Church of God International or Ang Dating Daan, Iglesia ni Cristo, Jehovah's Witness, Jesus Is Lord Church, Iglesia Evangelica Metodista En Las Islas Filipinas (IEMELIF) and other Evangelical or "Born-Again" groups, as well as Pentecostals. Islam is also practiced with the presence of Abu Bakr Mosque as the first Mosque established in the Town of Pandi, located at Barangay Masuso.
Remove ads
Economy
Summarize
Perspective
Poverty incidence of Pandi
5
10
15
20
25
30
2000
20.91
20.91
2003
11.46
11.46
2006
14.10
14.10
2009
7.58
7.58
2012
6.89
6.89
2015
8.75
8.75
2018
7.09
7.09
2021
21.04
21.04
Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23]

- Major Industries: Furniture Making, Garments and Embroidery, Metalcraft, Poultry and Hog Raising, Agriculture and Farming. Local Food Processing. Commercial Retail Dry Goods Business. Recreation Facilities for Tourism.
- Major Products: Local processed Food and Rice. Furnitures. Embroidered clothes, bed linens and kitchen linens.
- Minor Products: Orchid plants for retail. Mangoes for local consumption and other minor agricultural products sold in the local market as well as the markets of the next towns. Poultry products like table eggs and chicken meat. Duck raising and salted egg production. Little fishponds for raising Tilapia fish. This provides the town folks their livelihood.
Banks
The town of Pandi has two banks:
- Rural Bank of Pandi Incorporated, which currently has two branches, one in Pandi and another in Santa Maria, Bulacan next town to Pandi in the north-east. The third branch of the Rural Bank of Pandi will soon open in Guiguinto, Bulacan, 2012, which is north-west of Pandi, next to its mother town Balagtas, Bulacan. Rural Bank of Pandi is the pioneer bank of the town founded by Julita Cruz Andres, a resident of Pandi who is a native of Angat, Bulacan - baranggay 'Niyugan' and Atty. Ciriaco C. Santos, a native of Pandi. The banks primarily serve agricultural businesses and farmers and animal husbandry businesses.
- Gateway Rural Bank Incorporated - Gatebank, a chain of banks in Bulacan Province and Luzon island. The banks provide international money transfer. They primarily serve agricultural businesses and farmers, and animal husbandry businesses. The bank was founded 1997 by a native of Pandi, Bulacan - Mercedes G. Santos-Coloma, 2012 president. The parents of Mercedes are Atty. Ciriaco C. Santos and Belen Bernardo Galvez-Santos.
Remove ads
Government
Local government

- Mayor: Enrico A. Roque (NUP)
- Vice Mayor: Crispin DL. Castro (PFP)
- Municipal Councilors:
- Ex-Officio Members:
- Alejandro SJ. Angeles (ABC President)
- Prince Cedric G. Cervantes (SK President)
MAYOR'S FROM 1946 TO PRESENT
- Manuel G. Santos (1946-1948)
- Matias B. Salvador (1948-1952)
- Mamerto C. Bernardo (1952-1956/1964-1968)
- Atty. Jose E. Bernardo (1956-1960)
- Dr. Valeriano O. Domingo (1960-1964)
- Norberto J. Roque (1968-1971)
- Atty. Venustiano S. Roxas (1971-1979)
- Leonardo C. Andres (1980-1986/1988-1992)
- Anastacio Hilario (1986-1988)
- Oliver M. Andres (1998-2007/2009-2010)
- Roberto M. Oca Jr. (2007-2009)
- Celestino T. Marquez (2016-2019)
- Enrico A. Roque (2010-2013/2013-2016/2019-Present)
VICE MAYOR'S FROM 1946 TO PRESENT
- Matias B. Salvador (1946-1948)
- Alejandro Santos (1948-1952)
- Atty. Felipe D. De Jesus (1952-1956)
- Norberto J. Roque (1956-1960)
- Dr. Lauro C. Reyes (1960-1964)
- Dr. Valeriano O. Domingo (1964-1968)
- Benjamin Santos (1968-1971)
- Aurelio Valeriano (1971-1979)
- Ciriaco Santos (1980-1986)
- Gerardo Sta. Ana Sr. (1986-1988)
- Zoila De Leon (1988-1992)
- Roberto M. Rivera (1992-1995/1995-1998)
- Atty. Anicia C. Marquez (1998-2001)
- Atty. Napoleon Mauro C. Roxas (2001-2004)
- Gavino C. Austria (2004-2007)
- Oliver M. Andres (2007-2009)
- Richard A. Roque (2009-2010)
- Maria Rachel S. Oca, MD, MBAH (2010-2013)
- Oscar T. Marquez (2013-2016)
- Atty. Napoleon Mauro C. Roxas (2016-2019)
- Luisa P. Sebastian (2019-2022/2022-2025)
- Crispin DL. Castro (2025–Present)
Remove ads
Tourism


- Real de Kakarong de Sili: The site of revolutionary battle during Spanish Regime. It is located in barangay of 'Kakarong' where a monumental shrine is erected called Inang Filipina Shrine - Mother Philippines Shrine.
- Rizal Park: The mini park is in poblacion area that serves as recreation park where some town programs are held. The park has big monument of the Philippine National Hero - Dr. Jose P. Rizal Jose P. Rizal. It is a close replica of Rizal Monument in Luneta. The mini park was built during the term of Atty. Jose Espina Bernardo, the 3rd mayor of the town.
- Pandi Mineral Spring Resort: The oldest amusement park located in the poblacion area, which as of 2012 is closed. It was named owing to the nature of soft water that comes from a water well that supplied the whole central area of the town - Mineral Spring, the water well primarily supplied the central poblacion area. It was famous during earlier times and neighboring towns come to get water for drinking purpose in Pandi. Mineral Spring was built during the term of the 3rd mayor of the new town, Atty. Jose Espina Bernardo, there was an area used for washing clothes by the town folks. The water well as of 2012 no longer supplies water in the area, owing to the depth of the well which must have reached its saturation level.
- Residence Private Pool: A private resort best for family bonding and different special occasions located at Sitio Sto. Rosario, barangay Bagong Barrio.
- Dr. Totoy Resort: A mini resort built in the backyard of the residence of Dr. Totoy - Dr. Valeriano Crisostomo D.M.D. residential lot. The mini resort is suitable for more private family vacationers and little groups. It is situated in barangay 'Bunsuran 1'.
- Manatal Fresh Water Resort: A mini resort situated in barangay 'Manatal'.
- Villa Manaoag Nature Resort and Retreat House: A retreat house situated in poblacion area of the town in Amparo Subdivision. It has a little chapel and Station of the Cross life size images.
- Villa Conception Wet and Wild Waves, Inc.: An amusement park situated in barangay of 'Masuso'.
- Amana Water Park Resort: An amusement park situated in barangay of 'Bagong Barrio'. It is almost a 10-hectare park with lodging facilities and food chain stores. It is the largest water wave park in the Philippines.
- Sitio Antonio: A new amusement resort with large visual attractions and Giant Slides with amenities perfectly fit for Team Building activities. Also situated in Barangay Bagong Barrio and was named after the family name "Antonio"- a business minded family whom resides also at Bagong Barrio.
Remove ads
Society and culture
Summarize
Perspective
Sports and senior center
The town of Pandi in the central poblacion area along Manuel G. Santos Sr. Street has a sports complex ground - Pandi Sports Complex. The site is a semi playground for children and equipped with some facilities for sports. It has a Basketball Court. The sports complex houses a center for senior town folks where they do senior activities and meetings, election of yearly officials as well. And the various members that also assist in some outreach domestic programs in the town - Senior Citizen Center. Within the compound is a water well that supplies the poblacion area of water until the northmost area of the town managed by NAWASA: National Water and Sewerage Authority - Water supply and sanitation in the Philippines.
- Pandi Sports Complex aka Leonardo Andres Sports Complex
- Senior Citizen Center
- Office of Senior Citizen, located at "Masagana" was the first Senior Citizen office built not in town proper. It serves as the center of Senior citizen for the residence of Masagana.
- Saint Igmedius Sports Complex, newly built covered court located also at "Masagana" near at the Saint Igmedius Chapel. First of it owns (in Pandi) as this complex was equipped with proper sports equipment and also the Courts measurements was based on the standard sized and measure of a basketball/volleyball court. This was also the center for every celebration and any festivities of the Barangay. The elegant Chapel and fully equipped Sports Complex was built and sponsored by an influential family living in the Barangay.
Town festivities
The town celebrates every year before Christmas vacation Lantern Parade that goes around the poblacion area. It is sponsored by Mamerto C. Bernardo Memorial Central Public School wherein all students of the elementary school have their lantern designs. There is a lantern design competition and awarding of prizes to the students.
The Town Fiesta of Pandi is celebrated every first week of December for its town patroness - 'Our Lady of Immaculate Conception'. The town feast day is called Fiesta ng Pandi. The town celebrates it with band of musicians for 2 days usually Saturday and Sunday. The band goes around the central poblacion area. Along the streets are hanging 'Banderitas' - little multicolored flags lined in long ropes, a cultural heritage influenced by Spanish culture - Spain that colonized the country during the 15th century. During earlier periods the occasion was very festive with visitors of various families from different towns and regions. It is celebrated like a thanksgiving day of the town.
Remove ads
Infrastructure
Summarize
Perspective
Transportation facilities
Pandi town proper is serviced by for hire tricycle - motorcycle with side car, that can go as far as Baliuag, Bulacan in a short cut route through barangay road, as well as the route going to Santa Maria, Bulacan and Bocaue, Bulacan. Some regular options are the official jeepney schedule of Santa Maria, Bulacan route to Angat, Bulacan which passes by Pandi since the town is centrally situated in between this two towns. There is a jeepney route from Pandi to Balagtas, Bulacan where there are several commercial buses that passes by Bocaue, Bulacan exiting in baranggay 'Taal' to the Super Highway - formerly named North Diversion, North Luzon Expressway facilitating a short travel to Manila and other Metro Manila areas. There are several commercial buses as well in central poblacion of Santa Maria, Bulacan passing through the Super Highway.
Medical facilities and hospital
Pandi being the youngest town and smallest town do not have a government public hospital but mini Health Center that provides outreach medical services and midwifery services. As of 2012 a government hospital is being constructed in baranggay 'Bunsuran'. There are several private practitioners of family health care in the town and some barrios. For more extensive health care programs the town folks are accommodated in the Capital City of Malolos where Bulacan Medical Center formerly Provincial Hospital located.
Education
Summarize
Perspective

The Pandi Schools District Office governs all educational institutions within the municipality. It oversees the management and operations of all private and public, from primary to secondary schools.[24]
Primary and elementary schools
The Mamerto C. Bernardo Memorial Central School is a public school in the town proper named after Mamerto Carpio Bernardo. The school has satellite branches in all barrios of the town providing elementary education in the whole town of Pandi. The main central school is situated in the town proper providing education to the masses in the poblacion central area. The school is situated along Jose E. Bernardo Street, a major street named after another mayor Atty. Jose Espina Bernardo. Atty. Jose Espina Bernardo is a cousin to Mamerto Carpio Bernardo. He built the roads of the new town and central water supply. It was during his term that the new town reached its height of community development. He also built the 'Rizal Plaza' as a tribute to the Philippine National Hero Dr. José Rizal. Ponciano Bernardo past mayor of Quezon City is their cousin. Ponciano A. Bernardo's father migrated to Nueva Ecija with his cousin Francisco Bernardo Oliveros, whose sisters and cousins were left behind in Pandi, Bulacan.
- Aldersgate Phils. A. Formative School for Children
- Bagbaguin Elementary School
- Bagong Barrio Elementary School
- Baka-Bakahan Elementary School
- Bunsuran Elementary School
- Cacarong Elementary School
- Caring Jesus Educational Foundation
- Christian Academy of Pandi
- Cupang Elementary School
- Gentle Shepherd Montessori (1999)
- Global Seed Science School
- Eusebio Roque Elementary School
- Immaculate Conception Child Development Center (1981)
- Matias B. Salvador Memorial Elementary School
- Mamerto C. Bernardo Memorial Central School
- Malibong Bata Elementary School
- Malibong Matanda Elementary School
- Manatal Elementary School
- Manuel Guisano Santos Sr. Memorial School (1990)
- Mapulang Lupa Elementary School
- Masagana Elementary School
- Masuso Elementary School
- Montessori Academy of Malibu
- Pandi Heights Elementary School
- Pandi Residences Elementary School
- Pinagkuwartelan Elementary School
- Real De Cacarong Elementary School
- San Antonio Abad Elementary School
- San Roque Elementary School
- Siling Matanda Elementary School
- Cacarong Bata Elementary School
- Sto. Nino Elementary School
Secondary schools
- Bunsuran National High School is a public high school in barrio 'Bunsuran' 1st providing secondary education to nearby barangays. The whole town has three public high schools (that includes Masagana High School) and public elementary schools in every barangay - barrio of the municipality.
- Masagana National High School is public secondary school in barrio 'Masagana' (High School Annex of Bunsuran National High School).
- Virginia Ramirez Cruz Memorial School (Siling Bata National High School) is a secondary branch of Mamerto Carpio Bernardo Memorial School in barrio 'Siling Bata' providing secondary education (Bureau of Secondary Education) in different barrios and barangays adjacent to 'Siling Bata'. The school was named Virginia R. Cruz Memorial School after Virginia Bernardo Ramirez-Cruz, who donated the land where the public high school was erected and established. She was a past president of Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO), Philippine Lottery Draw. Her mother is Valentina Bernardo of Pandi, Bulacan who married Ponciano Ramirez of Bocaue, Bulacan. Virginia was born in Bocaue, Bulacan. Her husband is past Congressman of Bulacan, Atty. Erasmo Ramirez Cruz. Atty. Matias Bernardo Ramirez is her brother, a past mayor of Bocaue, Bulacan.
Higher educational institutions
- Bulacan Polytechnic College
- College of Mary Immaculate (1981)
- Holy Angels' College (Bulacan) (formerly Holy Angels' Academy, founded in 1951)
- Pandi Technological Institute
Remove ads
Gallery
- Nanay Drug and Alcohol Rehabilitation Center
- Mamerto C. Bernardo Memorial School Clock Tower
- Manatal Coop Empowerment Center
- Bulacan Polytechnic College - Pandi Campus
- Mayor Enrico Agustin Roque
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads