Asian Games
Asian multi-sport event From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Asian Games, also known as Asiad, is a continental multi-sport event held every four years for athletes of Asia.[1] The Games were regulated by Asian Games Federation from the first Games in New Delhi, India in 1951, until the 1978 Games.[2] Since the 1982 Games, they have been organized by the Olympic Council of Asia, after the breakup of the Asian Games Federation.[3] The Games are recognized by the International Olympic Committee and are the second largest multi-sport event after the Olympic Games.[4]
| Abbreviation | Asiad |
|---|---|
| Motto | Ever Onward |
| First event | 1951 Asian Games, New Delhi, India |
| Occur every | Four years |
| Last event | 2022 Asian Games, Hangzhou, China |
| Next event | 2026 Asian Games, Aichi Prefecture and Nagoya, Japan |
| Purpose | Multi-sport event for nations in Asia |
| Headquarters | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
| President | Raja Randhir Singh |
Nine nations have hosted the Asian Games. Forty-six nations have participated in the Games, including Israel, which was excluded from the Games after its last participation in 1974. The last edition of the Games was held in Hangzhou, China, from 23 September to 8 October 2023.
Since 2010, it has been common for the host of the Asian Games to host the Asian Para Games held shortly after the end of the Games. This event is exclusive to athletes with disabilities, just like Paralympic Games. But unlike the Paralympics where the host city's contract mentions the holding of both events, the case of Asia does not mention the mandatory holding of both. Instead, the exclusion of the Asian Para Games from the Asian Games host city's contract means that both events run independently from one other, and may lead to occasions in the future when the two events are held in different cities and countries.
History
Summarize
Perspective
Origins
The Far Eastern Championship Games existed previous to the Asian Games, the former mooted in 1912 for a location set between Japan, the Philippines, and China. The inaugural Far Eastern Games were held in Manila in 1913 with 6 participating nations. There were ten Far Eastern Games held by 1934. The second Sino-Japanese War in 1934, and Japan's insistence on including the Manchu Empire as a competitor nation in the Games, caused China to announce its withdrawal from participation. The Far Eastern Games scheduled for 1938 were cancelled. The organization was eventually discontinued.[5]
Formation
After World War II, several areas in Asia became sovereign states. Many of these countries sought to exhibit Asian prowess without violence. At the London 1948 Summer Olympics, a conversation started between China and the Philippines to restore the idea of the Far Eastern Games. Guru Dutt Sondhi, the Indian International Olympic Committee representative, believed that the restoration of the Far Eastern Games would sufficiently display the spirit of unity and level of achievement taking place in Asian sports. He proposed the idea of a new competition – which came to be the Asian Games. The Asian Athletic Federation would eventually be formed. A preparatory committee was set up to draft the charter for this new body. On 13 February 1949, the Asian Athletic Federation was formally inaugurated in New Delhi, announced as the inaugural host city to be held in 1950.[6][7]
Years of crises

In 1962, the Games were hit by several crises. The host country Indonesia refused to permit Israel and Taiwan to participate due to political recognition issues. The IOC terminated its sponsorship of the Games and terminated Indonesia's membership in the IOC.[8] The Asian Football Confederation (AFC),[9] International Amateur Athletics Federation (IAAF), and the International Weightlifting Federation (IWF) also removed their recognition of the Games.[10][11]
South Korea renounced its plan to host the 1970 Asian Games on the grounds of a national security crisis; the main reason was due to a financial crisis. The previous host, Thailand, would host the Games in Bangkok using funds transferred from South Korea.[12] Japan was asked to host but declined the opportunity as they were already committed to Expo '70 in Osaka.[13] This edition marked the Games' inaugural television broadcasting, worldwide.[14] In Tehran, in 1974, the Games formally recognized the participation of China, North Korea, and Mongolia. Israel was allowed to participate despite the opposition from the Arab world, while Taiwan was permitted to continue taking part (as "Chinese Taipei") although its status was abolished in a general meeting on 16 November 1973 by the Games Federation.[15]
Before the 1978 Games, Pakistan retracted its plan to host the 1975 Games due to a financial crisis and political issues.[16] Thailand offered to host and the Games were held in Bangkok. As in 1962, Taiwan and Israel refused participation by the Games Federation, amid political issues and security fears.[17] Several governing bodies protested the ban. The International Olympic Committee threatened to bar the participating athletes from the 1980 Summer Olympics.[18] Several nations withdrew before the Games opening.[19]
Reorganization and expansion
These events led the National Olympic Committees in Asia to revise the constitution of the Asian Games Federation. The Olympic Council of Asia was created in November 1981, excluding Israel and Taiwan.[20] India was scheduled to host in 1982 and the OCA decided to maintain the old AGF timetable. The OCA formally started to supervise the Games starting with the 1986 Asian Games scheduled for Seoul, South Korea.[21] In the 1990 Asian Games held in Beijing, Taiwan (Republic of China) was re-admitted, under pressure by the People's Republic of China to compete as Chinese Taipei.[22]
The 1994 Games held in Hiroshima included the inaugural participation of the former 5 republics of the Soviet Union who were part of Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. It was also the first edition of the Games held in a host country outside its capital city.[23] However, Iraq was suspended from the Games due to the 1990 Persian Gulf War. North Korea boycotted the Games due to political issues with the host country. The Games were hampered during the opening ceremony due to a heart attack that killed Nareshkumar Adhikari, the chief of the Nepalese delegation.[24]
The 1998 Games marked the fourth time the Games were held in Bangkok, Thailand. This time the city participated in a bidding process. The opening ceremony was on 6 December; the previous three were on 9 December. King Bhumibol Adulyadej opened the Games; the closing ceremony was on 20 December (the same date as all the previous games hosted by Thailand).

Background
Summarize
Perspective
Symbols
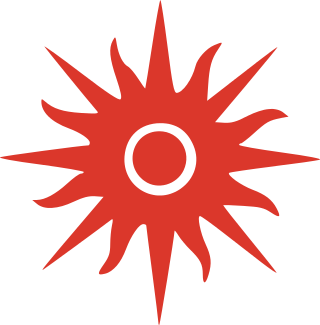
The Asian Games Movement uses symbols to represent the ideals embodied in the Asian Games charter. The Asian Games motto is "Ever Onward" which was designed and proposed by Guru Dutt Sondhi upon the creation of the Asian Games Federation in 1949. The Asian Games symbol is a bright sun in red with 16 rays and a white circle in the middle of its disc which represents the ever glimmering and warm spirit of the Asian people.
Mascots
Since the 1982 Asian Games in New Delhi, India, the Asian Games have had a mascot, usually an animal native to the area or occasionally human figures representing the cultural heritage.
Participation
All 45 members affiliated with the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA) are eligible to participate in the Games.
According to membership in the OCA, transcontinental Kazakhstan is an Asian country and could participate in the Asian Games, but this right could not apply to Egypt as the country had 6% of the territory on Sinai, participating in the African Games instead. Turkey and Russia/Soviet Union — whose major geographical parts are located in the Asian continent — participate in the European Games rather than the Asian Games. Similarly, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Cyprus, and Armenia are mostly located in Asia but participate in the European Games instead of the Asian Games.
In history, 46 National Olympic Committees (NOCs) have sent competitors to the Games. Israel has been excluded from the Games since 1976, the reason cited as being due to security reasons.[25] Israel requested to participate in the 1982 Games, but the request was rejected by the organizers due to the Munich massacre.[26] Israel is now a member of the European Olympic Committees (EOC) and competes at the European Games.
Taiwan, Palestine, Hong Kong, and Macau participate in the Asian Games according to membership in OCA. Due to its continuing ambiguous political status, Taiwan has participated in the Games under the flag of Chinese Taipei since 1990. Macau since 1990 has been allowed to compete as one of the NOCs in the Asian Games, despite not being recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) for participation in the Olympic Games.
In 2007, the President of OCA, Sheikh Ahmed Al-Fahad Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah, rejected the proposal to allow Australia to participate in the Games. He stated that while Australia would add good value to the Asian Games, it would be unfair to the Oceania National Olympic Committees (ONOC).[27] Being members of ONOC, Australia and New Zealand have participated in the Pacific Games since 2015. This motion was mooted again in 2017 after Australia participated in the 2017 Asian Winter Games as they are in discussions to become a full Asian Games member shortly.[28] However, the Australian Olympic Committee announced that Australia would be allowed a small contingent of athletes for the 2022 Games, as long as the qualification for Summer Olympics events such as basketball and volleyball are through the Asia-Pacific region.[29]
There are only seven countries, namely India, Indonesia, Japan, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Singapore, and Thailand, that have competed in all editions of the games.
Editions
| Edition | Year | Host | Games dates / Opened by[a] |
Countries | Competitors | Sports | Events | Top-ranked team | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1951 | 4–11 March 1951 President Rajendra Prasad |
11 | 489 | 6 | 57 | [30] | ||
| 2 | 1954 | 1–9 May 1954 President Ramon Magsaysay |
18 | 970 | 8 | 76 | [31] | ||
| 3 | 1958 | 24 May – 1 June 1958 Emperor Hirohito |
16 | 1,820 | 13 | 97 | [32] | ||
| 4 | 1962 | 24 August – 4 September 1962 President Sukarno |
12 | 1,460 | 13 | 88 | [33] | ||
| 5 | 1966 | 9–20 December 1966 King Bhumibol Adulyadej |
16 | 1,945 | 14 | 143 | [34] | ||
| 6 | 1970 | 9–20 December 1970 King Bhumibol Adulyadej |
18 | 2,400 | 13 | 135 | [35] | ||
| 7 | 1974 | 1–16 September 1974 Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi |
19 | 3,010 | 16 | 202 | [36] | ||
| 8 | 1978 | 9–20 December 1978 King Bhumibol Adulyadej |
3,842 | 19 | 201 | [37] | |||
| 9 | 1982 | 19 November – 4 December 1982 President Zail Singh |
23 | 3,411 | 21 | 147 | [38] | ||
| 10 | 1986 | 20 September – 2 October 1986 President Chun Doo-hwan |
22 | 4,839 | 25 | 270 | [39] | ||
| 11 | 1990 | 22 September – 7 October 1990 President Yang Shangkun |
31 | 6,122 | 27 | 310 | [40] | ||
| 12 | 1994 | 2–16 October 1994 Emperor Akihito |
42 | 6,828 | 34 | 338 | [41] | ||
| 13 | 1998 | 6–20 December 1998 King Bhumibol Adulyadej |
41 | 6,554 | 36 | 377 | [42] | ||
| 14 | 2002 | 29 September – 14 October 2002 President Kim Dae-jung |
44 | 7,711 | 38 | 419 | [43] | ||
| 15 | 2006 | 1–15 December 2006 Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani |
45 | 9,520 | 39 | 424 | [44] | ||
| 16 | 2010 | 12–27 November 2010 Premier Wen Jiabao[b] |
9,704 | 42 | 476 | [45] | |||
| 17 | 2014 | 19 September – 4 October 2014 President Park Geun-hye |
9,501 | 37 | 439 | [46] | |||
| 18 | 2018 | 18 August – 2 September 2018 President Joko Widodo |
11,300 | 46 | 465 | [47] | |||
| 19 | 2022 | 23 September – 8 October 2023[c] President Xi Jinping |
11,935 | 40 | 481 | [48] | |||
| 20 | 2026 | 19 September – 4 October 2026 Emperor Naruhito (expected) |
Future event | 41 | Future event | ||||
| 21 | 2030 | 4 – 19 November 2030 | Future event | ||||||
| 22 | 2034 | 29 November – 14 December 2034 | Future event | ||||||
Participating nations
45 nations whose NOCs are recognized by the OCA compete at the Asian Games.[49]
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Bangladesh
Bangladesh Bhutan
Bhutan Bahrain
Bahrain Brunei
Brunei Cambodia
Cambodia China
China Chinese Taipei
Chinese Taipei Timor-Leste
Timor-Leste Hong Kong
Hong Kong Indonesia
Indonesia India
India Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Jordan
Jordan Japan
Japan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kuwait
Kuwait Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Laos
Laos Lebanon
Lebanon Macau
Macau Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mongolia
Mongolia Myanmar
Myanmar Nepal
Nepal North Korea
North Korea Oman
Oman Pakistan
Pakistan Palestine
Palestine Philippines
Philippines Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Singapore
Singapore Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka South Korea
South Korea Syria
Syria Thailand
Thailand Tajikistan
Tajikistan Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan Vietnam
Vietnam Yemen
Yemen
List of sports
Summarize
Perspective
The historical average for the edition of events by the edition of the Asian Games is nearly 260 events with nearly 24 sports by edition. The last edition held in Hangzhou, China was the edition with the largest number of events when 481 finals in 40 sports were held. Until the 2018 edition, each host country was allowed to set up the program respecting their local demands, which led to a dizzying growth of the event. However, this flexibility rule ruled out the entry of some Olympic sports such as the modern pentathlon and triathlon of the programs of some editions between 1986 and 2006. This flexibility also increased the number of athletes participating in each edition. However, it forced the event to be massive, as there was no calculation of athlete quotas per NOC. To avoid gigantism, OCA established a new policy to be applied since the 2018 Asian Games which limited the number of sports to be played at the Games to 40. This new rule is by the Olympic program for the subsequent edition of the Summer Olympic Games and if there is any prior change, the entity will necessarily follow it. However, each region that makes up the body can nominate a regional sport according to its demands. Between one and two extra sports could also be included due to the local demands.[50][51]
Key: = Discontinued
|
|
Disciplines
| Sport | Disciplines | Years |
|---|---|---|
| Aquatics | Artistic Swimming | Since 1994 |
| Diving | All | |
| Marathon swimming | Since 2022 | |
| Swimming | All | |
| Water polo | All | |
| Baseball | Baseball | Since 1994 |
| Softball | Since 1990 | |
| Basketball | Basketball | All |
| 3x3 basketball | Since 2018 | |
| Board games | Chess | 2006–2010, 2022 |
| Contract bridge | 2018-2022 | |
| Go | 2010, 2022 | |
| Xiangqi | 2010, 2022 | |
| Canoeing | Slalom canoeing | Since 2010 |
| Sprint canoeing | Since 1990 | |
| Cycling | BMX racing | Since 2010 |
| BMX freestyle | 2026 | |
| Mountain biking | 1998–2002, since 2010 | |
| Road cycling | 1951, since 1958 | |
| Track cycling | 1951, 1958, since 1966 | |
| Dancesport | Ballroom | 2010 |
| Breaking | Since 2022 | |
| Gymnastics | Artistic gymnastics | Since 1974 |
| Rhythmic gymnastics | Since 1994 | |
| Trampoline | Since 2006 | |
| Martial arts | Pencak silat | 2018 |
| Sambo | 2018 | |
| Roller sports | Artistic roller skating | 2010, 2022 |
| Inline freestyle skating | 2022 | |
| Roller speed skating | 2010, 2018-2022 | |
| Skateboarding | Since 2018 | |
| Rugby union | Rugby union | 1998–2002 |
| Rugby sevens | Since 1998 | |
| Tennis | Tennis | 1958–1966, since 1974 |
| Soft tennis | Since 1994 | |
| Volleyball | Volleyball | Since 1958 |
| Nine-a-side volleyball | 1958–1962 | |
| Beach volleyball | Since 1998 |
Medal table
Summarize
Perspective
Of the 46 National Olympic Committees participating throughout the history of the Games, 43 have won at least a single medal in the competition, leaving three National Olympic Committees without a medal: Bhutan, Maldives, and Timor-Leste yet to win a single medal. 38 National Olympic Committees have won at least one gold medal (only Japan and India have done so at every Asian Games), while Japan and China became the only two NOCs in history to emerge as the first places at the Medal Tables.[52]
In the 2022 Games, India became the fourth nation in history after Japan, China, and South Korea to cross the 100-medal mark in one edition.[53][54] China, together with Japan and South Korea became the first three countries to cross the overall 200-medal mark in one edition during the 1986 Asian Games.[55] At the 2022 Games, China became the first NOC to surpass the threshold of 100 gold medals, 200 gold medals, 300 overall medals and 400 overall medals in a single edition.[56][57][58]
| Rank | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,674 | 1,105 | 791 | 3,570 | |
| 2 | 1,084 | 1,104 | 1,054 | 3,242 | |
| 3 | 787 | 722 | 916 | 2,425 | |
| 4 | 192 | 202 | 217 | 611 | |
| 5 | 183 | 239 | 357 | 779 | |
| 6 | 165 | 180 | 292 | 637 | |
| 7 | 144 | 189 | 311 | 644 | |
| 8 | 121 | 161 | 188 | 470 | |
| 9 | 118 | 164 | 304 | 586 | |
| 10 | 105 | 138 | 171 | 414 | |
| Totals (10 entries) | 4,573 | 4,204 | 4,601 | 13,378 | |
MVP table
The Most Valuable Player or MVP award was introduced in the 1998 Games in Bangkok, Thailand. The award was originally awarded to one individual. During the 2022 edition in Hangzhou, the Games started awarding a male and a female athlete separately.[59]
| Year | Athlete | Sport | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | |||
| 1998 | — | Athletics | [60] | |
| 2002 | — | Swimming | [60] | |
| 2006 | — | Swimming | [61] | |
| 2010 | — | Badminton | [62] | |
| 2014 | — | Swimming | [63] | |
| 2018 | — | Swimming | [64] | |
| 2022 | Swimming | [65] | ||
Centennial Festival
On 8 November 2012, the OCA decided at its 31st General Assembly in Macau to create a special multi-sport event called the Asian Games Centennial Festival in celebration of the 100th anniversary of the Oriental Games, now known as the Far Eastern Championship Games.[66] OCA awarded the Philippines the hosting rights as it was also the host 100 years previous. The event was originally scheduled to be held in Boracay, Malay, Aklan from 27 to 29 November 2013 but due to the events surrounding Typhoon Haiyan, it was moved to January 2014.[67]
See also
Notes
- Representing Hu Jintao, President of the People's Republic of China.
- Originally scheduled for 10–25 September 2022, the Games were postponed by one year due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.