Loading AI tools
Group of chemical compounds From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Oligomycins are macrolides created by Streptomyces that are strong antibacterial agents but are often poisonous to other organisms, including humans.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R,4E,5'S,6S,6'S,7R,8S,10R,11R,12S,14R,15S,16R,18E,20E,22R,25S,27R,28S,29R)-22-ethyl-7,11,14,15-tetrahydroxy-6'-[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]-5',6,8,10,12,14,16,28,29-nonamethyl-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-3H,9H,13H-spiro[2,26-dioxabicyclo[23.3.1]nonacosa-4,18,20-triene-27,2'-pyran]-3,9,13-trione | |
| Other names
Oligomycin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.334 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Oligomycins |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H74O11 | |
| Molar mass | 791.062 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS at Fermentek |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Oligomycins have use as antibiotics. However, in humans, they have limited or no clinical use due to their toxic effects on mitochondria and ATP synthase.[1]
Oligomycin A is an inhibitor of ATP synthase.[1] In oxidative phosphorylation research, it is used to prevent stage 3 (phosphorylating) respiration. Oligomycin A inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (FO subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production). The inhibition of ATP synthesis by oligomycin A will significantly reduce electron flow through the electron transport chain; however, electron flow is not stopped completely due to a process known as proton leak or mitochondrial uncoupling.[2] This process is due to facilitated diffusion of protons into the mitochondrial matrix through an uncoupling protein such as thermogenin, or UCP1.
Administering oligomycin to rats can result in very high levels of lactate accumulating in the blood and urine.[3]
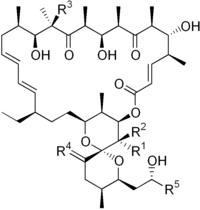 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | |
| Oligomycin A | CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin B | CH3 | H | OH | O | CH3 |
| Oligomycin C | CH3 | H | H | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin D (Rutamycin A) |
H | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin E | CH3 | OH | OH | O | CH3 |
| Oligomycin F | CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH2CH3 |
| Rutamycin B | H | H | H | H,H | CH3 |
| 44-Homooligomycin A | CH2CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| 44-Homooligomycin B | CH2CH3 | H | OH | O | CH3 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.