Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Nuri
Kushite cemetery in Sudan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Nuri is a place in modern Sudan on the west side of the Nile, near the Fourth Cataract. Nuri is situated about 15 km north of Sanam, and 10 km from Jebel Barkal.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
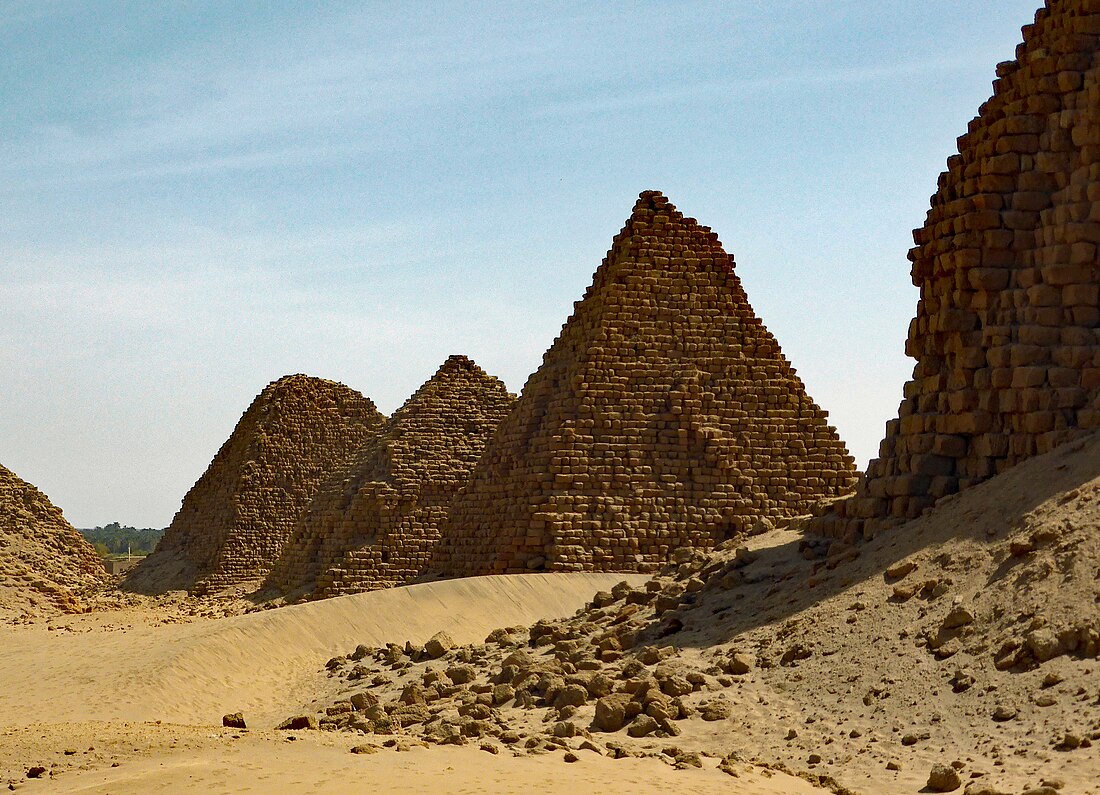
Nuri is the second of three Napatan burial sites and the construction of pyramids at Nuri began when there was no longer enough space at El-Kurru.[1] More than 20 ancient pyramids belonging to Nubian kings and queens are still standing at Nuri, which served as a royal necropolis for the ancient city of Napata, the first capital of the Nubian Kingdom of Kush. It is probable that, at its apex, 80 or more pyramids stood at Nuri, marking the tombs of royals. The pyramids at Nuri were built over a period of more than three centuries, from circa 670 BCE for the oldest (pyramid of Taharqa), to around 310 BCE (pyramid of king Nastasen).

The earliest known pyramid (Nu. 1) at Nuri belongs to king Taharqa which measures 51.75 meters square by 40 or by 50 metres high.[2] The pyramid of Taharqa was situated so that when observed from Jebel Barkal at sunrise on Egyptian New Year's Day, the beginning of the annual flooding of the Nile, the sun would rise from the horizon directly over its point.[3]
Tantamani, successor of Taharqa, was buried at el-Kurru, but all following Napatan kings and many of their queens and children until Nastasen (Nu. 15) (about 315 BC) were buried here, some 80 royals.[4] The pyramids at Nuri are, in general, smaller than the Egyptian ones and are today often heavily degraded (caused by both humans and nature), but often still contained substantial parts of the funerary equipment of the Kushite rulers who were buried here. During the Christian era, a church was erected here.[5] The church was built at least in part from reused pyramid stones, including several stelae originally coming from the pyramid chapels.
The pyramids were partially excavated by George Reisner in the early 20th century. In 2018, a new archaeological expedition began work at the site, directed by Pearce Paul Creasman.[6]
The pyramids of Nuri, together with other buildings in the region around Gebel Barkal, have been placed on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites since 2003.[7]
Remove ads
Tombs at Nuri
- See List of monarchs of Kush for more information.




The royal family of Kush was buried in the cemeteries of Nuri and el-Kurru.[8]
The King's Mothers were buried in the southern group, but this is not an area exclusively used for the burial of King's Mothers. Most of the King's Wives were buried in the parallel rows just north of Taharqa's tomb. The tombs to the far north were much smaller and may have been built for wives of lesser rank.[9] It was also found by Dows Dunham, an experienced archaeologist, that there were references to two other kings in three of the pyramids including King Taharqa. But, if they are buried there, their tombs have yet to be located and excavated.[10]
 Nuri 1 – King Taharqa,[11] the earliest and largest of the Nuri pyramids
Nuri 1 – King Taharqa,[11] the earliest and largest of the Nuri pyramids Nuri 2 – King Amaniastabarqa[12]
Nuri 2 – King Amaniastabarqa[12] Nuri 3 – King Senkamanisken[11]
Nuri 3 – King Senkamanisken[11] Nuri 4 – King Siaspiqa[12]
Nuri 4 – King Siaspiqa[12] Nuri 5 – King Malonaqen[11]
Nuri 5 – King Malonaqen[11] Nuri 6 – King Anlamani,[11] son of King Senkamanisken
Nuri 6 – King Anlamani,[11] son of King Senkamanisken Nuri 7 – King Karkamani[11]
Nuri 7 – King Karkamani[11] Nuri 8 – King Aspelta,[11] son of King Senkamanisken and Queen Naparaye
Nuri 8 – King Aspelta,[11] son of King Senkamanisken and Queen Naparaye Nuri 9 – King Aramatle-qo,[11] son of Aspelta
Nuri 9 – King Aramatle-qo,[11] son of Aspelta Nuri 10 – King Amaninatakilebte[11]
Nuri 10 – King Amaninatakilebte[11] Nuri 11 – King Malewiebamani[12]
Nuri 11 – King Malewiebamani[12] Nuri 12 – King Amanineteyerike, son of King Malewiebamani
Nuri 12 – King Amanineteyerike, son of King Malewiebamani Nuri 13 – King Harsiotef[12]
Nuri 13 – King Harsiotef[12] Nuri 14 – King Akhraten[12]
Nuri 14 – King Akhraten[12] Nuri 15 – King Nastasen[12]
Nuri 15 – King Nastasen[12] Nuri 16 – King Talakhamani[12]
Nuri 16 – King Talakhamani[12] Nuri 17 – King Baskakeren,[12] son of King Malewiebamani
Nuri 17 – King Baskakeren,[12] son of King Malewiebamani Nuri 18 – King Analmaye[11]
Nuri 18 – King Analmaye[11] Nuri 19 – King Nasakhma[12]
Nuri 19 – King Nasakhma[12] Nuri 20 – King Atlanersa,[11] Son of Taharqa
Nuri 20 – King Atlanersa,[11] Son of Taharqa- Nuri 21 – Possibly Takahatenamun, Queen. Wife of Taharqa
 Nuri 22 – Possibly Amanimalel, Queen. Wife of King Senkamanisken
Nuri 22 – Possibly Amanimalel, Queen. Wife of King Senkamanisken- Nuri 23 – Masalaye, Queen? Probably wife of King Senkamanisken
- Nuri 24 – Nasalsa, Queen. Daughter of Atlanersa, wife of King Senkamanisken
- Nuri 25 – Maletaral II, Queen?. Time of King Amaninatakilebte
- Nuri 26 – Amanitakaye, Queen. Daughter of Aspelta, sister-wife of Aramatle-qo, mother of Malonaqen
- Nuri 27 – Madiqen, Queen. Wife of Anlamani
- Nuri 28 – Henuttakhebit, Queen. Wife of Aspelta
- Nuri 29 – Pi'ankhqew-qa Queen? Possibly wife of King Siaspiqa
- Nuri 31 – Saka'aye, Queen. Probably mother of King Malewiebamani
- Nuri 32 – Akhrasan, Queen. Temp. King Malewiebamani
- Nuri 34 – Henutirdis, Queen. From the time of King Harsiotef
- Nuri 35 – Possibly Queen Abar, wife of Piye, Mother of Taharqa
- Nuri 36 – Atakhebasken Queen. Wife of Taharqa
- Nuri 38 – Akheqa, Queen. Daughter of Aspelta and wife of Aramatle-qo
- Nuri 39 – Maletasen, Queen. Wife of Aramatle-qo
- Nuri 40 – Meqemale, Queen. Possibly wife of Aspelta
- Nuri 41 – Maletaral(?) I, Queen. Wife of Atlanersa
- Nuri 42 – Asata, Queen. Wife of Aspelta
- Nuri 44 – Batahaliye, Queen. Wife of Harsiotef
- Nuri 45 – Tagtal (?), Queen. Wife of King Malonaqen
- Nuri 53 – Yeturow, Queen. Sister-Wife of Atlanersa
- Nuri 55 – Atmataka, Queen. Wife of Aramatle-qo
- Nuri 56 – Possibly Sekhmakh, Queen. Wife of Nastasen
- Nuri 57 – Piankhher( ?), Queen. Possible wife of Aramatle-qo
- Nuri 58 – Artaha, Queen. Possible wife of Aspelta
- Nuri 59 – Malaqaye, Queen. Possibly a wife of King Tantamani
- Nuri 61 – Atasamale, Queen. Possibly a wife of Amanineteyerike

Back row (left to right): Nuri 14 Akhraten, Nuri 13 Harsiotef, Nuri 15 King Nastasen (in the forefront), Nuri 12 Amanineteyerike, Nuri 11 Malewiebamani, Nuri 10 Amaninatakilebte, Nuri 9 Aramatle-qo, Nuri 8 Aspelta (best preserved pyramid), Nuri 7 Karkamani, Nuri 6 Anlamani, Nuri 5 Malonaqen
Front row (left to right): Nuri 4 Siaspiqa (in the middle of the image), Nuri 18 Analmaye (small ruins in the back), Nuri 19 Nasakhma (small ruins in the back), Nuri 3 Senkamanisken, Nuri 2 Amaniastabarqa
- A man walks among the pyramids
- Nastasen's pyramid is the most recent of the royal pyramids (335–315/310 BCE)
- Southern view of the Nuri pyramids in 1821 (top) and in 2020 (bottom)
Remove ads
Tomb artifacts
Summarize
Perspective

Numerous artifacts were found in the Nuri tombs, mainly excavated in 1916 by the Harvard University–Boston Museum of Fine Arts Expedition. It is noted that looting was present in all of the pyramids as they were accessible by digging a hole through the ground. Based on objects found within and around the tombs, it is likely that these looters came hundreds of years later. Of what remained, several fragments and completed Napatan red ware pottery were found within several tombs.[10]
- Gold flower shaped Diadem, found in the Pyramid of King Talakhamani (435–431 BCE), Nuri pyramid 16. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
- Jewelry found on the Mummy of Nubian King Amaninatakilebte (538–519 BCE), Nuri pyramid 10. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
- Unfinished granite stela with statue of Osiris found in the chapel of the Pyramid 3 of Senkamanisken at Nuri
- A Shabti, a funerary figure of King Senkamanisken, found in the chapel of the Pyramid 3 at Nuri
- Artifacts including large metal tweezers, decorated and inscribed vessels, gold sheaths, and a ewer marked for King Aspelta found in Nuri pyramid 8. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
- The Sarcophagus of King Aspelta found in Nuri pyramid 8. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
See also
References
Literature
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads