Norpipanone
Opioid analgesic drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Opioid analgesic drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
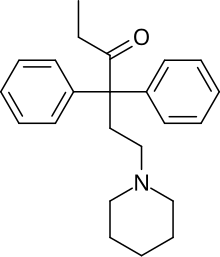
Norpipanone (INN, BAN; Hexalgon) is an opioid analgesic related to methadone which was developed in Germany and distributed in Hungary, Argentina, and other countries.[2][3] It had originally not been under international control but upon observation of case reports of addiction it was reviewed and shortly thereafter became a controlled substance.[2][3] In the United States, it is a Schedule I controlled substance (ACSCN 9636, zero annual manufacturing quota as of 2014). The salts in use are the hydrobromide (free base conversion ratio 0.806) and hydrochloride (0.902).
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Herchst 10495, NIH-7557 |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.383 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H29NO |
| Molar mass | 335.491 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |

Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.