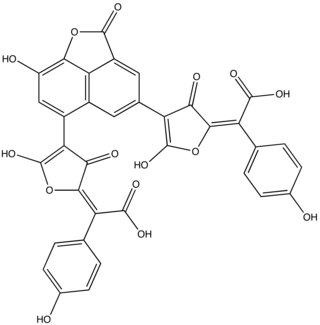
Norbadione A
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Norbadione A is a pigment found in the bay bolete mushroom (Boletus badius). A polyphenol, norbadione A is related to a family of mushroom pigments known as pulvinic acids.[1] The molecule has also been reported as a potassium salt from the mushrooms Pisolithus tinctorius (horse dung fungus)[2] and Chalciporus piperatus.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[2(32)E,52(6)E]-14,33,48,53,74-Pentahydroxy-35,42,55-trioxo-35H,42H,55H-4(4,6)-naphtho[1,8-bc]furana-3(2,4),5(4,2)-difurana-1,7(1)-dibenzenaheptaphane-2(32),52(6)-diene-2,6-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H18O15 | |
| Molar mass | 678.50842 gmol−1 |
| Appearance | red needles |
| Density | 1.902 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Properties
Summarize
Perspective
Norbadione A has seven acid-base functional groups, among which are two enolic and two carboxylic acid moieties.[4] These functional groups confer water-solubility to the molecule. It selectively complexes caesium cations (Cs+),[5] with an efficiency comparable to that of some calixarenes or crown ethers.[4] It has been investigated for its ability to provide a protective effect against the damaging effects of ionizing radiation, an effect attributed to its ability to protect DNA-related targets from irradiation.[6] Tests with cell cultures and mice show that although it has some protective effect, it is toxic to cells in higher doses.[7] A diverse array of synthetic derivatives of norbadione A has been created to explore the effect of structure on antioxidant properties and cytotoxicity.[8] A series of alkali chelators based on the structure of norbadione A has been reported.[9] The intramolecular protonation process has been determined. There is a pH-dependent Z to E isomer switch that occurs in both pulvinate moieties,[10] which yields four stereoisomeric forms (E/E, E/Z, Z/Z, Z/E). These stereoisomers may have a widely differing ability to form complexes with Cs+ in solution.[6]
Synthesis
Bourdreux and colleagues reported a total synthesis of norbadione A in 2008. The technique uses a regioselective Diels–Alder reaction and a double Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling.[11]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.