Nocona Formation
Geologic formation in Texas, United States From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Nocona Formation is a geological formation in Texas, dating back to the Wolfcampian series (Early Permian). As part of the Texas red beds, it is one of several formations renowned for dense bonebeds of terrestrial vertebrate fossils.[1][2][3]
| Nocona Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Early Permian, Wolfcampian (Sakmarian?–Artinskian?) | |
| Type | Formation |
| Unit of | Wichita Group |
| Underlies | Petrolia Formation |
| Overlies | Archer City Formation |
| Thickness | 350 ft. |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | mudstone |
| Other | sandstone, siltstone |
| Location | |
| Region | Texas |
| Country | United States |
| Type section | |
| Named by | Hentz & Brown, 1987 |
Geology
Summarize
Perspective
The Nocona Formation was named as a distinct geological unit in 1987; its fossil deposits were previously assigned to the Admiral Formation, a time-equivalent marine deposit located further southwest in Texas. The Nocona Formation is considered equivalent to most of the Admiral Formation (apart from the highest few layers), as well as the Coleman Junction Formation.[4][5] The Nocona Formation overlies the Archer City Formation and underlies the Petrolia Formation. A few sources consider the Nocona Formation to be part of the Archer City Formation,[6] but most regard it as a distinct unit.[7]
Reddish-brown mudstone is the most common rock type in the formation, though grey mudstone and other laminated fine sediments are predominant in bonebeds. 11 distinct layers of dark brown sandstone are thick and extensive enough to be mapped out on a regional scale. The formation is most well-exposed in Archer and Clay counties, extending as far northeast as the Red River which defines the Texas-Oklahoma border. It reaches its thickest extent of around 350 feet in Clay County, where individual sandstone beds can reach a thickness of 40 feet. The most southern extent of the Nocona Formation is the southwestern portion of Archer County.[4][5][8]
Bonebeds
One particularly notable bonebed is the Geraldine Bonebed in Archer County, discovered by Alfred Sherwood Romer in 1932.[1] Numerous partial and complete skeletons have been recovered from this site, including some of the best fossils of Edaphosaurus boanerges, Archeria crassidisca, Eryops megacephalus, and (to a lesser extent) Dimetrodon natalis.[2] The skeletons are generally preserved in straight, relaxed poses, with the skull aligned towards the east, southwest, or north. Both conditions are similar to modern abrupt mortality events where the animals' corpses end up in permanent bodies of water. Plant debris and charcoal are common in the bonebed as well. It is conceivable that most of the animals killed by a single catastrophe, perhaps a forest fire which polluted the air and water to kill both terrestrial and aquatic animals in the confines of a small lake or pond.[2]
Other productive Nocona Formation bonebeds in Archer County include the Briar Creek Bonebed,[1] Coprolite Bonebed (named for its concentration of shark coprolites), Loftin Bonebed, and Rattlesnake Canyon 2 Bonebed.[3] Their fossil content is more diverse than the Geraldine Bonebed, but also less well-preserved. Unlike the catastrophic scenario implied for Geraldine, these other bonebeds are assumed to be a product of gradual processes of death and decay experienced in calm pond environments.[3]
Paleobiota
Summarize
Perspective
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
Synapsids
An egg-like object was discovered by Llewellyn Price in the vicinity of Rattlesnake Canyon, and subsequently described by Romer and Price in 1939. It had a shell-like texture which was not easily comparable to nodules from the Permian of Texas, and the authors considered it to have potentially been laid by a "pelycosaur". If this identification is correct, it is the oldest amniotic egg in the fossil record.[9][1] Later investigations concluded that a distinct calcareous shell layer was not present, though the high concentration of phosphorus in the object suggests that it may still be an egg, albeit one with a softer outer membrane.[10][3]
| Synapsids of the Nocona Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Localities | Notes | Images |
| Ctenorhachis[11] | C. jacksoni[11] | Lake Kickapoo[11] | A large sphenacodontid with a rather low neural spine sail. |  |
| Dimetrodon | D. booneorum | Briar Creek[1][12] | A medium-sized sphenacodontid of uncertain validity. | |
| D. limbatus[1] | Briar Creek?,[1][12][13] Coprolite, Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | A large sphenacodontid with a tall neural spine sail. |  | |
| D. natalis | Geraldine,[2][8] Briar Creek,[1][12][13] Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | A small sphenacodontid with a tall neural spine sail. Represented by three partial skeletons. Sometimes regarded as a juvenile of D. limbatus,[2][3] but confirmed to be a unique species with small adults, according to histological analyses.[12] |  | |
| Edaphosaurus | E. boanerges[1] | Geraldine,[1][2][14][8] Briar Creek,[1][13] Coprolite, Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2?[3] | A medium-sized herbivorous edaphosaurid.[1][14] One of the most common and characteristic fossils of the Geraldine bonebed, with multiple articulated skeletons displayed in museums around the world.[2] |  |
| Lupeosaurus | L. kayi | Briar Creek,[1] Coprolite?[3] | A large edaphosaurid known from rare fragments. |  |
| Ophiacodon | O. retroversus | Rattlesnake Canyon[1][15] | An ophiacodontid. |  |
| O. uniformis | (vicinity of) Geraldine,[2][8] Briar Creek[1][15] | An ophiacodontid. |  | |
| Secodontosaurus | S. obtusidens | Briar Creek[1][12] | A medium-sized sphenacodontid. |  |
Reptiles
| Reptiles of the Nocona Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Localities | Notes | Images |
| Araeoscelis | A. casei[16] | Godwin Creek[16] | An araeoscelidian initially named as a new genus, Ophiodeirus.[16] |  |
| Bolosaurus | B. striatus | Geraldine,[2][8] Briar Creek, Godwin Creek[17] | A bolosaurid parareptile. |  |
| Captorhinidae indet. | Loftin[3] | Rare captorhinid vertebrae.[18][3] | ||
Amphibians
| Amphibians of the Nocona Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Localities | Notes | Images |
| Archeria | A. crassidisca | Geraldine,[19][2][14][8] Briar Creek,[20] Coprolite, Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | A large archeriid embolomere. Multiple articulated skeletons have been found in the Geraldine bonebed, representing the most complete and well-described fossils of this species.[19][2][14] |  |
| Cardiocephalus | C. sp. | Geraldine[8] | Rare microsaur teeth. | |
| Diadectes | D. sideropelicus | Geraldine,[2] Briar Creek,[20] Coprolite, Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | A large diadectid diadectomorph. |  |
| Diplocaulus | D. sp. | Loftin[3] | A diplocaulid nectridean. | |
| Eryops | E. megacephalus | Geraldine,[2][8] Briar Creek,[20] Coprolite, Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | An eryopid, a type of large semiaquatic temnospondyl. Articulated skeletons and other remains are common in the Geraldine bonebed.[2] | 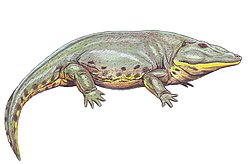 |
| Rubeostratilia[21] | R. texensis[21] | "east of Henrietta"[21] | An amphibamiform, a type of small terrestrial temnospondyl. |  |
| Scapanops[22] | S. neglecta[22] | Halsell Hill[22] | A eucacopine dissorophid, a type of small terrestrial temnospondyl. Previously consider a specimen of Conjunctio.[22] | |
| Trimerorhachis | T. insignis | (vicinity of) Geraldine,[2][8] Godwin Creek,[23] Rattlesnake Canyon,[23] Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3][23] | A trimerorhachid dvinosaur, a type of small aquatic temnospondyl. |  |
| Zatrachys | Z. serratus | (vicinity of) Geraldine,[2] Rattlesnake Canyon 2 | A zatracheid temnospondyl, a type of medium-sized terrestrial temnospondyl. |  |
Fish
Indeterminate palaeoniscoids are known from the Geraldine,[8] Coprolite, Loftin, and Rattlesnake Canyon 2 bonebeds.[3] Iniopterygian tooth whorls have been reported from the Rattlesnake Canyon area.[8]
| Fish of the Nocona Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Localities | Notes | Images |
| Acanthodes | A. sp. | Geraldine[8] | Acanthodian fin spines and scales |  |
| Barbclabornia | B. luedersensis | Rattlesnake Canyon[24] | Rare xenacanth shark teeth | |
| Ectosteorhachis | E. nitidus | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite, Loftin[3] | A megalichthyid tetrapodomorph |  |
| Helodus | H. sp. | Geraldine[8] | Rare holocephalan teeth | |
| Hybodus | H. sp. | Coprolite[3] | A hybodont shark | |
| Janassa? | J.? sp. | Geraldine[8] | A single petalodont tooth | |
| Orthacanthus | O. platypternus | Geraldine[8] | Xenacanth shark teeth |  |
| O. texensis | Geraldine,[2][8] Briar Creek,[8] Coprolite,[25] Loftin, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | Very common xenacanth shark teeth and coprolites | ||
| Platysomus? | P.? sp. | Geraldine[8] | A single palaeoniscoid tooth | |
| Progyrolepis | P. tricessimalaris[26] | Rattlesnake Canyon[26] | A palaeoniscid known from a partial skeleton. | |
| Sagenodus | S. periprion | (vicinity of) Geraldine,[2][8] Coprolite, Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | Lungfish teeth | |
| Spermatodus | S. pustulosus | Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | A coelacanth | |
| Xenacanthus | X. sp. | Geraldine[8] | Xenacanth shark spine fragments |  |
Plants
Plant fossils are known from several bonebeds of the Nocona Formation, though they are subordinate to vertebrate fossils at most sites.[27][2] Insect damage has been recorded on leaves from the Coprolite Bonebed. It is uncommon (only a third as frequent as in modern plants), even when compared to only slightly younger sites such as the Taint locality in the Waggoner Ranch Formation. Despite the rarity of insect damage, the Coprolite Bonebed shows the oldest occurrence of skeletonization (removal of all but the veins), as well as galls, which are rarely found in Permian plant fossils.[28]
| Plants of the Nocona Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Localities | Notes | Images |
| Annularia | A. cf. stellata | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[28] | Foliage of a large calamitacean sphenophyte (horsetail) which formed thickets in shallow water and shorelines. | |
| Autunia | A. cf. conferta | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[28] | Foliage of a peltasperm "seed fern", previously considered a species of Callipteris.[2] Abundant in the Geraldine and Coprolite bonebeds.[2][28] | |
| Calamites | C. undulatus | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[3][28] | Common stem impressions of a large calamitacean sphenophyte (horsetail) which formed thickets in shallow water and shorelines. | |
| Callipteridium | C. cf. pteridium | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a medullosalean "seed fern". | |
| C. virginianum | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a medullosalean "seed fern". | ||
| Cordaites | C. principalis | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[28] | Foliage of a cordaitalean gymnosperm, a small tree found in both swamps and uplands. Common in the Geraldine and Coprolite bonebeds.[2][28] | |
| Dadoxylon | D. sp. | Geraldine,[2] Rattlesnake Canyon 2[3] | Conifer wood and charcoal. | |
| Odontopteris | O. genuina | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a medullosalean "seed fern". | |
| O. cf. lingulata | Coprolite[3] | Foliage of a medullosalean "seed fern". | ||
| O. cf. osmundaeformis | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a medullosalean "seed fern". | ||
| Pecopteris | P. arborescens | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a marattialean tree fern, among the most common trees in Permian swamp environments. | |
| P. candolleana | Geraldine[2] | |||
| P. hemitelioides | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[3][28] | |||
| P. unita | Geraldine[2] | |||
| Psaronius | P. sp. | Geraldine,[2] Loftin[3] | Stems and roots of a marattialean tree fern, likely the same plant which produced Pecopteris leaves.[3] | |
| Russellites[29] | R. taeniata | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[28] | Foliage of a cycadophyte, previously referred to Tingia. Common in the Coprolite Bonebed.[28] | |
| Samaropsis | S. spp. | Geraldine[2] | Two species of gymnosperm seeds, possibly from the same plants as Walchia and Cordaites.[2] | |
| Sigillaria | S. brardii | Geraldine[2] | Bark and stems of a lycophyte. | |
| Sphenophyllum | S. oblongifolium | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a fern. | |
| Sphenopteris | S. cf. macilenta | Geraldine[2] | Foliage of a fern or "seed fern". | |
| Walchia | W. piniformis | Geraldine,[2] Coprolite[3][28] | Foliage of an early conifer, a small tree accustomed to dry uplands. Associated stems and charcoal show similarity to the form genus Schizodendron.[3] Very common in the Geraldine and Coprolite bonebeds.[2][28] | |
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.