Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Niosome
Non-ionic surfactant-based vesicle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
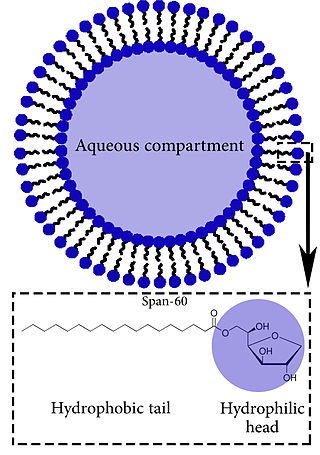
Niosomes are vesicles composed of non-ionic surfactants, incorporating cholesterol as an excipient.[1] Niosomes are utilized for drug delivery to specific sites to achieve desired therapeutic effects.[2] Structurally, niosomes are similar to liposomes as both consist of a lipid bilayer. However, niosomes are more stable than liposomes during formation processes and storage.[3] Niosomes trap hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, either in an aqueous compartment (for hydrophilic drugs)[4] or in a vesicular membrane compartment composed of lipid material (for lipophilic drugs).[3]

Remove ads
Structure
Niosomes are microscopic lamellar structures formed by non-ionic surfactants and cholesterol. They exhibit a bilayer structure, with hydrophilic ends facing outward and hydrophobic ends facing inward. Their unique structure makes them ideal for diverse applications, notably in drug delivery systems. Niosomes excel in encapsulating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, enhancing drug stability and bioavailability. They are adaptable for tailored drug release and have garnered interest across pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture for their biocompatibility and versatile properties.[5]
Remove ads
Methods of preparation
Various methods used to prepare liposomes are also suitable for niosome preparation,[1] such as the ether injection method, the handshaking method, the reverse phase evaporation method, the trans-membrane pH gradient method, the "bubble" method, the microfluidization method, formation from proteasomes,[5] the thin-film hydration method, the heating method, the freeze and thaw method, and the dehydration-rehydration method.
Remove ads
Uses
Niosomes are used as biodegradable and non-immunogenic drug delivery compounds,[6] as they have a low toxicity risk in biological systems.[7] They can also be used to entrap hydrophilic pharmaceuticals within aqueous compartments[4] or lipophilic drugs into vesicular bilayer membranes. Niosomes shield drug molecules from the biological environment, which can be utilized to improve the therapeutic performance of various drug molecules. Additionally, they can be used in a sustained drug delivery system to more directly affect target cells and delay clearance from circulation.[7][4] Niosomes are used in a variety of applications, including gene delivery,[8][9] drug targeting,[4] antineoplastic treatment,[10] delivery of peptide drugs, carriers for hemoglobin, transdermal drug delivery systems,[11] and cosmetics.[12] They are also being studied for their potential use as a treatment for different forms of leishmaniasis[13]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads