Niobium nitride
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Niobium nitride is a compound of niobium and nitrogen (nitride) with the chemical formula NbN. At low temperatures (about 16 K) NbN becomes a superconductor, and is used in detectors for infrared light.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Niobium nitride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.132 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NbN | |
| Molar mass | 106.91 g/mol |
| Appearance | gray solid |
| Density | 8.470 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,573 °C (4,663 °F; 2,846 K) |
| reacts to form ammonia | |
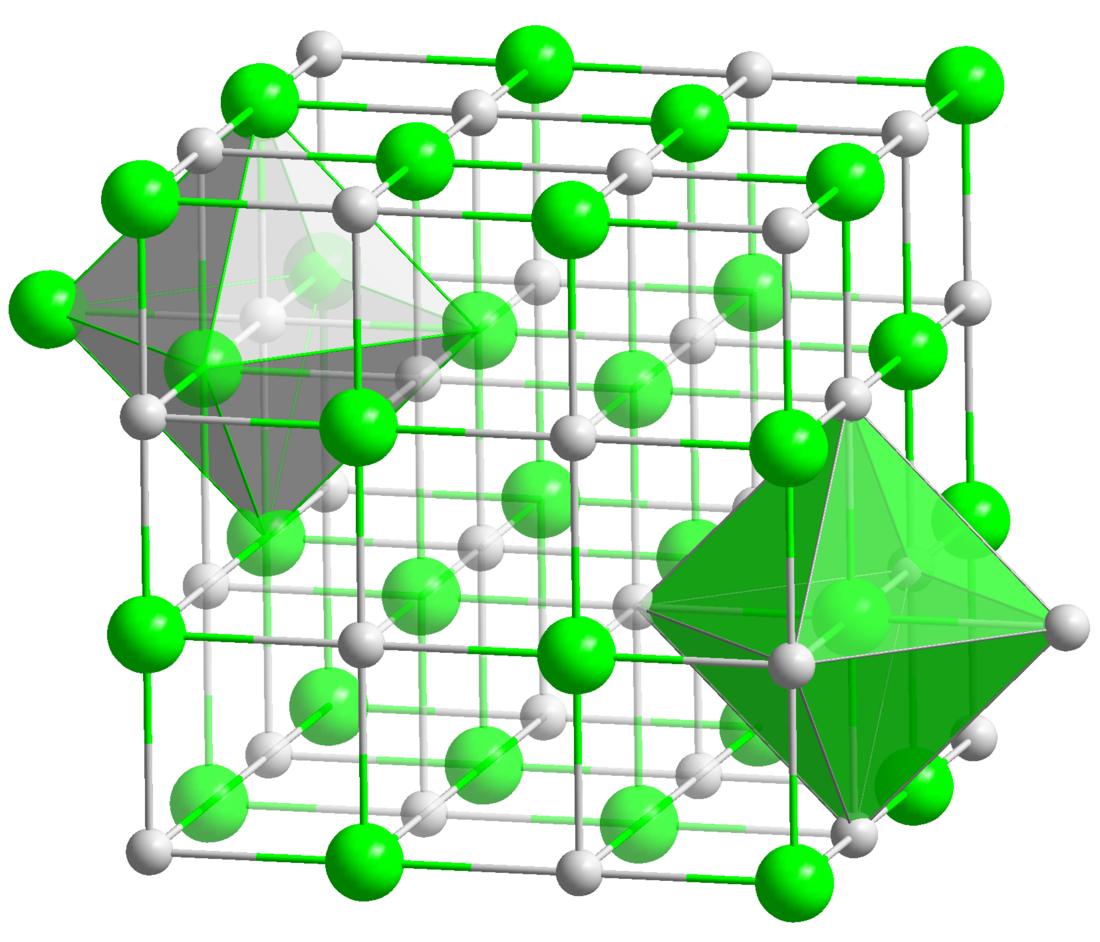
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Vanadium nitride Tantalum nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Uses
- Niobium nitride's main use is as a superconductor.
- Detectors based on it can detect a single photon in the 1-10 micrometer section of the infrared spectrum,[4] which is important for astronomy and telecommunications. It can detect changes up to 25 gigahertz.
- Superconducting NbN nanowires can be used in particle detectors with high magnetic fields.[5]
- Niobium nitride is also used in absorbing anti-reflective coatings.
- In 2015, it was reported that Panasonic Corp. has developed a photocatalyst based on niobium nitride that can absorb 57% of sunlight to support the decomposition of water to produce hydrogen gas as fuel for electrochemical fuel cells.[6]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.