New methylene blue
A substance used as a blue dye or stain and as a medication From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
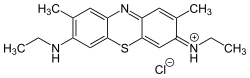
New methylene blue (also NMB)[clarify] is an organic compound of the thiazine class of heterocycles. It is used as a stain and as an antimicrobial agent. It is classified as an azine dye, and the chromophore is a cation, the anion is often unspecified.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.833 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22N3S:SCl ZnCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 484.22 g/mol |
| Melting point | 239 °C (462 °F; 512 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P317, P321, P330, P362+P364, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Applications
NMB is a staining agent used in diagnostic cytopathology and histopathology, typically for staining immature red blood cells. It is a supravital stain.[2] It is closely related to methylene blue, an older stain in wide use.
Safety
New methylene blue is toxic. Skin contact or inhalation should be avoided.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.