Nasolacrimal duct
Carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
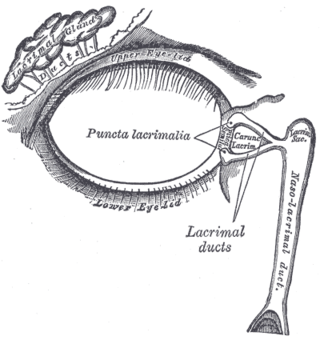
The nasolacrimal duct (also called the tear duct) carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity.[1][2] The duct begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct into the inferior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity is partially covered by a mucosal fold (valve of Hasner or plica lacrimalis).[3]
| Nasolacrimal duct | |
|---|---|
 The lacrimal apparatus. Right side. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus nasolacrimalis |
| MeSH | D009301 |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.070 |
| TA2 | 6859 |
| FMA | 9703 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Excess tears flow through the nasolacrimal duct which drains into the inferior nasal meatus. This is the reason the nose starts to run when a person is crying or has watery eyes from an allergy, and why one can sometimes taste eye drops. This is for the same reason when applying some eye drops it is often advised to close the nasolacrimal duct by pressing it with a finger to prevent the medicine from escaping the eye and having unwanted side effects elsewhere in the body as it will proceed through the canal to the nasal cavity.
Like the lacrimal sac, the duct is lined by stratified columnar epithelium containing mucus-secreting goblet cells, and is surrounded by connective tissue.
Nasolacrimal canal
| Nasolacrimal canal | |
|---|---|
 Tear system. a = lacrimal gland b = superior lacrimal punctum c = superior lacrimal canal d = lacrimal sac e = inferior lacrimal punctum f = inferior lacrimal canal g = nasolacrimal canal | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | canalis nasolacrimalis |
| MeSH | D009301 |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.070 |
| TA2 | 6859 |
| FMA | 9703 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The canal containing the duct is called the nasolacrimal canal. It is formed by indentations in the inferior nasal conchae, maxilla and lacrimal bone. The canal drains into the nasal cavity through the anterior portion of the inferior meatus, which is between the inferior concha and the floor of the nasal cavity.
Clinical significance
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct may occur.[4][5][6] This leads to the excess overflow of tears called epiphora (chronic low-grade nasolacrimal duct occlusion).[7] A congenital obstruction can cause cystic expansion of the duct and is called a dacryocystocele or Timo cyst. Persons with dry eye conditions can be fitted with punctal plugs that seal the ducts to limit the amount of fluid drainage and retain moisture.
During an ear infection, excess mucus may drain through the nasolacrimal duct in the opposite way tears drain. [citation needed]
In humans, the tear ducts in males tend to be larger than the ones in females.[8]
Additional image
- Roof, floor, and lateral wall of left nasal cavity
- The seven bones which articulate to form the orbit.
- Outline of bones of face, showing position of air sinuses.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.