Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
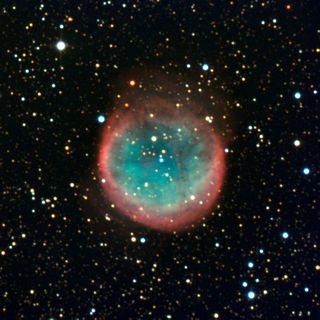
NGC 6781
Planetary nebula in the constellation Aquila From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
NGC 6781, also known as the Snowglobe Nebula,[5] is a planetary nebula located in the equatorial constellation of Aquila, about 2.5° east-northeast of the 5th magnitude star 19 Aquilae.[3] It was discovered July 30, 1788 by the Anglo-German astronomer William Herschel.[6] The nebula lies at a distance of 1,500 ly from the Sun.[2] It has a visual magnitude of 11.4 and spans an angular size of 1.9 × 1.8 arcminutes.[3]
The bipolar dust shell of this nebula is believed to be barrel-shaped and is being viewed from nearly pole-on.[7] It has an outer angular radius of 61″; equivalent to a physical radius of 0.44 ly (0.135 pc). The total mass of gas ejected as the central star passed through its last asymptotic giant branch (AGB) thermal pulse event is 0.41 M☉, while the estimated dust mass is 1.53 M☉.[2]
The magnitude 16.88 central star of the planetary nebula is a white dwarf with a spectral type of DAO. It has an M-type co-moving companion at a projected separation of under 5,000 AU.[8] The white dwarf progenitor star had an estimated initial mass of ~2.5 M☉. It left the AGB and entered the cooling stage around 9,400 years ago.[2]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads