Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Mu Pegasi
Star in the constellation Pegasus From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
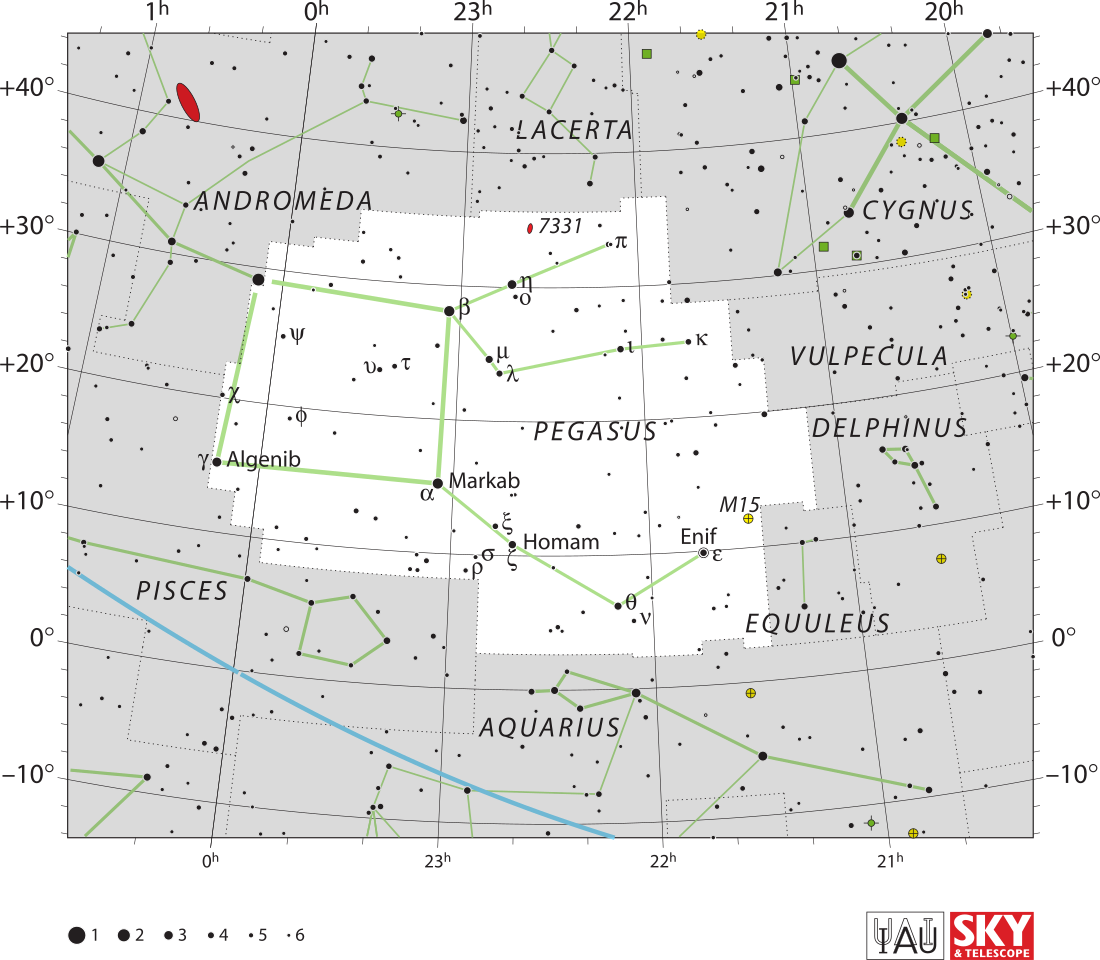
Mu Pegasi or μ Pegasi, formally named Sadalbari (/ˌsædəlˈbɛəri/),[10] is a star in the northern constellation of Pegasus. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 3.5,[2] which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye even on a moonlit night. Based upon parallax measurements taken by the Gaia spacecraft, it is approximately 113 light-years (35 parsecs) from the Sun.[1]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
μ Pegasi (Latinised to Mu Pegasi) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Sadalbari, which derives from Arabic: سعد بارع saʿd al-bāriʿ, the “auspicious star of the splendid one.”[11] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[12] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Sadalbari for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[10]
In Chinese, 離宮 (Lì Gōng), meaning Resting Palace, refers to an asterism consisting of Mu Pegasi, Lambda Pegasi, Omicron Pegasi, Eta Pegasi, Tau Pegasi and Nu Pegasi.[13] Consequently, the Chinese name for Mu Pegasi itself is 離宮二 (Lì Gōng èr, "the Second Star of Resting Palace").[14]
Remove ads
Properties
The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of G8 III.[3] The luminosity class of 'III' means that it has exhausted the hydrogen fuel at its core and evolved into a giant star. It is 520 million years old and 2.6 times more massive than the Sun,[6] but has expanded to nine times the Sun's radius.[7] The effective temperature of the outer atmosphere is about 4,961 K,[8] which is cooler than the Sun and gives it the yellow hue of a G-type star.[15][16] The abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium, what astronomers term the metallicity, is a bit smaller than the abundance in the Sun.[8]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads