Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Mired
Unit of reciprocal color temperature From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Contracted from the term micro reciprocal degree, the mired (/ˈmaɪrɛd/[1]) is a unit of measurement used to express color temperature. Values in mireds are calculated by the formula:
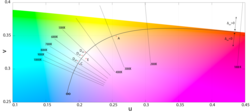
Close up of the Planckian locus in the CIE 1960 color space
Isotherms in mireds
Isotherms in kelvins
Note the even spacing of the isotherms when using the reciprocal temperature scale. The even spacing of the isotherms on the locus implies that the mired scale is a better measure of perceptual color difference than the temperature scale. The range of isothermal color temperatures for both diagrams is from 1000 K (1000 MK−1) to 10000 K (100 MK−1).
where T is the colour temperature in units of kelvins and M denotes the resulting mired dimensionless number. The constant 1000000 K is one million kelvins.
The SI term for this unit is the reciprocal megakelvin (MK−1), shortened to mirek, but this term has not gained traction.[2]
For convenience, decamireds are sometimes used, with a decamired equaling ten mireds.
The use of the term mired dates back to Irwin G. Priest's observation in 1932 that the just noticeable difference between two illuminants is directly related to the difference of the reciprocals of their temperatures, rather than to the difference in their temperatures.[3]
Remove ads
Examples
Summarize
Perspective
A blue sky, which has a color temperature T of about 25000 K, has a mired value of M = 40 mireds, while a standard electronic photography flash, having a color temperature T of 5000 K, has a mired value of M = 200 mireds.
Remove ads
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
Photographic filter and gel

In photography, mireds are used to indicate the color temperature shift provided by a filter or gel for a given film and light source. For instance, to use daylight film (5700 K) to take a photograph under a tungsten light source (3200 K) without introducing a color cast, one would need a corrective filter or gel providing a mired shift
This corresponds to a color temperature blue (CTB) filter.[6][7] Color gels with negative mired values appear green or blue, while those with positive values appear amber or red.
CCT calculation
A number of mathematical methods, including Robertson's, calculate the correlated color temperature of a light source from its chromaticity values. These methods exploit the relatively even spacing of the mired uint internally.[8]
Color description
Apple's HomeKit uses the mired unit for specifying color temperature.[9]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads