Metanilic acid
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
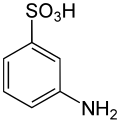
Metanilic acid is an isomer of sulfanilic acid with molecular formula C
6H
7NO
3S and molecular weight 173.18968 g/mol.[2][3][4][5] It is a white powder that is slightly soluble in water.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
3-Aminobenzenesulfonic acid m-Anilinesulfonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.067 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2585 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 173.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Beige powder |
| Density | 1.69 |
| Melting point | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Less than 1 mg/mL at 22 °C (72 °F) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.74 (H2O)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Disappearing polymorph
The crystal structure called Form I is a disappearing polymorph that cannot be produced by researches anymore while Form II and III still exist.[6] The reason for this is that Form I is converted to another polymorph upon contact with a seed crystal and most places are contaminated with tiny amounts of Form II or III that are enough to prevent any viable amounts of Form I to be produced.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
